02 - Process Control System
Summary
TLDRThe video script focuses on the principles of process control systems, highlighting key elements like sensors, controllers, and final control elements. It explains how sensors measure variables such as temperature or flow rate, while controllers use this data to determine the necessary adjustments. Final control elements, like valves, act on these instructions to maintain desired conditions. The script also delves into common control strategies like feedback control, using a heat exchanger example to illustrate how control systems are applied in real-world industrial settings to optimize processes and handle disturbances.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses the fundamentals of process control in industrial settings, highlighting its importance in maintaining optimal performance.
- 😀 The script outlines the three key elements of a control system: sensor, controller, and final control element.
- 😀 Sensors play a crucial role in measuring variables such as temperature, flow rate, pressure, and composition, which are vital for control systems.
- 😀 Controllers interpret data from sensors and determine the necessary actions to achieve desired process conditions, like adjusting temperature or flow rate.
- 😀 The final control element, such as a valve, is responsible for making physical adjustments to processes based on commands from the controller.
- 😀 The system operates by reading the desired setpoint and adjusting process variables like temperature or flow to maintain those setpoints.
- 😀 The process control system aims to reduce disturbances that can negatively impact process stability and product quality.
- 😀 Disturbances, such as fluctuations in input variables or environmental changes, are common in industrial processes and must be minimized for consistency.
- 😀 Key steps in process control include understanding control objectives, selecting variables to measure, and identifying the right control strategy (e.g., feedback control).
- 😀 The video emphasizes the use of feedback control systems, which are widely adopted because they effectively correct deviations and maintain desired output values.
- 😀 The script concludes with an example involving a heat exchanger system, illustrating how control strategies are applied in real-world process control scenarios.
Q & A
What are the three key elements of a control system discussed in the transcript?
-The three key elements of a control system are the sensor, the controller, and the final control element.
What role does the sensor play in a control system?
-The sensor measures variables like temperature, flow rate, composition, or pressure within the system and provides data for further processing.
How does the controller interact with the sensor in a control system?
-The controller receives the information from the sensor, processes it, and determines the necessary action to maintain the desired system conditions.
What is the function of the final control element?
-The final control element, such as a valve, adjusts the system by controlling parameters like flow or temperature based on the controller's instructions.
Can you explain the process of controlling temperature in a system using a sensor and controller?
-To control temperature, a thermocouple sensor measures the temperature. The controller compares this measurement with the desired setpoint and instructs the final control element to adjust the system (e.g., increasing steam flow) if the temperature is off target.
What is a typical example of a sensor used in industrial process control?
-Examples of sensors used in industrial process control include thermocouples for temperature, flowmeters for flow rate, and gas chromatographs for composition analysis.
What is meant by a 'setpoint' in a control system?
-The setpoint refers to the desired value for a controlled variable (e.g., temperature, pressure), which the control system aims to maintain.
What control strategies are mentioned in the transcript for controlling a process?
-The transcript mentions feedback control, feedforward control, and differential control as common strategies for process control.
Why is feedback control the most commonly used control strategy in industrial settings?
-Feedback control is commonly used because it continuously adjusts the system based on the difference between the measured variable and the desired setpoint, ensuring stability and minimizing errors.
What steps are necessary to implement an effective process control system?
