Classification pt 1 Pure Substances
Summary
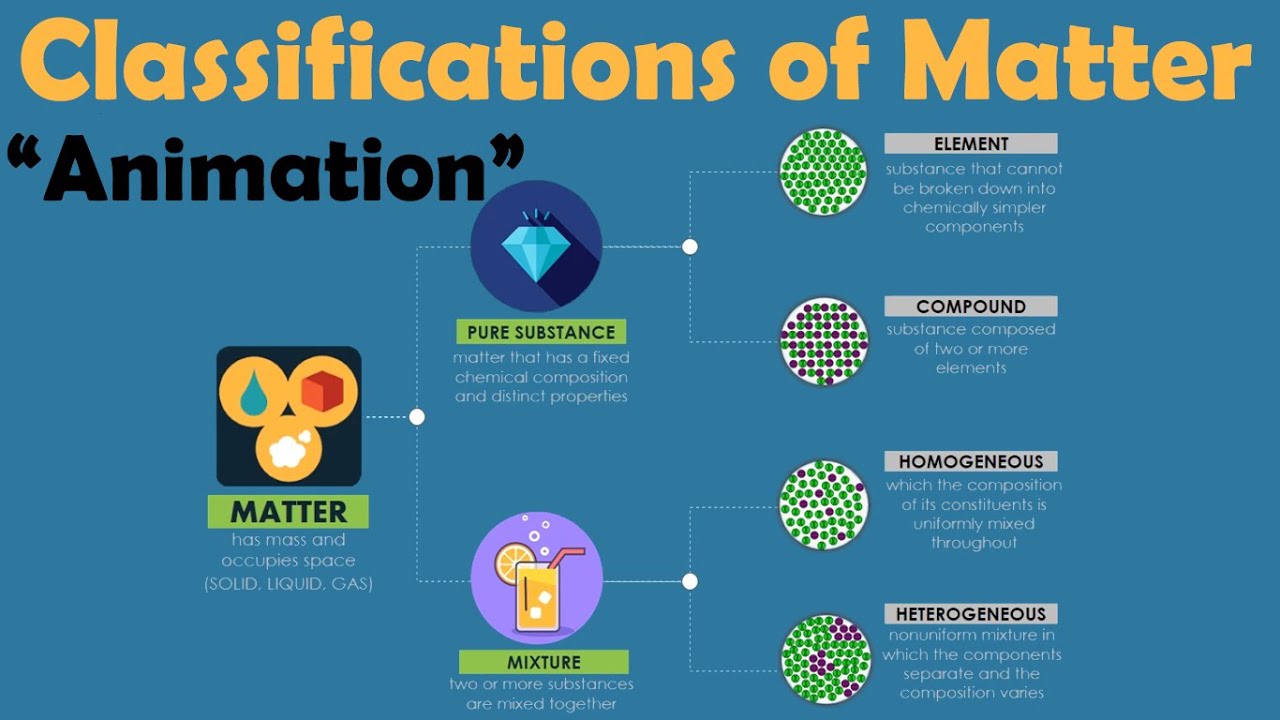
TLDRIn this educational video, the concept of classifying matter is explored, distinguishing between pure substances and mixtures. Pure substances are further divided into elements, which consist of one type of atom, and compounds, which are molecules made up of different atoms chemically bonded together. The script emphasizes the importance of understanding particles and their relationships, using examples like water (H2O) molecules and sucrose to illustrate these points. It also highlights the significance of chemical formulas and the difference between elements and compounds.
Takeaways
- 🧬 **Matter Classification**: The script focuses on classifying matter into two broad categories: pure substances and mixtures.
- 🔬 **Definition of Matter**: Matter is defined as anything that has mass and takes up space, excluding energy and light.
- 🌐 **Chemistry's Role**: Chemistry involves breaking down matter into different categories, which is a common practice in various scientific fields.
- 🧪 **Pure Substances**: Pure substances consist of a single type of particle, which can be either an element or a compound.
- 🔍 **Elements vs. Compounds**: Elements are pure substances made of one type of atom, while compounds consist of molecules with different types of atoms chemically bonded together.
- 💧 **Example of a Compound**: Water (H2O) is highlighted as a compound, made up of one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms chemically bonded.
- 🌿 **Example of an Element**: Helium is given as an example of an element, which is a pure substance composed of identical atoms.
- 📚 **Mixtures**: Mixtures are composed of more than one type of particle, which can be different atoms or molecules that are not chemically bonded.
- 🧂 **Example of a Mixture**: Dissolving salt in water creates a mixture with water molecules, sodium ions, and chloride ions.
- 🔑 **Importance of Particles**: The script emphasizes understanding matter in terms of particles and their relationships, which is crucial for grasping chemical concepts.
- 📈 **Chemical Formulas**: Chemical formulas and subscripts are introduced as a way to represent the composition of compounds, such as sucrose (C12H22O11).
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video script?
-The primary focus of the video script is to explain the classification of matter, particularly distinguishing between pure substances and mixtures.
What is the definition of matter as discussed in the script?
-Matter is defined as anything that has mass and takes up space, excluding energy and light from traditional definitions.
What are the two broad categories of matter mentioned in the script?
-The two broad categories of matter mentioned in the script are pure substances and mixtures.
What is a pure substance according to the script?
-A pure substance is composed of one type of particle, which can be a single type of atom or a single type of molecule.
What is a mixture, and how does it differ from a pure substance?
-A mixture consists of more than one type of particle that are not chemically bonded together, differing from a pure substance which has only one type of particle.
What is the difference between an element and a compound in the context of pure substances?
-An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom, while a compound is a pure substance consisting of molecules that include different types of atoms chemically bonded together.
Why is it important to think in terms of particles when studying chemistry?
-Thinking in terms of particles helps to understand the composition and interactions of matter at a fundamental level, which is essential for conceptualizing chemistry.
What is a chemical formula and why is it important?
-A chemical formula represents the composition of a compound, showing the types and quantities of atoms in a molecule. It is important for understanding the structure and properties of compounds.
What is the significance of subscripts in chemical formulas?
-Subscripts in chemical formulas indicate the number of atoms of a particular element within a molecule, which is crucial for understanding molecular composition.
How does the script differentiate between elements and compounds found on the periodic table?
-The script clarifies that while elements can be found on the periodic table, compounds, which are combinations of elements, are not listed as individual entities on the table.
What is the difference between a capital letter and a lowercase letter in chemical symbols as per the script?
-The script emphasizes that a capital letter followed by a lowercase letter in a chemical symbol represents an element, whereas two capital letters represent a different element, highlighting the importance of distinguishing between them.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Types of Matter - Elements, Compounds, Mixtures, and Pure Substances

💧 Sustancias Puras y Mezclas ⚗️ [Fácil y Rápido] | QUÍMICA |

Types of Matter: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures

Is Matter around us Pure? Full Chapter (Animation) | Class 9 Science chapter 2 | CBSE | NCERT

Classification of matter | Structure and properties of matter | High school chemistry | Khan Academy
CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER | Animation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)