Wireless Connections with Access Point in Cisco Packet Tracer
Summary
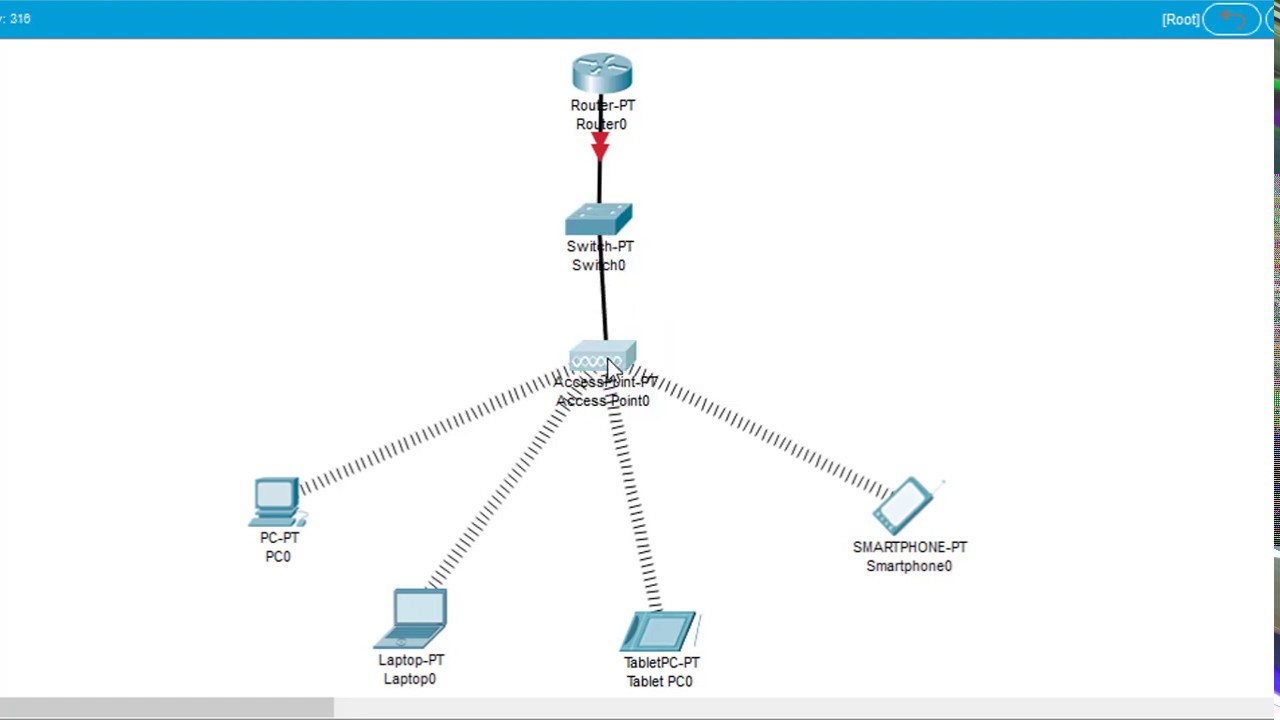
TLDRThis video walks viewers through setting up a wireless network using an access point, connecting multiple devices including a PC, laptop, and smartphone. The tutorial covers configuring the SSID, setting a WPA2 password, and connecting each device to the access point. It also highlights troubleshooting steps, such as adding wireless modules to devices that don’t have them by default. The connection is tested with packet simulation to ensure stable communication between the devices. The guide is aimed at helping users understand the basics of network setup and testing in a visual and interactive environment.
Takeaways
- 😀 Choose a simple access point for the wireless connection setup (PT).
- 😀 Select multiple devices (PC, laptop, smartphone) to test the wireless network.
- 😀 Configure the access point by setting an SSID (e.g., DG Dev) and a WPA2-PSK password for security.
- 😀 Devices like smartphones may connect instantly if no password is set initially.
- 😀 The access point uses port 0 for wireless connections, and port 1 for wired connections.
- 😀 For PC and laptop, replace wired modules with wireless modules to enable wireless connectivity.
- 😀 After installing the wireless module, use the desktop's wireless menu to select the SSID and input the password.
- 😀 The smartphone needs manual configuration to connect to the wireless network, including setting the SSID and password.
- 😀 Assign static IP addresses to devices (e.g., 10.1 for PC, 10.11 for laptop, and 10.12 for smartphone) for network communication.
- 😀 Test the connection by sending a packet from the PC to the smartphone, verifying that the packet reaches the correct destination.
- 😀 Troubleshooting: Ensure proper patience when waiting for devices to detect the network and manually configure the SSID and password if needed.
Q & A
What is an access point in a wireless network?
-An access point (AP) is a device that allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network. It provides a signal that wireless devices, such as smartphones, PCs, and laptops, can connect to for internet or local network access.
Why is WPA2-PSK used for the access point password?
-WPA2-PSK (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 - Pre-Shared Key) is used because it is one of the most secure methods of encryption for wireless networks. It ensures that only devices with the correct password can connect to the access point.
What is the purpose of setting the SSID for an access point?
-The SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the name of the wireless network. It helps users easily identify and connect to the correct network when scanning for available Wi-Fi networks on their devices.
What module is needed to enable wireless connection on the PC?
-The VMP 300N module is needed to enable the wireless connection on the PC. The module must replace the default wired connection module to allow the PC to connect to a wireless network.
Why do laptops in Cisco Packet Tracer not have wireless modules by default?
-Laptops in Cisco Packet Tracer do not have wireless modules by default because the simulation environment requires users to manually add wireless modules to laptops, simulating real-world configurations.
How can a smartphone connect to a wireless network in this setup?
-The smartphone connects to the wireless network by manually entering the SSID and password in the 'config' tab under the 'Wireless' section. Once these details are entered, the device connects to the access point.
What is the significance of the 'Signal Strength' in the wireless configuration?
-Signal strength indicates the quality of the wireless connection. The 'purple circle' on the visual menu represents the range of the signal, and a stronger signal generally means a more stable connection.
How are IP addresses assigned to the devices in this setup?
-The IP addresses are set statically for each device. For instance, the PC gets the IP address 192.168.1.10, the laptop 192.168.1.11, and the smartphone 192.168.1.12. This ensures fixed IP assignments for easier network management.
What does the 'Simulation Mode' in Cisco Packet Tracer do?
-The 'Simulation Mode' in Cisco Packet Tracer allows users to simulate network traffic. In this case, packets can be sent between devices, helping to visualize how data flows through the network and to test connectivity.
What happens when a packet is sent from the PC to the smartphone?
-When a packet is sent from the PC, it passes through the access point and is directed to the smartphone. The smartphone then sends the packet back to the access point, which forwards it back to the PC, demonstrating successful communication between the devices.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Konfigurasi Access Point Cisco di Packet Tracer

Cara Setting Access Point TP-Link TL-WA701ND || Konfigurasi Dasar Wireless Access Point WAP

Konfigurasi Mikrotik Dasar Part 3 Membuat Hotspot Pada Mikrotik

Cara Membuat Koneksi Printer Wireless Untuk Semua Device - Cisco Packet Tracer
#GenerasiTutorial Cara Konfigurasi Wireless Access Point di Cisco Packet Tracer

Setting Pakai HP: TP-Link WR840N (ID) Mode AP Hotspot Voucher
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)