ATOMS - GCSE Chemistry (AQA Topic C1)
Summary
TLDRThis educational script delves into the fundamental concepts of chemistry, explaining the composition of substances from atoms to compounds like water (H2O). It covers chemical reactions, emphasizing the importance of balancing equations and the conservation of atoms. The script also touches on physical processes like filtration, crystallization, and distillation, distinguishing them from chemical reactions. It introduces the periodic table, atomic structure, and electron configurations, highlighting the properties and reactivity trends of elements. The video aims to clarify the differences between metals, non-metals, and noble gases, and how their electron configurations influence their chemical behavior.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The periodic table represents elements with unique symbols and categorizes them based on the types of atoms they consist of.
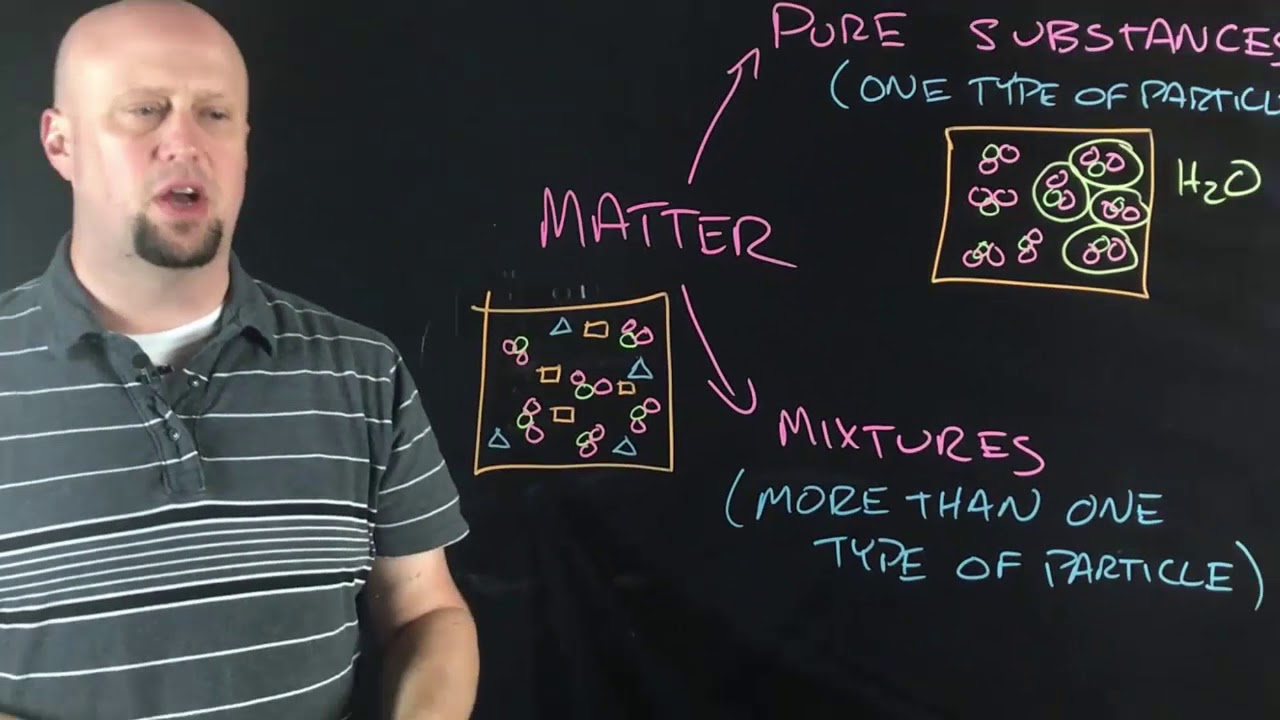
- 💧 A compound, such as water (H2O), is formed by chemically bonding two or more different types of atoms together.
- ⚖️ Chemical reactions adhere to the law of conservation of mass, ensuring an equal number of each type of atom before and after the reaction.
- 🔄 Balancing chemical equations involves adjusting coefficients to ensure equal numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation.
- 🌬️ Mixtures consist of different elements and compounds not chemically bonded, like air and saltwater, and can be separated through physical processes.
- 💧 Filtration removes large insoluble particles from liquids, while crystallization and distillation separate dissolved solutes from solvents.
- 🔥 Physical changes, such as melting and evaporation, involve energy transfer without altering the substance's chemical composition.
- 📊 The periodic table provides essential information about atoms, including atomic number, which defines the element, and relative atomic mass.
- 🔋 Electrons were discovered to exist in shells or orbitals around the nucleus, with different configurations determining an element's chemical properties.
- 🧲 The atomic structure consists of a positively charged nucleus with protons and neutrons, and negatively charged electrons orbiting around it.
- 🌌 The periodic table's organization was refined over time, with Dmitri Mendeleev's predictions of undiscovered elements highlighting its accuracy.
- 🏭 Metals tend to donate electrons and are found on the left side of the periodic table, while non-metals accept electrons and are on the right.
Q & A
What is the basic unit of matter?
-The basic unit of matter is the atom, which can be different types or elements represented by a symbol in the periodic table.
What is a compound?
-A compound is a substance that contains two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded together, such as water (H2O) which is made up of hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
How is the chemical formula for water represented?
-The chemical formula for water is H2O, indicating that each molecule of water is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
What is the significance of the numbers in a chemical formula?
-The numbers in a chemical formula indicate the ratio of atoms of each element in a compound. If there's no number, it implies an invisible one, meaning there is one atom of that element.
What is a chemical reaction and how is it represented?
-A chemical reaction is a process where atoms change what they're bonded to and how they're bonded. It can be represented with a word equation and a chemical equation using symbols.
Why is it important to balance chemical equations?
-Balancing chemical equations is important because atoms are not created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. There must be the same number of each type of atom on both sides of the equation.
What is a mixture and how is it different from a compound?
-A mixture is a combination of different types of elements and compounds that are not chemically bonded together, such as air or salt water. It differs from a compound because in a mixture, the components are not chemically bonded.
What are the three main states of matter?
-The three main states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. For example, water can exist as ice (solid), liquid water, and water vapor (gas).
What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical reaction?
-A physical change involves a change in the state or form of a substance without altering its chemical composition, such as melting or evaporation. A chemical reaction, on the other hand, involves the formation of new substances with different chemical properties.
What is the significance of the atomic number in the periodic table?
-The atomic number, found at the bottom of the periodic table, is the number of protons in an atom's nucleus and determines the element's identity.
How do the properties of elements vary within a group in the periodic table?
-The properties of elements within a group in the periodic table tend to be similar due to having the same number of electrons in their outer shell. However, reactivity and other properties can change as you move down the group due to increasing distance of the outer electrons from the nucleus.
What is an ion and how does it form?
-An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons. For example, if an atom loses an electron, it becomes a positively charged ion (cation), and if it gains an electron, it becomes a negatively charged ion (anion).
What are isotopes and how do they differ?
-Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers, resulting in different relative atomic masses.
How was the modern periodic table developed?
-The modern periodic table was developed by organizing elements not just by atomic weight but also by their chemical properties. Dmitri Mendeleev's periodic table, which left gaps for undiscovered elements, was a significant step in the development of the modern table.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)