Mapel Geografi Kelas X " Dinamika Litosfer "
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Ardi Channel explores the dynamics of the Earth's lithosphere. The video covers the structure of the Earth's layers, including the core, mantle, and crust, and introduces the concept of the lithosphere. It explains the types of rocks—igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic—and the processes that shape the Earth's surface, such as tectonism, volcanism, and seismic activity. Viewers learn about tectonic movements, the formation of mountains, volcanic eruptions, and earthquakes, along with their effects on the environment and life. The video highlights both the positive and negative impacts of these geological phenomena.
Takeaways
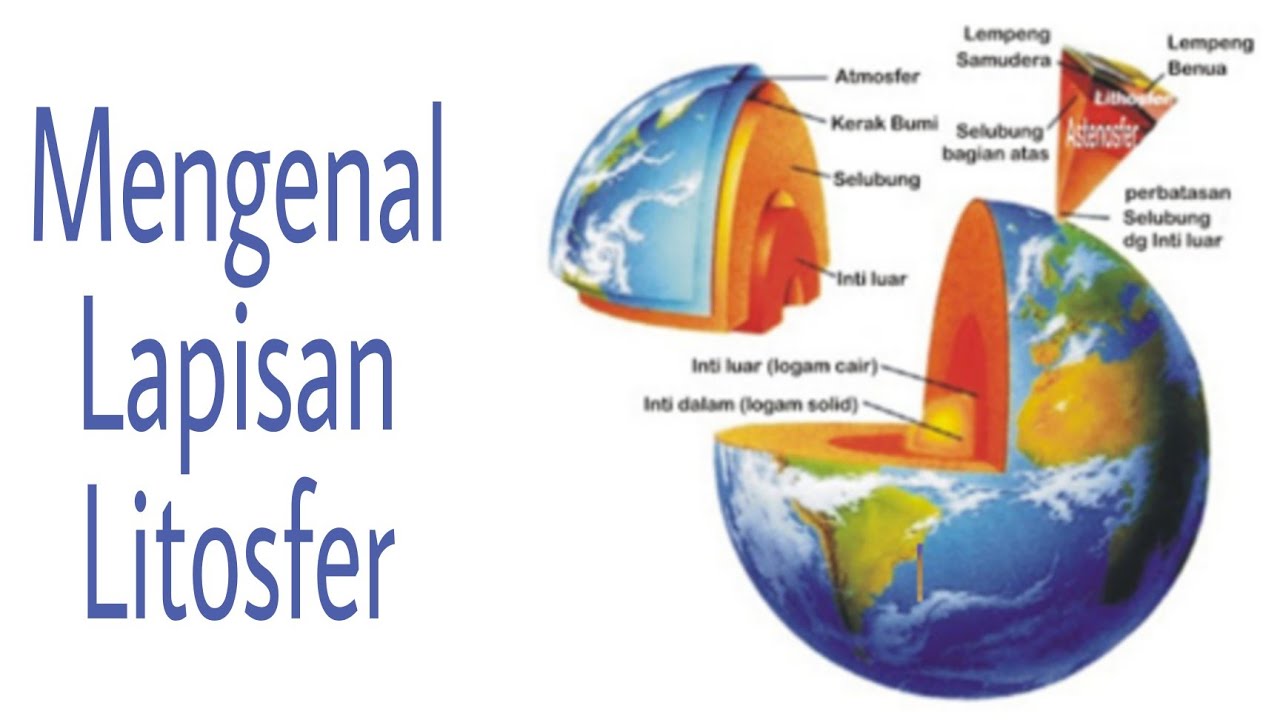
- 😀 The Earth's structure consists of three main layers: the core, mantle, and crust, with the core having a radius of 3500 km, the mantle's thickness being 2900 km, and the crust averaging 32 km in thickness.
- 😀 The lithosphere is divided into two parts: the sial (aluminum) and sima (magnesium), and it forms the solid outer layer of the Earth.
- 😀 Earth's crust is made up of three types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, sedimentary rocks from the deposition of particles, and metamorphic rocks from heat and pressure.
- 😀 Tectonism refers to the horizontal and vertical movement of the Earth's lithosphere due to the movement of tectonic plates.
- 😀 There are two types of tectonic movements: epirogenetic (slow, wide-scale shifts) and orogenetic (fast, mountain-building movements).
- 😀 Epirogenetic movements are classified into positive (land sinking) and negative (land rising), which affect the appearance of sea levels.
- 😀 Orogenetic movements are faster than epirogenetic ones and result in mountain formation through folding and faulting.
- 😀 Volcanoes are formed when magma from deep within the Earth rises to the surface. There are three types of volcanoes: Maar, cone-shaped, and shield volcanoes.
- 😀 Volcanoes can have negative impacts, such as lava flows and tsunamis, but also bring positive benefits like fertile soil and valuable minerals.
- 😀 Earthquakes can be caused by three factors: collapse (landslides), volcanic activity, and tectonic plate movements that result in faults or folds.
Q & A
What is the lithosphere?
-The lithosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth, consisting of rocks that make up the Earth's crust. It follows the shape of the Earth and is divided into two parts: the sial (aluminum) layer and the sima (magnesium) layer.
What are the three main layers of the Earth?
-The three main layers of the Earth are the core (with a radius of approximately 3500 km), the mantle (2900 km thick), and the crust (averaging 32 km thick).
What are the three types of rocks that make up the Earth's crust?
-The three types of rocks are igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks form from the cooling of molten magma, sedimentary rocks are formed from the deposition of materials like sand or minerals, and metamorphic rocks result from changes caused by high pressure or temperature.
What are igneous rocks and how are they classified?
-Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of magma. They are classified into three categories: plutonic (intrusive), volcanic (extrusive), and hypabyssal (intermediate).
What is sedimentary rock?
-Sedimentary rocks are formed when particles like sand, clay, or organic matter accumulate and are compacted over time. These rocks can be further categorized based on their composition, such as clastic, chemical, and organic.
How are metamorphic rocks formed?
-Metamorphic rocks are formed under high pressure and temperature conditions that alter the original rock, either igneous or sedimentary. This process can change the texture and mineral composition of the rock.
What are endogenous and exogenous forces in geology?
-Endogenous forces are those originating within the Earth, such as tectonism, volcanism, and seismic activity. Exogenous forces come from outside the Earth, including weathering and erosion.
What is tectonism and how does it affect the Earth?
-Tectonism refers to the movement and shifting of the Earth's lithospheric plates, which can occur both horizontally and vertically. This leads to the formation of landforms like mountains and valleys, and is caused by the movement of tectonic plates.
What is the difference between epirogenetic and orogenetic movements?
-Epirogenetic movements are slow, large-scale vertical movements of Earth's crust that can cause the land to rise or sink, affecting large areas. Orogenetic movements, on the other hand, are faster and result in the formation of mountain ranges.
What is volcanism and how does it impact life on Earth?
-Volcanism refers to the eruption of magma from the Earth's interior, forming volcanoes. Volcanoes can be classified into maar, cone, and shield volcanoes. While volcanic eruptions can be destructive, they also bring benefits like fertile soil and the potential for tourism.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

#1 #Kelas10 #Geografi #smstr2 | Lapisan Bumi dan Karakteristiknya

Plate Tectonics Theory | World Physical Geography | Geomorphology | Dr. Krishnanand
GEOGRAFI - MENGENAL LAPISAN LITOSFER

Dinamika Litosfer: Tenaga Endogen

LAPISAN BUMI PART 2. LITOSFER & HIDROSFER : IPA SMP KELAS 7

KEB02 Tektonik Lempeng | Materi OSN/KSN Kebumian SMA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)