Chapter 1 - Overview of Databases
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the fundamentals of databases, explaining the key concepts such as data, information, and database management systems (DBMS). It contrasts traditional file-based systems with modern databases, highlighting the advantages of using a DBMS in terms of reducing redundancy, improving data integrity, and enabling efficient data access. The video also explores current technological trends like Industry 4.0, IoT, big data, and AI, all of which rely heavily on databases. Finally, it discusses the various types of database users, including end users, database designers, application programmers, and database administrators, concluding with the importance of databases in today’s digital world.
Takeaways
- 😀 A database is a structured set of data stored on a computer system and is essential for managing data in organizations.
- 😀 Data processing involves converting raw data into useful information, which is crucial for decision-making in organizations.
- 😀 Information is the result of processing data, where raw facts are organized and interpreted to make them meaningful.
- 😀 Databases are used to store logically related data, ensuring that data from different departments or areas can be integrated and managed effectively.
- 😀 File-based systems, though once popular, have significant limitations, such as data redundancy, program-data dependency, and data integrity issues.
- 😀 The database approach minimizes data redundancy, reduces program-data dependency, and provides better data integrity and security compared to file-based systems.
- 😀 Industry 4.0 emphasizes the use of databases to manage large volumes of data from interconnected devices, enabling real-time data analysis and decision-making.
- 😀 Cloud computing, big data, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are driving the need for more advanced database technologies to handle vast amounts of data.
- 😀 A Database Management System (DBMS) is essential for creating, managing, and controlling access to databases, ensuring data integrity and security.
- 😀 There are different types of database users, including end users, database designers, application programmers, and database administrators (DBAs), each with specific roles and responsibilities in managing data.
Q & A
What is a database?
-A database is a centralized and structured set of data stored in a computer system. It stores various types of data, such as numbers, text, files, pictures, videos, and audios, and provides facilities to transform retrieved data into useful information.
What is data processing?
-Data processing is the conversion of raw data into a usable and desired form. It involves organizing, structuring, and calculating data to produce meaningful information that organizations can use for decision-making.
How does a database support organizational activities?
-A database supports organizational activities by collecting and storing logically related data. This data is then processed using queries and software tools to generate useful information, which helps organizations make informed decisions and generate reports.
What is the difference between data and information?
-Data consists of raw facts such as numbers, text, or images, while information is the result of processing this data to make it meaningful. For example, raw student test scores are data, while the class average score calculated from these scores is information.
What are the limitations of the traditional file-based system?
-Traditional file-based systems suffer from data redundancy, program-data dependency, data integrity issues, and difficulties with concurrent access. These problems arise because each application manages its own files independently, leading to inefficiency and inconsistency.
Why was the database management system (DBMS) created?
-A DBMS was created to address the problems inherent in file-based systems. It enables efficient management of data, reducing redundancy, enforcing data integrity, and allowing concurrent access to the data by multiple users.
What is Industry 4.0, and how does it relate to databases?
-Industry 4.0 refers to the new phase in the industrial revolution, focusing on interconnectivity, automation, and real-time data processing. Databases play a crucial role in managing the large amounts of data generated in this environment, particularly in manufacturing, supply chains, and IoT systems.
What are the advantages of using a database over a traditional file system?
-The main advantages of using a database are reduced data redundancy, program-data independence, improved data integrity, and support for concurrent access. Databases store data in a central location and provide controlled access, reducing inefficiencies and errors.
Who are the different types of database users?
-There are four main types of database users: end users, database designers, application programmers, and database administrators (DBA). End users interact with the database through applications, while DBAs are responsible for managing the database. Database designers and application programmers handle the creation and maintenance of the system.
What is the role of a database administrator (DBA)?
-A DBA is responsible for overseeing the database system, including defining the database schema, managing access, ensuring data security, and performing backup and recovery. The DBA plays a critical role in maintaining the integrity, availability, and performance of the database system.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Bancos de Dados - Aula 01 - Visão geral sobre banco de dados e motivação

Apa Itu Data, Basis Data dan DBMS

SBD1 Pertemuan 1 | 3IA09,3IA10,3IA11,3IA13,3IA16
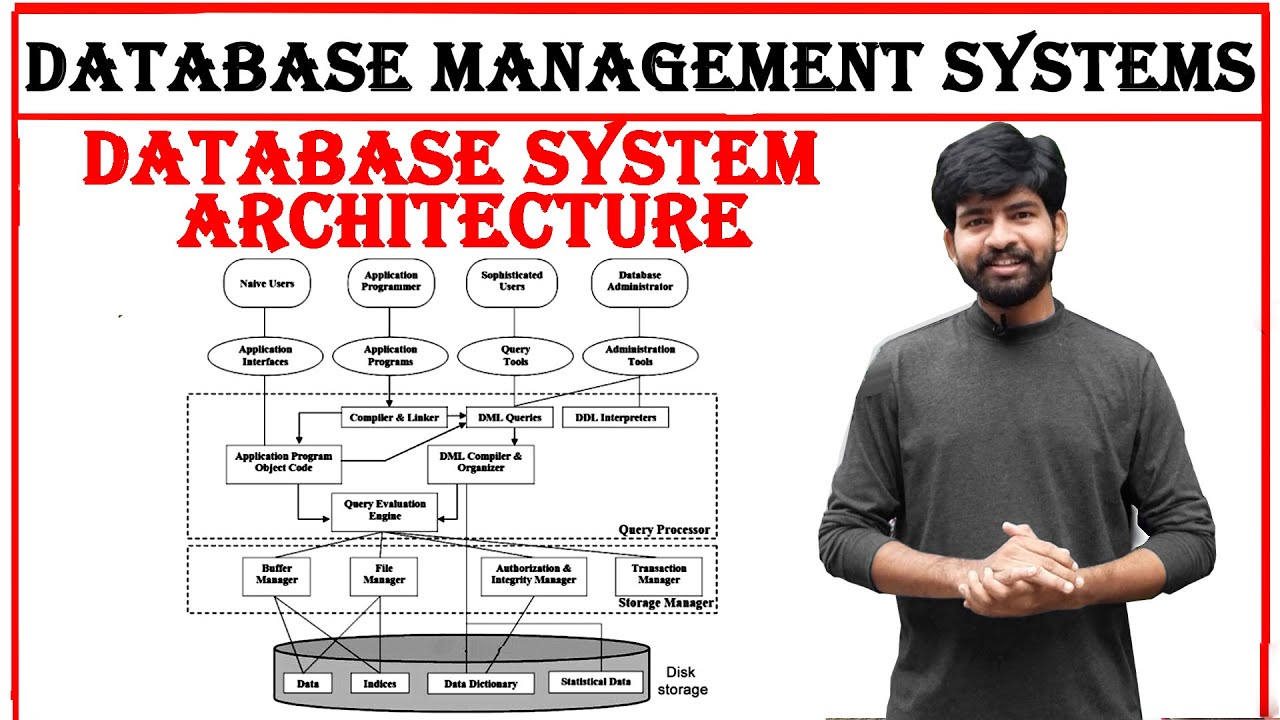
database system architecture in dbms | database management system | Architecture | DBMS | btech
Learn What is Database | Types of Database | DBMS

What is Database & SQL?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)