[BGD01B-ID] Introduction to Databases
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the concept of database systems, explaining their advantages over traditional file-based systems. It highlights key issues with file systems such as lack of concurrent access and data inconsistency, and contrasts these with the benefits of databases, including centralized data management and improved data consistency. The video also touches on the roles of people involved in database systems, like database administrators, designers, and application developers, while acknowledging the higher complexity and costs of database systems. Ultimately, it demonstrates how databases address the limitations of file systems and offer greater efficiency for organizations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Database systems provide a better solution compared to file systems, which have limitations in simultaneous access by multiple users.
- 😀 File systems struggle with data spread across different locations, making it harder for multiple parties to access the same data.
- 😀 Data structure differences in file systems can cause confusion, even when the data itself is the same.
- 😀 File systems often limit access to data based on the application used to create it, like Microsoft Excel files only being accessible within that program.
- 😀 A database is a collection of logically connected data that resides in one location and can be accessed simultaneously by different users.
- 😀 A Database Management System (DBMS) is responsible for controlling access, managing data, and ensuring proper usage of the database by users.
- 😀 Key components of a database environment include hardware, software, data, procedures, and people (users).
- 😀 Roles in a database system include database administrators, database designers, application developers, and end users.
- 😀 The primary benefit of databases is reducing data duplication by storing information in a single location, ensuring data consistency and accessibility across users.
- 😀 Some challenges of using databases include their high complexity, expensive software, and the cost of necessary hardware, although free versions are available with limitations.
Q & A
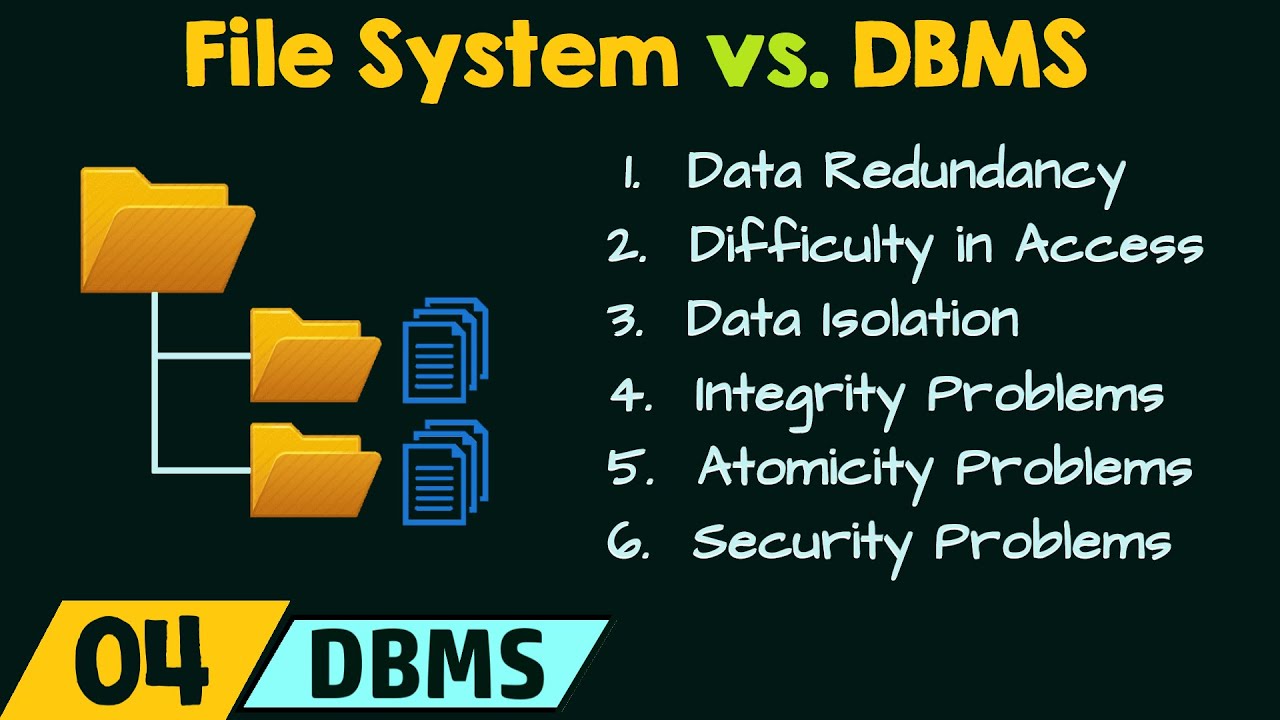
What are the main problems encountered with file systems?
-File systems face issues such as the inability to be accessed by multiple users simultaneously, leading to delays in updates. Data is often scattered across different locations, making it difficult to access, and the data structures vary, causing confusion. Additionally, file systems depend on specific applications, limiting their accessibility.
