RANTAI TRANSPOR ELEKTRON | Belajar lebih mudah dengan Lagu Mnemonic Kedokteran | Dosen Musisi
Summary
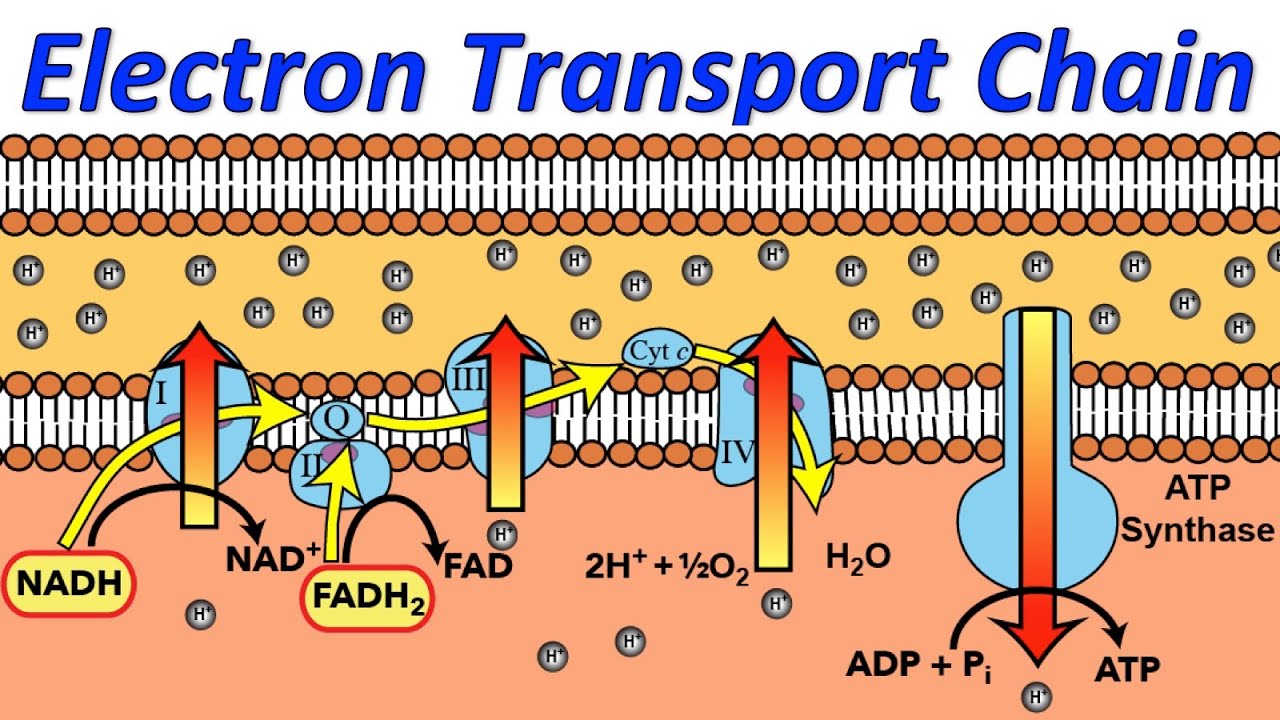
TLDRThis video explains the process of energy production in cells, focusing on how ATP is created within the mitochondria. The mitochondrion, often referred to as the cell's energy factory, features a two-layer membrane with a matrix where the Krebs cycle occurs. Through the electron transport chain, electrons from NADH and FADH2 move through various complexes, pumping protons into the intermembrane space, which creates an electrochemical gradient. ATP is then synthesized by the enzyme ATP synthase as protons diffuse back into the matrix, ultimately producing ATP and water as a byproduct.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for energy production.
- 😀 The mitochondrion has two membranes: an outer membrane and an inner membrane.
- 😀 The matrix inside the mitochondrion is where the Krebs cycle occurs, generating NADH and FADH2.
- 😀 NADH and FADH2 carry electrons to the electron transport chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- 😀 The electron transport chain consists of four protein complexes (I-IV) that pass electrons from one to the other.
- 😀 As electrons move through the electron transport chain, protons (H+) are pumped into the intermembrane space, creating a proton gradient.
- 😀 Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, combining with electrons and protons to form water.
- 😀 The proton gradient created in the electron transport chain is used to drive ATP synthesis.
- 😀 ATP synthase, an enzyme in the inner membrane, allows protons to flow back into the matrix, providing the energy to convert ADP and inorganic phosphate into ATP.
- 😀 The movement of electrons through the electron transport chain generates energy that is ultimately used to produce ATP, the cell's energy currency.
Q & A
What is the role of mitochondria in cells?
-Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. They are responsible for producing ATP, the energy currency of the cell, through processes like the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation.
What are the two membranes of the mitochondria?
-Mitochondria have two membranes: an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The inner membrane is where the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis occur.
What is the mitochondrial matrix, and what occurs there?
-The mitochondrial matrix is the inner space of the mitochondrion, enclosed by the inner membrane. It is the site of the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle), where energy from food is captured in molecules like NADH and FADH2.
How does the electron transport chain work in the mitochondria?
-The electron transport chain transfers electrons through a series of enzyme complexes in the inner mitochondrial membrane. As electrons move from one complex to another, they pump protons (H+) across the membrane, creating a proton gradient.
What role does oxygen play in the electron transport chain?
-Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. It combines with electrons and protons (H+) to form water, which helps drive the entire chain by maintaining the flow of electrons.
What is ATP synthase, and how does it work?
-ATP synthase is an enzyme located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It uses the energy from the flow of protons (H+) back into the mitochondrial matrix to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi).
What is the significance of the proton gradient in mitochondria?
-The proton gradient, created by the pumping of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, is essential for ATP production. This gradient drives the ATP synthase to produce ATP through a process called chemiosmosis.
Why can't protons diffuse directly across the mitochondrial membrane?
-Protons cannot diffuse freely across the mitochondrial membrane due to the membrane's lipid nature. The proton gradient is maintained by active transport through enzyme complexes and ATP synthase channels.
What is the function of NADH and FADH2 in cellular respiration?
-NADH and FADH2 are electron carriers that transfer high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain, helping to generate the proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
How does the process of oxidative phosphorylation generate ATP?
-Oxidative phosphorylation occurs as electrons pass through the electron transport chain, creating a proton gradient. The flow of protons back into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase drives the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)