Tenaga Endogen Part 1 : TEKTONISME
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fascinating processes that shape Earth's surface, focusing on endogenic forces such as tectonism, volcanism, and seismic activity. It explains how these forces create landforms like mountains, valleys, and islands. The video delves into tectonic movements, distinguishing between epirogenetic and orogenetic forces, and illustrates the differences between folding and faulting. It also highlights various landforms, such as the Victoria Falls and Tengger Mountains, which are shaped by these geological processes. The visual explanations make these complex concepts accessible, offering insights into the dynamic nature of Earth's surface.
Takeaways
- 😀 Waterfalls like Victoria Falls and unique geological formations such as mushroom-shaped rocks are products of complex natural processes over time.
- 😀 The Earth's surface is shaped by both internal (endogenous) and external (exogenous) forces.
- 😀 Endogenous forces are driven by internal energy, leading to the formation of mountains, valleys, and more, while exogenous forces cause erosion and destruction.
- 😀 Endogenous forces can be categorized into three types: tectonism, volcanism, and seismic activity (earthquakes).
- 😀 Exogenous forces include weathering, erosion, mass wasting, and sedimentation, which contribute to the destruction of Earth's surface features.
- 😀 Tectonism, which can occur vertically or horizontally, causes shifts in Earth's layers and can be divided into epirogenetic and orogenetic movements.
- 😀 Epirogenetic movements involve slow, large-scale shifts of Earth's crust, which can result in either positive (lowering) or negative (rising) landforms.
- 😀 Orogenetic movements are faster and occur on a smaller scale, causing crustal deformation such as folding and faulting.
- 😀 Folding occurs due to horizontal or vertical pressure and can lead to various formations like anticlines (upward folds) and synclines (downward folds).
- 😀 Faulting involves the breaking and displacement of Earth's crust, leading to landforms like grabens (downward-sloping faults) and horsts (uplifted blocks).
Q & A
What are the two types of forces that shape the Earth's surface?
-The two types of forces that shape the Earth's surface are endogenic (internal) forces and exogenic (external) forces.
What is the difference between endogenic and exogenic forces?
-Endogenic forces come from within the Earth and are responsible for building the Earth's surface, such as through the formation of mountains and valleys. Exogenic forces, on the other hand, come from external factors like weather and erosion, and are responsible for eroding or destroying the Earth's surface.
Can you explain the term 'tektonisme' and its role in shaping the Earth's surface?
-'Tektonisme' refers to the movement of the Earth's crust due to internal forces, which can be vertical or horizontal. These movements result in the shifting of rock layers and the formation of landforms such as mountains and valleys.
What is the distinction between 'epirogenetik' and 'orogenetik' movements?
-Epirogenetik movements involve slow and gradual shifts in the Earth's surface over large areas, either causing land to sink or rise. Orogenetik movements, in contrast, are faster and occur over smaller areas, typically leading to the formation of mountain ranges through folding or faulting.
What is the difference between 'positive' and 'negative' epirogenetic movements?
-Positive epirogenetic movement occurs when the land sinks, leading to a rise in sea level. Negative epirogenetic movement, on the other hand, occurs when the land rises, causing a decrease in sea level.
What are some examples of the effects of epirogenetic movements?
-Epirogenetic movements can lead to the creation of new islands, the submergence of small islands, and changes in the coastline.
What is the difference between a 'fold' and a 'fault' in orogenic movements?
-A fold is a bend or curve in the Earth's crust caused by compressive forces, while a fault occurs when the crust breaks due to stress, leading to the displacement of rock layers.
What are some different types of folds that can form due to tectonic forces?
-Different types of folds include upright folds, inclined folds, overturned folds, isoclinal folds, and recumbent folds. These are classified based on the angle and shape of the fold.
What is a 'graben' and how does it form?
-A 'graben' is a type of fault block that sinks due to tectonic forces, creating a depression in the Earth's surface. It is typically surrounded by higher land areas or horsts.
How does the Victoria Falls relate to tectonic forces?
-Victoria Falls was formed due to faulting, a type of tectonic force, which resulted in the creation of a waterfall as the Zambezi River encountered a fault line.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Tenaga Endogen - Dinamika Litosfer - Materi Geografi

Geografi Kelas X (20) Tenaga Pembentuk Muka Bumi | Tenaga Endogen dan Eksogen

Dinamika Litosfer dan Dampaknya Terhadap Kehidupan

TENAGA ENDOGEN DAN EKSOGEN
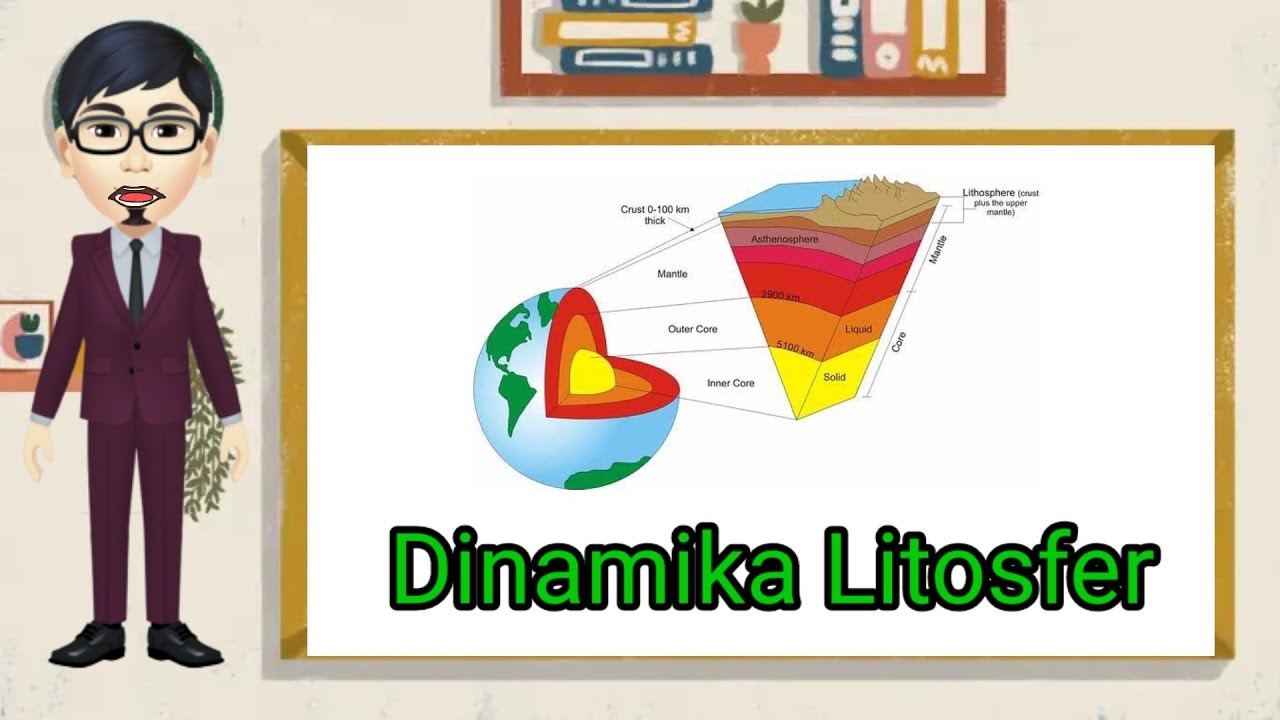
Mapel Geografi Kelas X " Dinamika Litosfer "

IPS (Geografi) Kelas 10 - Tenaga Endogen (Tektonisme) | GIA Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)