How Cathodic protection system working |Types |Application
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we explore the importance of cathodic protection in preventing corrosion in pipelines, tanks, and underground structures, particularly in industries like oil and gas. The video covers two main types of cathodic protection systems: sacrificial anodes and impressed current systems. Viewers will learn about the applications of these techniques to ensure the longevity and safety of essential infrastructure. The video also offers practical tips for monitoring and maintaining effective protection systems. Watch to gain valuable insights on how cathodic protection plays a crucial role in industrial safety and infrastructure preservation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Introduction to the concept of cathodic protection and its importance in preventing corrosion of underground pipelines.
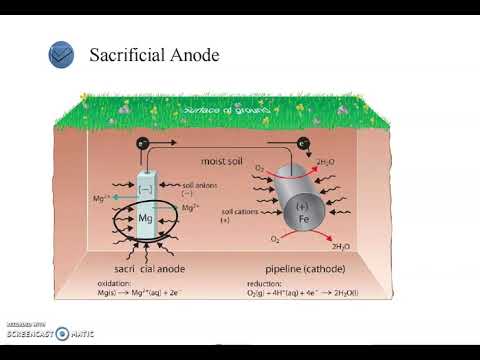
- 😀 Explanation of how cathodic protection works using rectifiers and sacrificial anodes to protect metal structures, such as pipelines, from corrosion.
- 😀 Discussion on various types of protection systems like sacrificial anode systems and impressed current systems.
- 😀 Overview of the role of protective measures in the oil and gas industry, emphasizing the need to safeguard infrastructure from damage.
- 😀 Mention of testing techniques for cathodic protection systems, including rectifier tests and monitoring the pipeline system for any signs of deterioration.
- 😀 Highlighting the risks posed by corrosion in pipelines, especially in high-risk areas like gas pipelines, and the importance of prevention measures.
- 😀 The role of anodes in reducing corrosion and preventing damage to essential structures by providing an electrical current to protect the metal.
- 😀 Importance of regular maintenance and monitoring of cathodic protection systems to ensure long-term effectiveness and prevent costly repairs.
- 😀 Addressing the application of these protection systems in various industries, including shipping, electrical systems, and water infrastructure.
- 😀 Conclusion with an encouragement to subscribe to the channel for more information on electrical and protection technologies and related careers.
Q & A
What is cathodic protection and how does it work?
-Cathodic protection is a technique used to prevent corrosion of metal surfaces, particularly in pipelines and storage tanks. It works by making the metal structure the cathode of an electrochemical cell, where corrosion is suppressed by the flow of electrical current, typically from a sacrificial anode or an impressed current system.
What are the different types of protection systems discussed in the video?
-The video mentions two main types of protection systems: sacrificial anode systems and impressed current systems. Sacrificial anode systems use a more reactive metal to corrode instead of the protected structure, while impressed current systems apply a continuous electrical current to protect the structure.
How does cathodic protection prevent damage to pipelines?
-Cathodic protection prevents corrosion by ensuring that the pipeline or metal structure becomes the cathode in an electrochemical reaction. This prevents the metal from corroding by redirecting the corrosive processes to the sacrificial anodes or managing current flow in an impressed system.
What is the role of rectifiers in cathodic protection systems?
-Rectifiers are used in impressed current cathodic protection systems to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). This DC is then supplied to the protected pipeline or structure to create the necessary electrochemical environment to prevent corrosion.
What types of structures benefit from cathodic protection?
-Cathodic protection is beneficial for any metal structures that are exposed to corrosive environments. This includes pipelines, gas pipelines, storage tanks, ships, and underground structures such as water tanks or foundations.
Why is testing important in cathodic protection systems?
-Testing is crucial to ensure that cathodic protection systems are functioning effectively. It helps monitor the protection levels, detect potential failures, and ensure that the protection current is adequately distributed across the structure to prevent corrosion.
How does cathodic protection relate to the oil and gas industry?
-In the oil and gas industry, cathodic protection is essential for safeguarding pipelines and other metal infrastructure that are exposed to corrosive elements like water, gas, and soil. This helps ensure the longevity and safety of critical infrastructure, reducing maintenance costs and preventing leaks or failures.
What maintenance practices are important for cathodic protection systems?
-Regular maintenance for cathodic protection systems includes checking and replacing sacrificial anodes, inspecting rectifiers and electrical components, measuring the protection current, and ensuring the system is properly grounded. This ensures the system continues to function effectively and prevent corrosion.
What challenges might arise during the installation of cathodic protection systems?
-Challenges during installation can include difficult soil conditions, access to pipelines or tanks, and ensuring correct placement of anodes and rectifiers. It’s also important to avoid interference with other electrical systems and ensure that the system meets safety regulations.
What are the benefits of using a cathodic protection system?
-The primary benefits of cathodic protection include extended service life for metal structures, reduced maintenance costs, enhanced safety by preventing leaks or failures, and protection against environmental and corrosive damage, ultimately preserving the structural integrity of critical infrastructure.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Korosi | Kimia SMA

Cathodic Protection on water pipes
Corrosion Prevention

Storage Tanks: What are Storage Tanks | What are Storage Tank Uses and Types | Design

02. MG6028, S01 Korosi Dalam Air (Aqueous Corrosion/Wet Corrosion)

Protection from corrosion l sacrificial anodic protection l cathodic coating l Dr. Avani pareek
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)