BAB 1 : PENGUKURAN DALAM KEGIATAN KERJA ILMIAH | IPA SMA Kelas 10 Kurikulum Merdeka
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Miss Maya introduces the concept of measurement in scientific activities, focusing on the principles of accurate measurement, the importance of using correct tools like rulers, vernier calipers, and micrometers, and the significance of understanding units, dimensions, and derived quantities. Through examples such as measuring bolts and the surface area of a bottle cap, the video emphasizes the relationship between measurement tools, units, significant figures, and uncertainty in scientific measurements. Miss Maya also touches on key topics like dimensional analysis, scientific notation, and error reduction in repeated measurements to enhance learning and practical application in science.
Takeaways
- 😀 Measurement is the activity of comparing an unknown quantity with a standard unit of measurement.
- 😀 Scientific measurement tools include rulers, thermometers, speedometers, vernier calipers, and more.
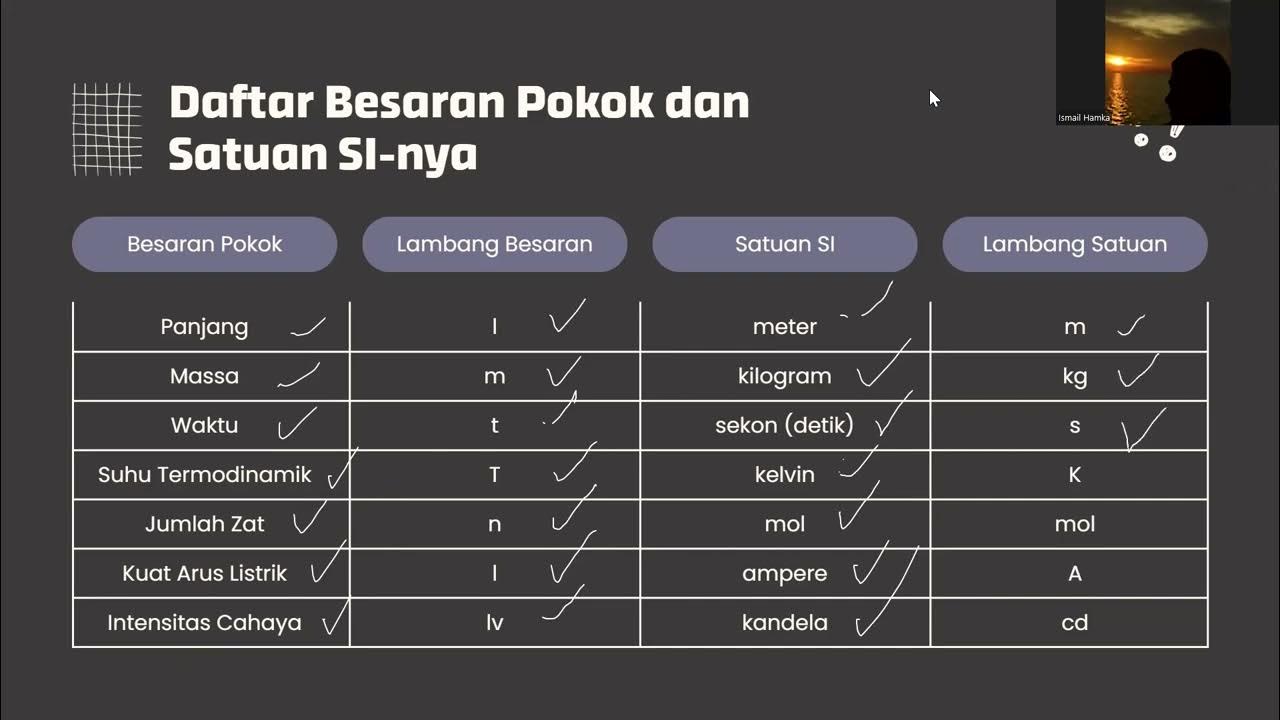
- 😀 Quantities are divided into two categories: basic quantities (length, mass, time) and derived quantities (speed, volume, force).
- 😀 There are various unit systems, such as the SI system, used globally to standardize measurements.
- 😀 Dimensions describe how a derived quantity is expressed based on its base quantities (e.g., speed as L/T).
- 😀 Vernier calipers measure lengths, and their accuracy can be determined by reading the main scale and nonius scale.
- 😀 Screw micrometers are used to measure the length, diameter, and thickness of objects with high precision.
- 😀 Significant figures indicate the accuracy of measurement and help to present data concisely.
- 😀 Scientific notation simplifies large or small numbers by expressing them in powers of 10 (e.g., 0.0075 becomes 7.5 * 10^-3).
- 😀 Measurement errors are inevitable, but repeated measurements can help minimize uncertainty and improve accuracy.
- 😀 Uncertainty in measurements can be quantified using standard deviation and relative uncertainty, helping to assess the reliability of results.
Q & A
What is measurement, and why is it important in scientific work?
-Measurement is the activity of comparing an unknown quantity with a standard unit. It's essential in scientific work to ensure precision and accuracy when observing and analyzing objects or phenomena.
What are the differences between basic quantities and derived quantities?
