RESUMÃO: eletrodinâmica
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Professor Artur Neto explains key concepts in electrodynamics, focusing on Ohm's Law, series and parallel circuits, resistance, and power. The video breaks down how voltage (ddp), resistance, and current interact, and how these principles apply to real-world devices like lamps and heaters. Professor Neto also clarifies methods to calculate power in different contexts and introduces important units like watts and kilowatt-hours. The tutorial covers both theoretical concepts and practical applications, helping viewers better understand and prepare for exams on the topic.
Takeaways
- 😀 A battery provides a voltage (ddp) in a circuit, which drives the flow of electrical current.
- 😀 Resistance (measured in ohms) opposes the flow of current in electrical devices like lamps or irons.
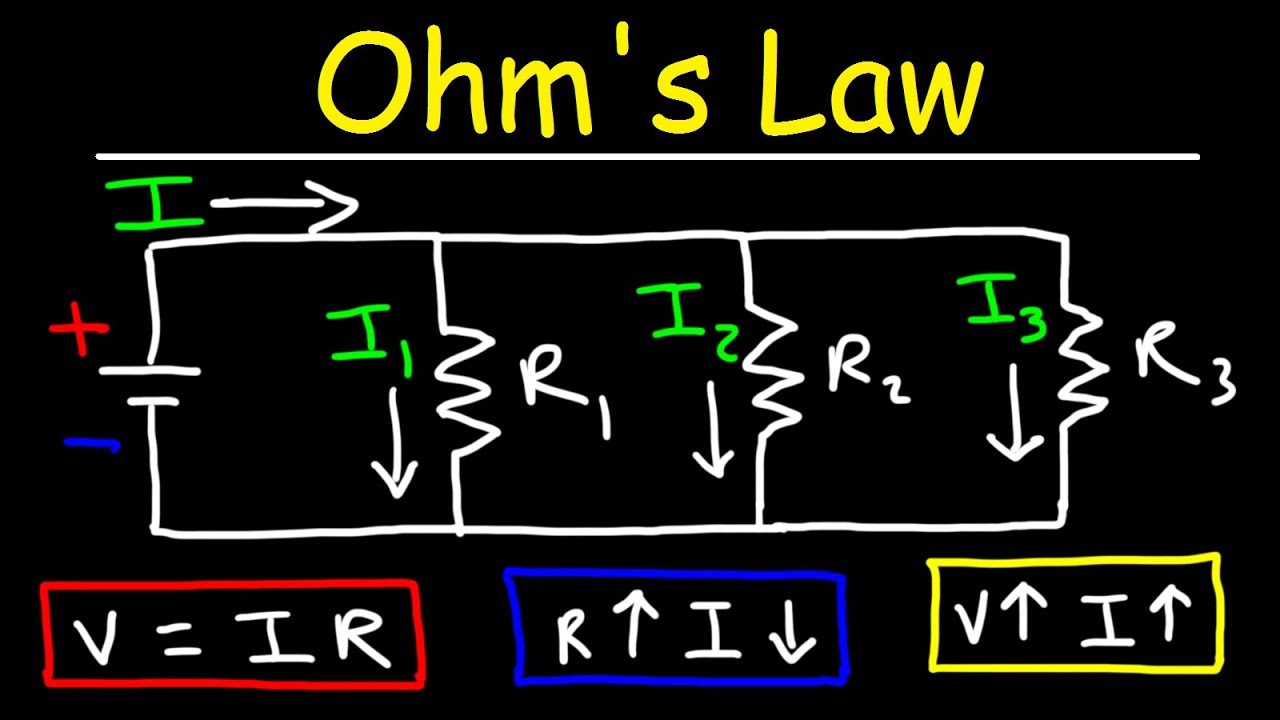
- 😀 Ohm's Law states that voltage (V) is equal to the current (I) multiplied by the resistance (R): V = I * R.
- 😀 The resistance of a conductor can be calculated using the formula R = ρ * (L / A), where ρ is the resistivity, L is the length, and A is the cross-sectional area of the conductor.
- 😀 A series circuit has the same current flowing through all components, with the total voltage divided among them.
- 😀 In a parallel circuit, all components share the same voltage, and the total current divides among the components.
- 😀 A mixed circuit combines both series and parallel connections, where some components are in series and others in parallel.
- 😀 Power (measured in watts) is the rate at which energy is consumed over time: P = E / t.
- 😀 Power can also be calculated using formulas like P = V * I, P = I² * R, or P = V² / R, depending on the known variables.
- 😀 Electrical energy is commonly measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), where 1 kWh = 1000 watts used for 1 hour.
- 😀 The understanding of these basic concepts and formulas is essential for solving problems in electrodynamics, especially in electrical circuits.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is a summary of electro-dynamics, focusing on concepts like voltage, current, resistance, Ohm's law, and circuit configurations.
What is the role of the battery in the circuit?
-The battery serves as a source of voltage, providing a potential difference (V) that drives the flow of electric current through the circuit.
What does the resistance in the circuit represent?
-Resistance represents the opposition to the flow of electric current in the circuit, and it is measured in Ohms (Ω). The higher the resistance, the harder it is for the current to flow.
What is Ohm's Law and how is it applied?
-Ohm's Law states that voltage (V) equals the current (I) multiplied by the resistance (R), expressed as V = I * R. It is a fundamental equation in electro-dynamics used to calculate any one of the three variables when the other two are known.
What is the significance of the second law of Ohm?
-The second law of Ohm helps calculate the resistance of a conductor based on its material properties and physical dimensions. The resistance (R) is determined by the formula R = ρ * (L / A), where ρ is resistivity, L is the length, and A is the cross-sectional area.
How do series and parallel circuits differ in terms of current and voltage?
-In a series circuit, the current is the same through all components, but the voltage is divided among them. In a parallel circuit, all components experience the same voltage, but the current is divided among the branches.
What is the formula for calculating total resistance in a series circuit?
-In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances: R_total = R_1 + R_2 + ... + R_n.
What is the formula for calculating total resistance in a parallel circuit?
-In a parallel circuit, the total resistance (R_total) is calculated using the reciprocal formula: 1 / R_total = 1 / R_1 + 1 / R_2 + ... + 1 / R_n.
What does power represent in an electrical circuit?
-Power in an electrical circuit represents the rate at which energy is consumed or produced. It is measured in watts (W), and is calculated using the formula P = E / t, where E is energy and t is time.
What are the different ways to calculate electrical power?
-Electrical power can be calculated using several formulas: P = V * I (where V is voltage and I is current), P = I² * R (where I is current and R is resistance), or P = V² / R (where V is voltage and R is resistance). All formulas give the same result but depend on the known variables.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

ФИЗИКА ЗА 5 МИНУТ - ЭЛЕКТРОДИНАМИКА

[NEW VERSION!] RANGKAIAN PARALEL DAN SERI PARALEL | Rangkaian Listik Arus Searah - Fisika Kelas 12

ASSOCIAÇÃO DE RESISTORES: em série e em paralelo | Cortes dos Aulões do Enem | Física | Antônio

Resistive circuits in series

5 Formulas Electricians Should Have Memorized!
Ohm's Law
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)