-The steps to implement an effective process control system include understanding the control objective, identifying the variables to measure and manipulate, and choosing the appropriate control strategy.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

SISTEM KONTROL DALAM OTOMASI INDUSTRI
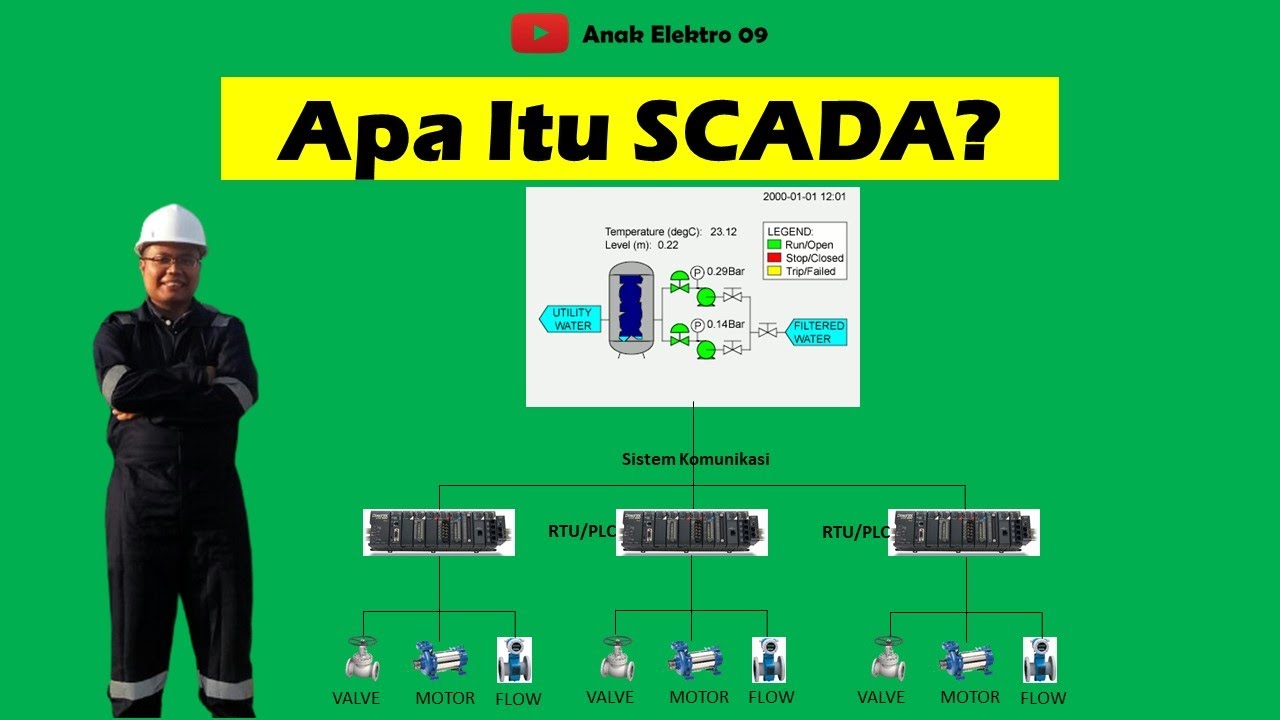
Pengenalan SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition)
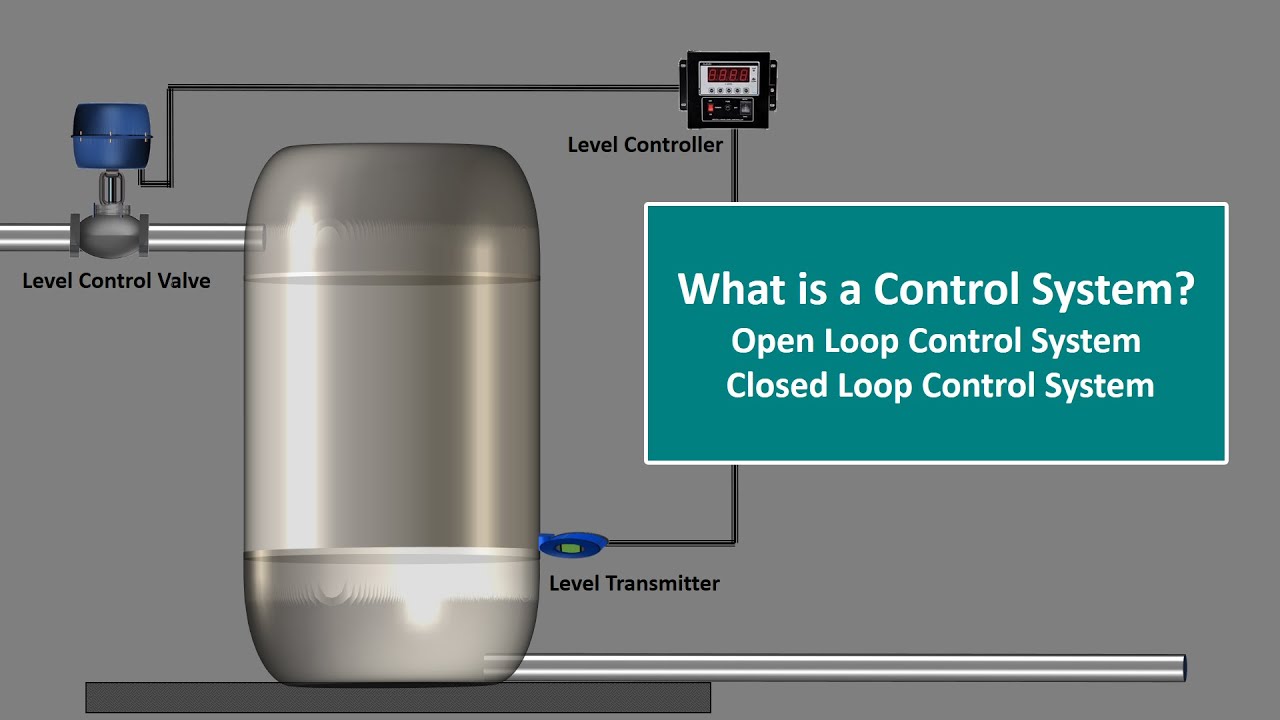
What is Control System.Control System Engineering.Open Loop and Closed Loop Control System.Explained

What is a Safety Instrumented System?