-Basic quantities are fundamental measurements such as length, mass, and time, each with a defined unit. Derived quantities, on the other hand, are formed by combining basic quantities, such as speed (length/time) and volume (length³).
Can you explain the significance of SI units in scientific measurements?
-SI (International System of Units) provides a standardized set of units for measuring basic and derived quantities, ensuring consistency and uniformity in scientific work worldwide. For example, the SI unit for length is the meter, and for mass, it's the kilogram.
What is the role of dimensions in understanding derived quantities?
-Dimensions represent the fundamental quantities involved in derived units. For example, speed's dimension is L/T (length over time), where L represents length and T represents time. Dimensional analysis helps express derived quantities in terms of basic quantities.
How do you measure the size of an object using a ruler, and what does it demonstrate?
-Using a ruler, you measure the length of an object by comparing it to a standard unit (e.g., centimeter or meter). This demonstrates how measurement allows us to determine the unknown quantity (object length) in relation to a known standard (ruler).
What are significant figures, and why are they important in scientific measurement?
-Significant figures indicate the precision of a measurement, showing how accurate a measuring instrument is. The more significant figures, the more precise the measurement. They help express the uncertainty of the measurement.
What are some examples of measuring instruments and the quantities they measure?
-Examples include: rulers (measuring length), thermometers (measuring temperature), vernier calipers (measuring internal and external dimensions), and speedometers (measuring speed). Each instrument is designed to measure a specific quantity.
How do vernier calipers work, and what are their main components?
-Vernier calipers measure the dimensions of an object with high accuracy. Main components include inner jaws (for internal measurements), outer jaws (for external measurements), depth gauge (for depth measurements), and a nonius scale for precise readings.
What is the formula to calculate the surface area of a bottle cap, and how do you calculate it?
-The surface area of a bottle cap can be calculated using the formula A = 1/4 π d², where 'd' is the diameter of the bottle cap. After measuring the diameter, squaring the result and applying the formula gives the surface area.
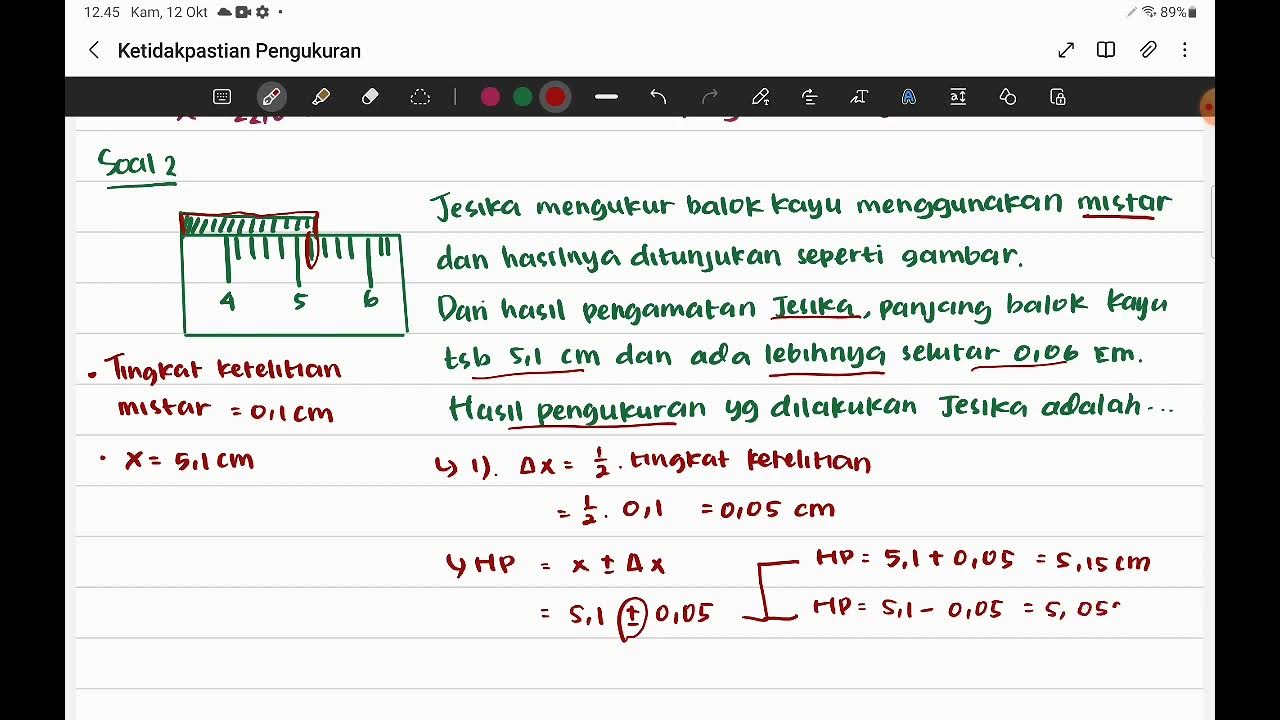
What is the purpose of calculating uncertainty in repeated measurements, and how is it done?
-The purpose of calculating uncertainty is to understand how much error may exist in the measurements. This can be done by taking multiple measurements, calculating the standard deviation, and using it to determine the uncertainty percentage, which reflects the reliability of the results.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)