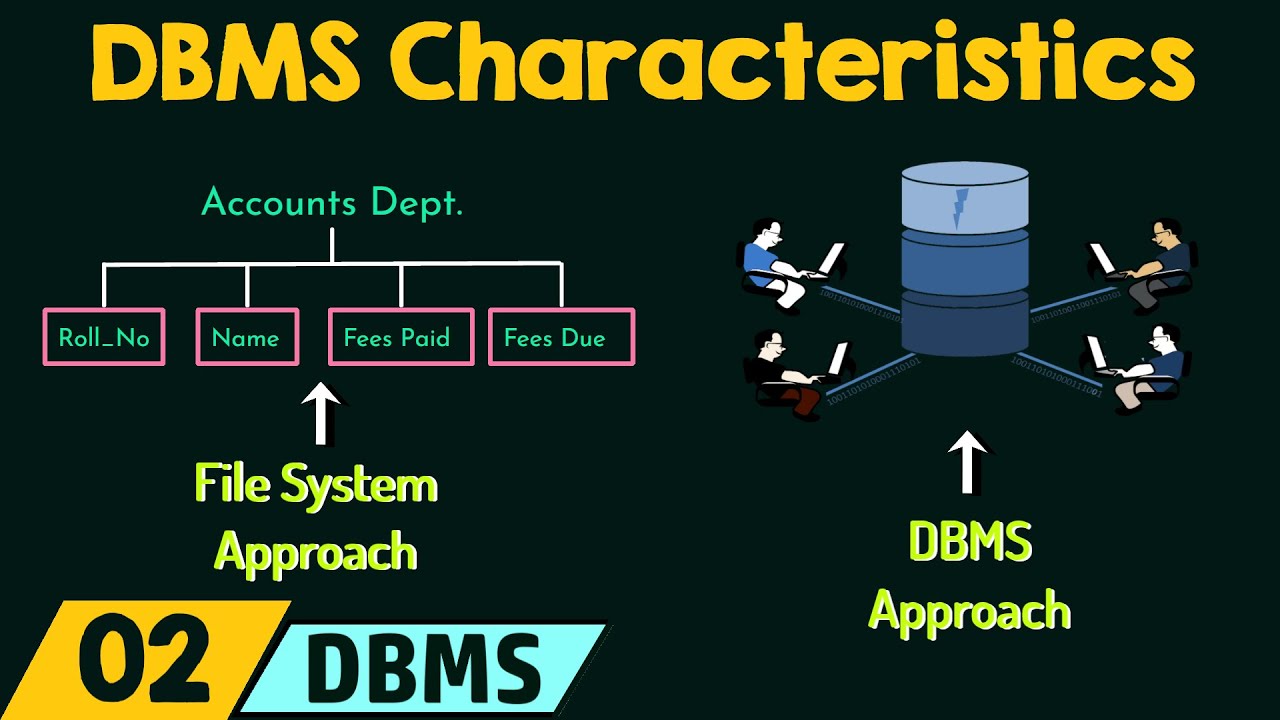
What is a database, and how does it differ from a file system?
-A database is a collection of logically connected data that is stored in a single location and can be accessed by multiple users simultaneously. Unlike file systems, which can be fragmented and difficult to manage, databases allow for centralized management of data and ensure consistency across users.
What does a Database Management System (DBMS) do?
-A DBMS is responsible for managing the database. It controls who can access the data, ensures that multiple users can interact with the data at the same time, and maintains the integrity and security of the data.
What are the five components of a database environment?
-The five components of a database environment are: 1) Hardware (servers), 2) Software (DBMS), 3) Data, 4) Procedures (rules for handling data), and 5) People (administrators, developers, users).
What roles do people play in a database system?
-In a database system, there are several roles: Database Administrators (DBA) who manage and secure the database; Database Designers who structure the database; Application Developers who create applications interacting with the database; and End Users who use the applications to interact with the data.
What is the role of a Database Administrator (DBA)?
-The DBA is responsible for managing the database, ensuring data security, controlling access rights, and maintaining the integrity of the database system.
Why is data consistency important in a database system?
-Data consistency is crucial because it ensures that all users have access to the same version of data. When one user updates data, the changes should be visible to all other users, preventing issues such as data duplication and outdated information.
What are the benefits of using a database instead of a file system?
-The main benefits of using a database are improved data consistency, reduced data duplication, and better management of concurrent access. A database allows data to be stored in one location, ensuring that updates are automatically reflected across all users, thus maintaining accurate and up-to-date information.
What are some disadvantages of using a database?
-The disadvantages of using a database include its complexity, the high cost of DBMS software, and the required investment in hardware infrastructure. While free versions of DBMS exist, they often come with limitations.
How does a database ensure that data is not duplicated?
-A database ensures that data is not duplicated by centralizing storage and access, so that all users interact with the same set of data. When changes are made to the data, they are immediately updated for all users, avoiding inconsistent versions of the data.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)