1. Introduction - Process Control Instrumentation -
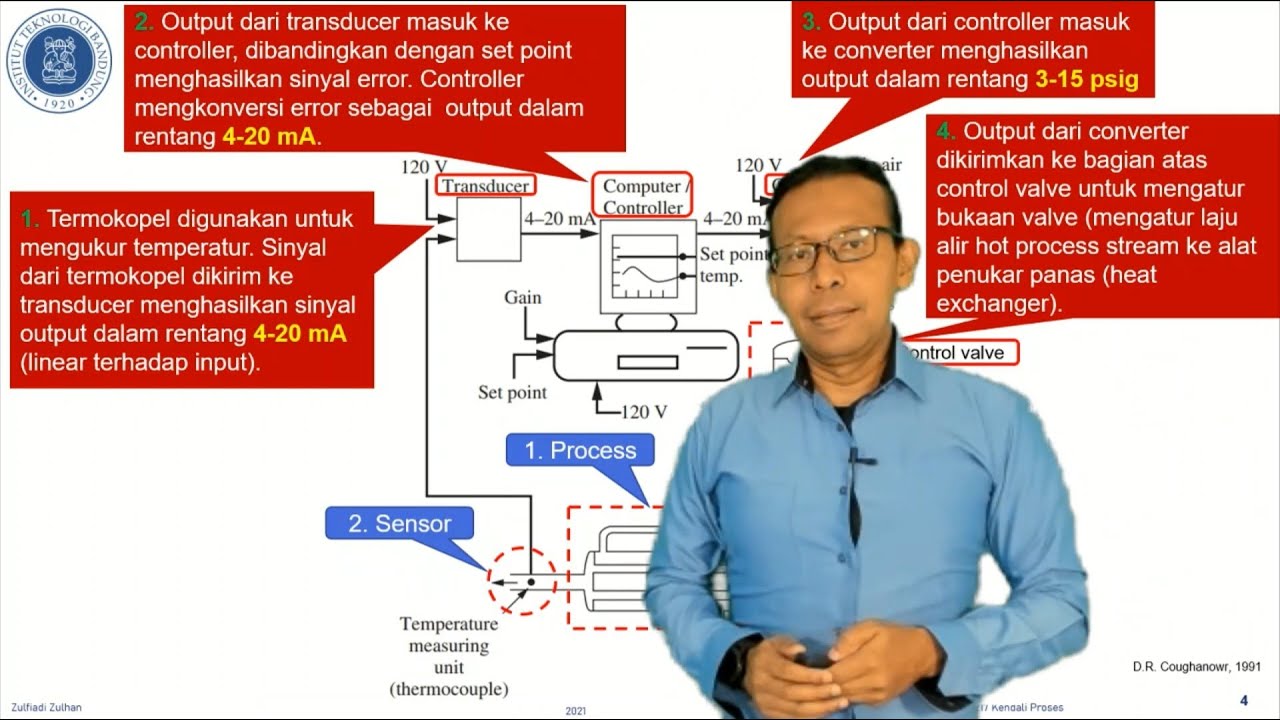
06. MG3217 Kendali Proses S01: Penyederhanaan Diagram Blok
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)