Mitochondria
Summary
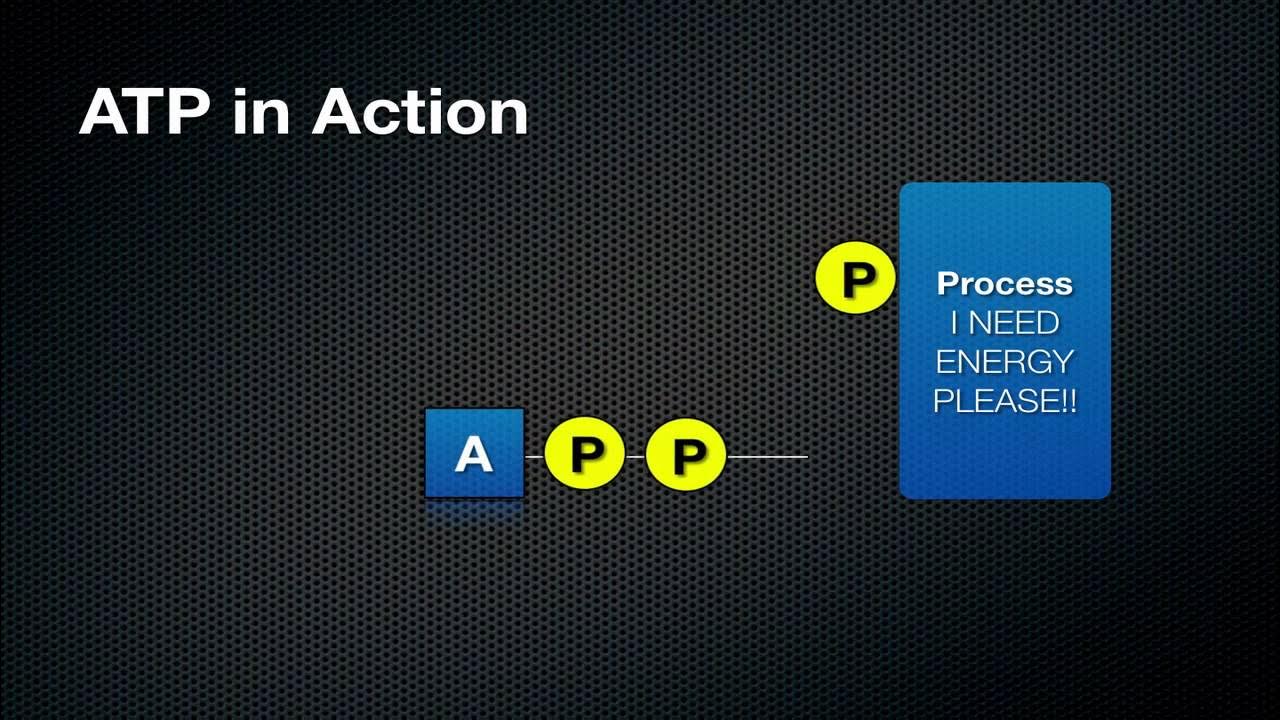
TLDRThis video explains the essential role of mitochondria in the human body. Mitochondria are the energy powerhouses within cells, converting food into ATP, the fuel that powers bodily functions. The process of cellular respiration, where organic molecules are transformed into ATP, occurs in mitochondria. Muscle cells, which need more energy, contain more mitochondria. With their unique double membrane structure, mitochondria sort molecules for energy production. Scientists believe mitochondria evolved from bacteria and now live within human cells. By breathing in oxygen, we support the ancient organisms inside us, enabling aerobic respiration and the generation of energy.
Takeaways
- 😀 The human body requires energy to perform basic functions like movement, eating, and breathing.
- 😀 Mitochondria, located within cells, are responsible for converting food into chemical energy, which is called ATP.
- 😀 ATP is the primary fuel used by the human body to carry out various processes.
- 😀 Cellular respiration is the process by which organic nutrients are converted into ATP within mitochondria.
- 😀 Mitochondria are crucial for energy production, and cells that require more energy contain more mitochondria.
- 😀 Muscle cells contain more mitochondria due to the high ATP demands for muscle contraction.
- 😀 Mitochondria have a double membrane structure, consisting of an outer and an inner membrane, which helps in the process of cellular respiration.
- 😀 The double membrane structure of mitochondria allows for sorting molecules essential for chemical processes.
- 😀 Mitochondria are believed to have evolved from bacteria and were once independent single-celled organisms.
- 😀 Mitochondria contain their own genetic information, supporting the theory that they were once separate organisms.
- 😀 The oxygen you breathe is used by mitochondria during cellular respiration, a process known as aerobic respiration.
- 😀 Breathing supports an ancient life form (mitochondria) inside your cells, highlighting a mutual relationship between humans and mitochondria.
Q & A
What is the role of mitochondria in the human body?
-Mitochondria are responsible for converting organic molecules from food into chemical energy in the form of ATP, which is used by cells for various functions.
What is ATP, and why is it important?
-ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the chemical energy that cells use for fuel. It is essential for processes like movement, eating, and breathing.
What is the process of cellular respiration?
-Cellular respiration is the process by which organic nutrients from food are converted into ATP within cells, providing energy for the body.
Why are mitochondria important to cellular function?
-Mitochondria are crucial for producing the ATP that cells need for energy. Cells with higher energy requirements, like muscle cells, contain more mitochondria.
What are the two membranes found in mitochondria?
-Mitochondria have an outer membrane and an inner membrane. These membranes are vital for sorting molecules used in chemical processes during cellular respiration.
How does the double membrane structure of mitochondria aid in cellular respiration?
-The double membrane structure allows mitochondria to sort and manage molecules effectively, supporting the process of cellular respiration and ATP production.
What theory explains the origin of mitochondria?
-The theory suggests that mitochondria evolved from bacteria and were once independent organisms. Over time, they were incorporated into larger cells, where they continue to function.
How is mitochondrial DNA different from nuclear DNA?
-Mitochondria contain their own genetic material, which is separate from the nuclear DNA found in the cell's nucleus. This supports the theory that mitochondria were once independent organisms.
What role does oxygen play in cellular respiration?
-Oxygen is essential for aerobic cellular respiration, where it is used by mitochondria to produce ATP. The oxygen you breathe is directly used by mitochondria to create energy.
How does breathing relate to mitochondria and energy production?
-When you breathe in oxygen, it enters your body and is used by mitochondria during cellular respiration to generate ATP, supporting your body's energy needs.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Organelles: Structure and Function (AP BIOLOGY)

How to Supercharge Your Mitochondria for Energy, Endurance, and Longevity! - A Comprehensive Guide

Sistema respiratório - Visão geral - Fisiologia veterinária - Aula 1

Zellorganellen und ihre Funktion [Zellbestandteile tierischer Zellen] - Aufbau Zelle [Biologie]

Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology - Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues
What ATP is and How it Works - BioVid Episode 3
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)