SISTEM KONTROL DALAM OTOMASI INDUSTRI
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fundamental principles and components of control systems in industrial automation. It covers key control types such as feedback and feedforward systems, including PID and adaptive controls. The video delves into open and closed-loop control systems, highlighting their applications in industrial processes like temperature, pressure, and speed control. The importance of controllers, sensors, actuators, and feedback in optimizing production processes and ensuring high-quality outputs is emphasized. The video aims to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of control systems' roles in improving efficiency and product consistency in industrial settings.
Takeaways
- 😀 Control systems are vital in industrial automation, enabling efficient and accurate production processes.
- 😀 Basic principles of control systems involve feedback and feedforward mechanisms to regulate and monitor processes.
- 😀 A feedback control system compares the system's output to the desired value, adjusting inputs to reduce errors.
- 😀 Feedforward control anticipates changes in the system and adjusts inputs before changes can affect the output.
- 😀 Types of control systems include on/off, proportional, integral, derivative (PID), and adaptive control systems.
- 😀 Industrial control systems consist of key components: controllers, sensors, actuators, feedback systems, and the process plan.
- 😀 The controller processes information and sends control signals to regulate the system, ensuring desired output.
- 😀 Sensors detect and measure variables in the system, converting physical data into electrical signals for processing.
- 😀 Actuators translate control signals into physical actions that affect the production process, such as regulating fluid flow or temperature.
- 😀 Open control systems do not use feedback, making them less efficient and potentially prone to errors, while closed control systems use feedback for continuous adjustments, ensuring greater accuracy and efficiency.
Q & A
What are the basic principles of control systems?
-The basic principles of control systems include the use of feedback and feedforward to regulate and monitor the process. Feedback compares the actual output with the desired value and adjusts the input to correct any discrepancies. Feedforward predicts disturbances and adjusts inputs to prevent the disturbance from affecting the output.
What is the role of feedback in control systems?
-Feedback in control systems involves using information from the system's output to compare it with the desired set point. The system then adjusts the input based on the difference (error) between the actual output and the setpoint, aiming to bring the output to the desired level.
What is the difference between open and closed control systems?
-An open control system does not use feedback to regulate the process, meaning it cannot measure the impact of its adjustments. A closed control system, on the other hand, uses feedback to continuously adjust the process until the actual output matches the desired output, making it more accurate and efficient.
What are the types of control systems mentioned in the script?
-The types of control systems mentioned include on-off control systems, proportional control systems, integral control systems, derivative control systems, PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control systems, and adaptive control systems.
How does a PID control system work?
-A PID control system combines three types of control: Proportional, Integral, and Derivative. The proportional part adjusts the output based on the current error, the integral part eliminates steady-state error by considering the sum of past errors, and the derivative part anticipates future errors by considering the rate of change of the error.
What is the purpose of feedforward in control systems?
-Feedforward in control systems predicts potential disturbances or changes and adjusts the input beforehand to prevent the disturbance from affecting the output. For example, in temperature control systems, feedforward can anticipate environmental changes and compensate by adjusting the input temperature.
What are the key components of an industrial control system?
-The main components of an industrial control system include the controller, process plan, sensor, actuator, and feedback. These components work together to ensure the system operates efficiently and meets the desired control objectives.
How does a controller function in an industrial control system?
-The controller acts as the brain of the industrial control system. It processes data from sensors, compares it to the desired setpoint, and generates control signals to regulate the system output accordingly.
What is the role of an actuator in industrial control systems?
-The actuator is responsible for translating the control signals from the controller into physical actions that affect the process or system. This could involve regulating fluid flow, driving a motor, or adjusting a temperature, depending on the application.
Can you give examples of open and closed control systems used in industry?
-Examples of open control systems include temperature control in ovens, pressure control on tanks, and speed control on machines. Closed control systems include product quality control in factories, chemical process control in petrochemical plants, and electrical production control in nuclear power plants.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Industrial Actuators Types of Actuators Actuator Working Principle Actuator Control Methods PLC
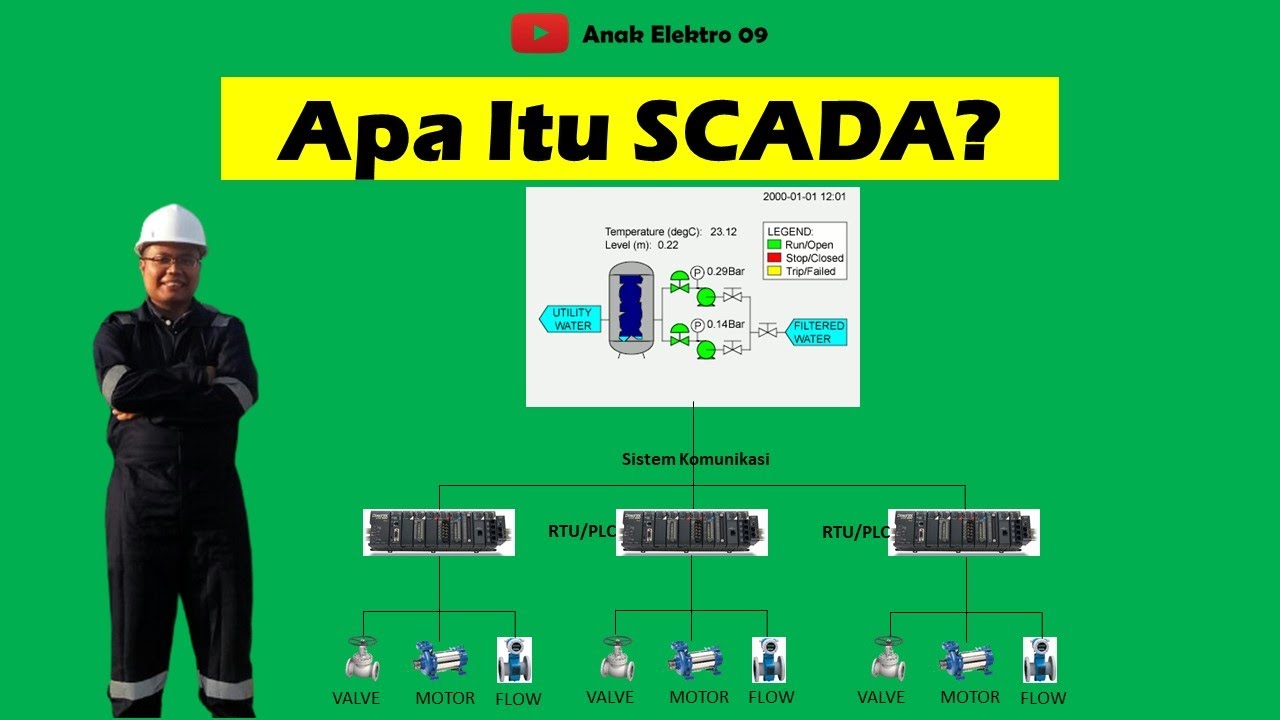
Pengenalan SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition)

Pertemuan 3. Sistem Kendali Pada Robot | Robotic and Control System

The Inductive and Capacitive Sensor | Different types and applications
Programable Logic Controller Basics Explained - automation engineering

Pemrograman SCADA - Level 3 (SKI berbasis Telemetry)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)