1 Voltage regulators-Linear, series, shunt and switching voltage regulators
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of voltage regulation and the different types of voltage regulators. It covers the importance of maintaining a constant output voltage, regardless of input voltage variations. The script delves into series, shunt, and switching voltage regulators, explaining their working principles, components, and the effect of input voltage and load changes. Key terms like line regulation and load regulation are also discussed. The video highlights the advantages of each type of regulator and emphasizes the role of transistors, diodes, and feedback mechanisms in ensuring stable voltage output.
Takeaways
- 😀 Voltage regulation ensures a constant output voltage regardless of changes in input voltage.
- 😀 The main components of a voltage regulator circuit include a transformer, rectifier, filter, and the voltage regulator IC.
- 😀 A transformer converts AC voltage to the desired amplitude, which is then rectified into DC and filtered for a smoother output.
- 😀 Line regulation ensures a constant output voltage even when there are fluctuations in the input voltage.
- 😀 Load regulation maintains a stable output voltage despite variations in the load current.
- 😀 Series voltage regulators use a pass element (like a transistor) in series with the load to adjust output voltage.
- 😀 In a series voltage regulator, the output voltage is controlled by a comparator that adjusts the pass element based on changes in input or load.
- 😀 Shunt voltage regulators divert excess current to maintain a constant output voltage, using a feedback loop with a comparator.
- 😀 Switching voltage regulators are more efficient than linear regulators, using switching elements (like transistors) to control the output.
- 😀 Switching regulators can be classified into three types: step-down (buck), step-up (boost), and polarity-inverting regulators, each serving different voltage conversion needs.
- 😀 A step-down switching regulator reduces the output voltage, while a step-up version increases it. A polarity-inverting regulator reverses the output polarity.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a voltage regulator?
-The primary function of a voltage regulator is to maintain a constant output voltage regardless of variations in the input voltage.
What are the two basic categories of voltage regulation?
-The two basic categories of voltage regulation are line regulation and load regulation.
How does line regulation work in a voltage regulator?
-Line regulation ensures a constant output voltage even when the input voltage changes. It is calculated by the formula: (change in output voltage / output voltage) * (100 / input voltage).
What is load regulation and how does it work?
-Load regulation maintains a constant output voltage despite changes in load current. It is calculated by: (V_no_load - V_full_load) / (V_full_load) * 100%.
What are the three types of voltage regulators mentioned?
-The three types of voltage regulators are series voltage regulators, shunt voltage regulators, and switching voltage regulators.
How does a series voltage regulator function?
-A series voltage regulator uses a control element (like a transistor) in series with the load to adjust the output voltage. It maintains constant output by reducing or increasing the voltage based on fluctuations.
What role does the zener diode play in a series voltage regulator?
-In a series voltage regulator, the zener diode provides a stable reference voltage. It ensures that the output voltage remains consistent by controlling the base-emitter voltage of the transistor.
What happens when the input voltage increases in a series voltage regulator?
-When the input voltage increases, the output voltage increases as well. The base-emitter voltage of the transistor decreases, causing the transistor's conduction level to reduce, which compensates by lowering the output voltage.
What is the main difference between series and shunt voltage regulators?
-The main difference is that in a series voltage regulator, the control element is in series with the load, adjusting the output voltage. In a shunt voltage regulator, the control element is parallel to the load and adjusts the current shunted away from the load to maintain a constant output voltage.
Why are switching voltage regulators more efficient than linear regulators like series and shunt regulators?
-Switching voltage regulators are more efficient because they convert power using a switch (transistor) that rapidly turns on and off, minimizing energy loss as heat, unlike linear regulators that dissipate excess energy as heat.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Linear Voltage Regulators (LM7805) | AO #17

What is a Voltage Regulator? How Does it Work?

Zener Diode (Basics, Symbol, Characteristics, Applications, Pros & Cons) Explained
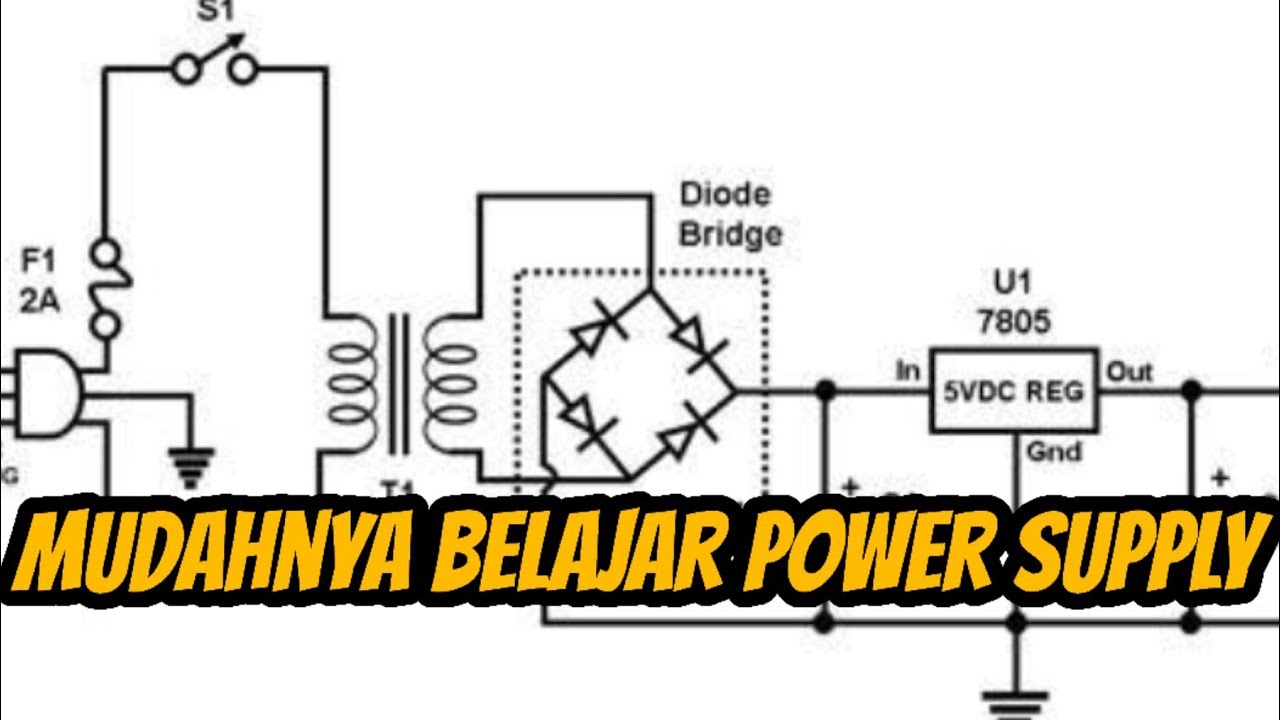
Mudahnya belajar Power Supply dari prinsip kerja, komponen PSU dibahas dengan detail dan lengkap

What is a zener diode and how does it work? | Intermediate Electronics
Cures for Low Frequency Disturbances |Power Quality & Management|
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)