RS-232 Explained: Working Principle, Pinout, Cables & Applications
Summary
TLDRRS-232 is a serial data transfer standard commonly used in industrial automation for legacy systems. This video covers the RS-232 protocol, including its pinout (DB9 and DB25 connectors), how it facilitates data transmission, and the necessary cables for connecting devices. It also explores the advantages and limitations of RS-232, such as its ease of use, slow data speeds, and susceptibility to interference. Despite its drawbacks, RS-232 remains widely used in industrial environments for point-to-point communication with equipment like PLCs, robots, and vision systems.
Takeaways
- 😀 RS-232, also known as TIA-232, is a widely used serial data transfer standard for communication between devices.
- 😀 The RS-232 standard typically uses DB9 and DB25 connectors, with DB9 being more common due to its compactness and cost-effectiveness.
- 😀 The RS-232 DB9 pinout includes pins for data transmission (TXD, RXD), control (RTS, CTS), and signal ground (GND).
- 😀 Data communication between devices using RS-232 requires proper connections of TXD, RXD, and GND pins for basic functionality.
- 😀 The RS-232 protocol employs voltage levels (positive for logic 0 and negative for logic 1) to encode and transmit data.
- 😀 A standard RS-232 data frame includes a start bit, eight data bits, a parity bit for error detection, and a stop bit.
- 😀 RS-232 supports both full-duplex communication, allowing simultaneous transmission and reception of data.
- 😀 Hardware flow control in RS-232 ensures that data transmission can pause and resume through RTS/CTS signaling.
- 😀 RS-232 cables come in different varieties: straight-through cables for DTE to DCE connections, and null-modem cables for DTE to DTE connections.
- 😀 RS-232 is commonly used in industrial automation for short-range, low-speed data transmission in devices like PLCs, CNC machines, and robots.
- 😀 Despite its limitations, such as low data transmission speeds (up to 19.2 kbps) and limited cable length (around 50 feet), RS-232 remains popular in legacy systems due to its simplicity and reliability.
Q & A
What does RS-232 stand for?
-RS-232 stands for Recommended Standard 232, which is a standard for serial data communication, used for transferring data between devices like computers and industrial equipment.
What are the key types of connectors used in RS-232 communication?
-The RS-232 standard uses D-subminiature connectors, most commonly DB9 and DB25 connectors. The DB9 connector has 9 pins, and the DB25 connector has 25 pins.
Why is the DB9 connector preferred over the DB25 in most RS-232 setups?
-The DB9 connector is preferred because it is more compact, cost-effective, and has enough pins to support most RS-232 connections, unlike the larger DB25 connector.
What are the functions of the pins on the DB9 connector?
-The pins on the DB9 connector serve various functions: Pin 1 (DCD) for carrier detection, Pin 2 (RXD) for receiving data, Pin 3 (TXD) for transmitting data, Pin 4 (DTR) for terminal readiness, Pin 5 (GND) for signal ground, Pin 6 (DSR) for set readiness, Pin 7 (RTS) for request to send, Pin 8 (CTS) for clear to send, and Pin 9 (RI) for ring indicator.
How does the RS-232 protocol ensure reliable communication between two devices?
-RS-232 ensures reliable communication by using control signals like DTR/DSR and RTS/CTS to indicate the readiness of devices to send or receive data, preventing data loss or mismatched communication.
What is hardware flow control in RS-232, and how does it work?
-Hardware flow control in RS-232 uses control signals like RTS (Request to Send) and CTS (Clear to Send) to manage the timing of data transmission between devices, allowing them to pause and resume data transfer as needed.
How does software flow control in RS-232 differ from hardware flow control?
-Software flow control uses special control characters, such as Xon and Xoff, to manage the data flow between devices. When the receiver is ready, it sends an Xon packet; when it needs to pause, it sends an Xoff packet.
What is the voltage convention in RS-232 for transmitting data?
-RS-232 transmits binary data using voltage levels: a positive voltage (Spacing) represents a binary 0, and a negative voltage (Marking) represents a binary 1.
What are the limitations of the RS-232 standard in terms of speed and cable length?
-RS-232 has a data transfer speed limit of up to 19.2 kilobits per second and can only reliably transmit data over cable lengths of up to 50 feet. It is also susceptible to radio frequency and electromagnetic interference.
In which industrial applications is RS-232 commonly used?
-RS-232 is commonly used in industrial automation for connecting devices such as PLCs, human-machine interfaces, industrial PCs, motor drives, robots, CNC machines, and vision systems.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What is Modbus and How does it Work?
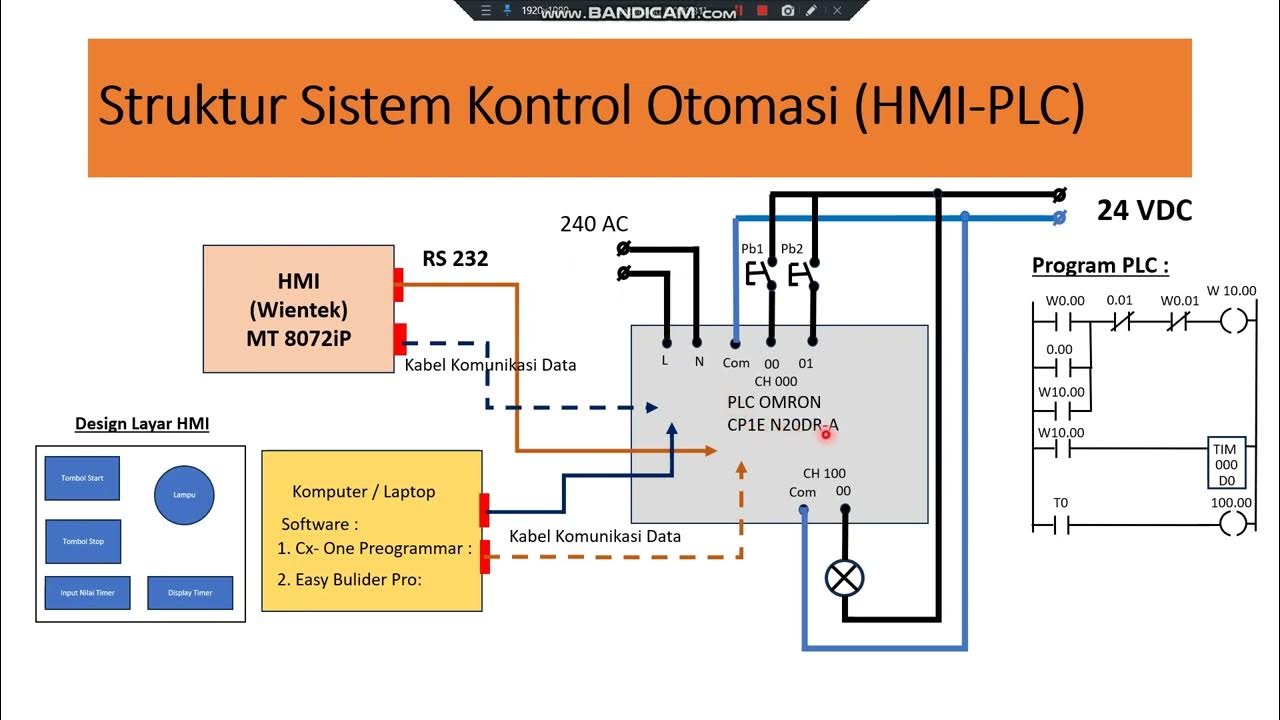
Part. 02 Komunikasi HMI-PLC -PC

