Linear Voltage Regulators (LM7805) | AO #17
Summary
TLDRThis video from AD Ohms explains the basics of voltage regulators, focusing on linear regulators like the popular LM7805. It highlights the difference between linear and switching regulators, emphasizing how linear regulators are simple but less efficient. The tutorial also covers low dropout (LDO) regulators, thermal shutdown protection, and the importance of decoupling capacitors in maintaining stable voltage output. Key concepts like voltage drop, heat dissipation, and current flow are explained, making it easier for viewers to understand how linear voltage regulators function in electronic circuits.
Takeaways
- 🔋 Linear voltage regulators convert a higher input voltage into a stable lower output voltage, commonly using 5V from USB or other sources.
- ⚡ There are two main types of voltage regulators: linear and switching. Linear regulators are simple but less efficient, while switching regulators are more efficient but complex to design.
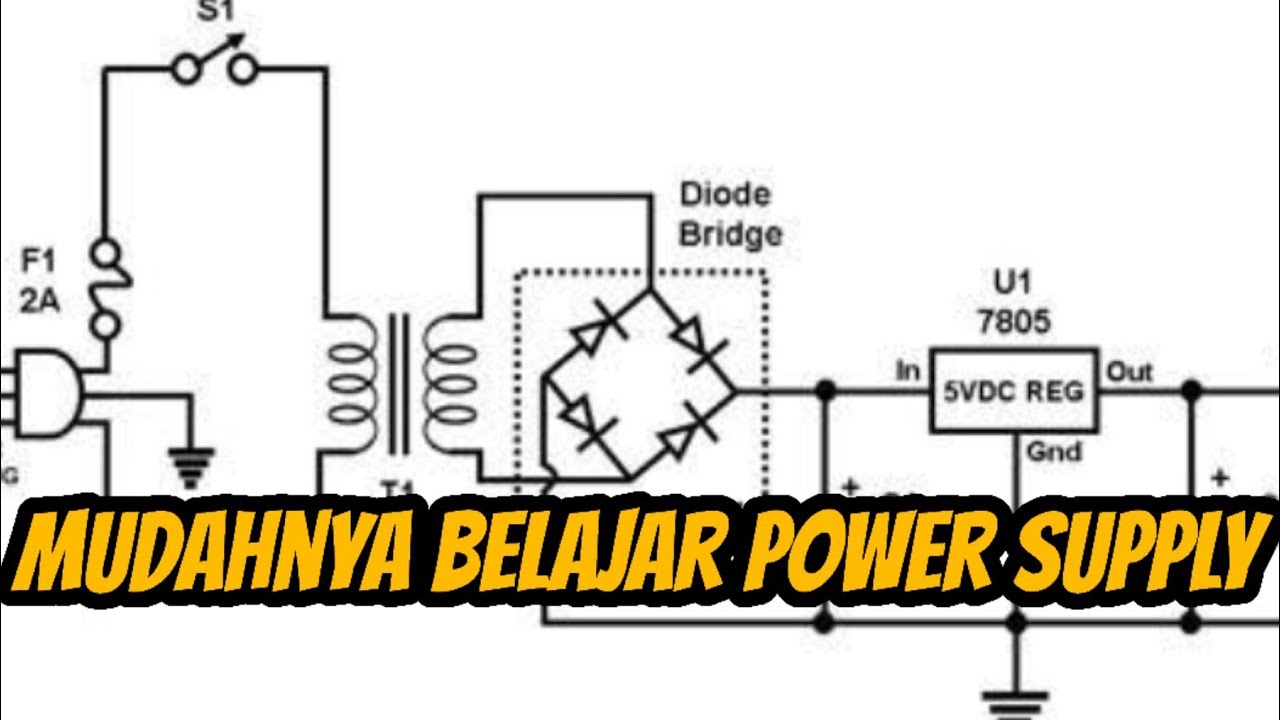
- 📏 The LM7805 is a popular linear voltage regulator, known for its simplicity, reliability, and availability in different packaging styles like the TO-220.
- 🔌 For a linear regulator to function properly, the input voltage must be higher than the output voltage by at least 2 volts. The difference is known as the dropout voltage.
- 🔄 LDO (Low Dropout) regulators, such as the NCP1117, require less headroom than standard regulators, meaning they can operate with a smaller input-to-output voltage difference.
- 🌡️ The difference between input and output voltage generates heat. For example, if 12V is input and 5V is output at 1A, 7 watts of power is dissipated as heat.
- 🔥 Linear regulators have built-in thermal shutdown protection to prevent overheating in case of excessive power dissipation or short circuits.
- 💡 Decoupling capacitors are critical for stabilizing output voltage and reducing ripple. Without them, the output may become unstable, especially with varying input or load conditions.
- 📊 The values of decoupling capacitors, such as 330 nanofarads for input and 100 nanofarads for output, are often provided in the regulator's datasheet.
- 🛠️ Linear voltage regulators are ubiquitous in electronics and are essential components for managing power in circuits. Further details will be covered in future tutorials.
Q & A
What is the role of a voltage regulator in a circuit?
-A voltage regulator takes a voltage input on one side and outputs a stable, different voltage on the other side, ensuring that the circuit gets the required voltage for proper operation.
What are the two major types of voltage regulators?
-The two major types of voltage regulators are linear regulators and switching regulators. Linear regulators are simple and easy to use but inefficient, while switching regulators are more efficient but harder to design.
Why is the LM7805 voltage regulator considered important in electronics?
-The LM7805 is considered important because it is a widely used voltage regulator that is easy to integrate into circuits, available in various forms like the TO220 package, and can dissipate a significant amount of heat.
What is a Dropout voltage in the context of linear voltage regulators?
-The Dropout voltage is the minimum difference between the input voltage and the output voltage required for a linear voltage regulator to function correctly. If the input voltage is too low, the regulator becomes unstable.
What makes an LDO (Low Dropout Regulator) different from a standard linear regulator?
-An LDO requires less voltage headroom between the input and output compared to a standard linear regulator. For example, it can regulate the voltage with a smaller difference, like 1 volt, between input and output.
How is the power dissipation in a linear voltage regulator calculated?
-The power dissipation is calculated by multiplying the voltage drop across the regulator by the current passing through it. For example, if the input is 12V, the output is 5V, and the current is 1A, the power dissipation would be 7 watts.
Why do linear voltage regulators have thermal shutdown protection?
-Thermal shutdown protection is implemented to prevent the regulator from overheating and damaging itself. When the internal temperature exceeds a safe limit, the regulator shuts down or reduces output to protect the circuit.
What role do decoupling capacitors play in voltage regulation?
-Decoupling capacitors help stabilize the voltage output by reducing fluctuations or ripples in the output voltage when the input voltage or load changes, ensuring a more stable power supply to the circuit.
What might cause a voltage regulator's output to be incorrect?
-The output could be incorrect due to thermal shutdown caused by overheating, or improper decoupling of the input and output voltages, leading to fluctuations or instability.
How do you determine the appropriate values for decoupling capacitors?
-The appropriate decoupling capacitor values can be found in the voltage regulator's datasheet. For the LM7805, for example, typical values suggested are 330 nanofarads for the input capacitor and 100 nanofarads for the output capacitor.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What is a Voltage Regulator? How Does it Work?
Mudahnya belajar Power Supply dari prinsip kerja, komponen PSU dibahas dengan detail dan lengkap

1 Voltage regulators-Linear, series, shunt and switching voltage regulators

Zener Diode (Basics, Symbol, Characteristics, Applications, Pros & Cons) Explained

What is a zener diode and how does it work? | Intermediate Electronics

EVERYTHING you need to know about about robot power
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)