IoT Protocols | MQTT | CoAP | OPC-UA | Modbus | LoRA | Industrial Automation IIoT

Peripheral Cables - CompTIA A+ 220-1101 - 3.1

Serial communication protocols - what are the differences?
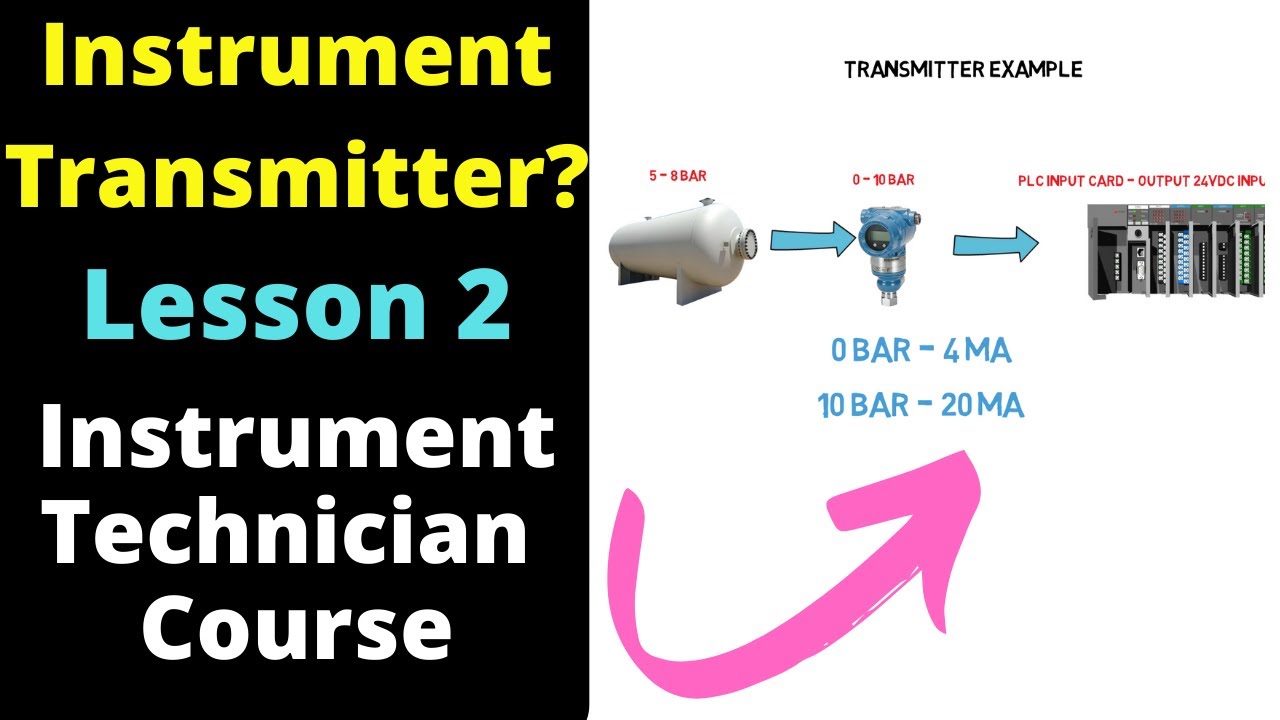
What is a Transmitter -Instrumentation Technician Course - Lesson 2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)