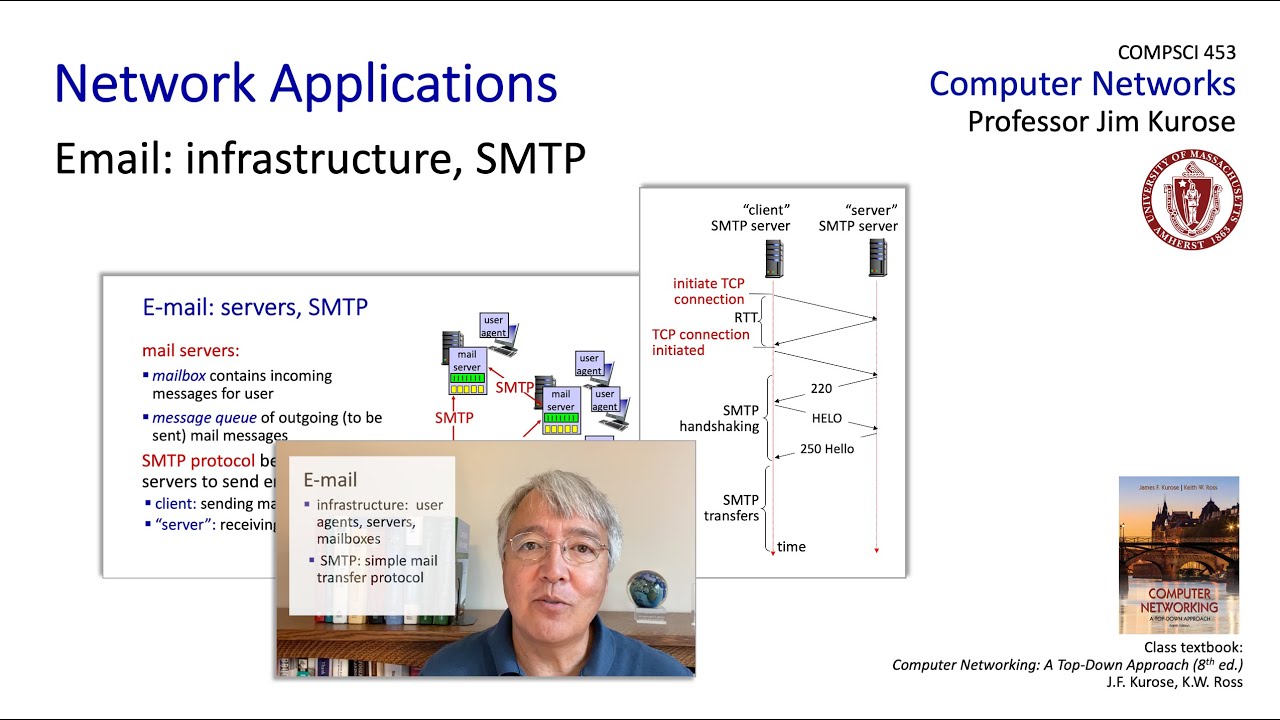
Email Protocols: SMTP, POP and IMAP
Summary
TLDRThis video explores key email protocols, focusing on SMTP, POP, and IMAP. SMTP is explained as the protocol for sending outbound emails from the client to the mail server. In contrast, POP and IMAP handle incoming emails, with POP downloading and deleting emails from the server, while IMAP keeps emails synced across devices. The video highlights the differences in functionality, emphasizing that POP works for single-device access, while IMAP is ideal for multi-device synchronization, ensuring users can manage their emails seamlessly across platforms.
Takeaways
- 😀 SMTP is an application layer protocol responsible for sending outbound emails.
- 😀 The client (email application) sends an email to a mail server using SMTP.
- 😀 The mail server routes the email to the recipient's mail server using DNS, based on the email's domain.
- 😀 POP (Post Office Protocol) is used for retrieving emails, but it doesn't sync the server and client.
- 😀 With POP, emails are deleted from the server as soon as they are downloaded to the client.
- 😀 IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) allows for two-way synchronization between the server and client.
- 😀 IMAP stores emails on the server, allowing them to be accessed from multiple devices.
- 😀 When using IMAP, actions like moving emails to folders are reflected across all devices.
- 😀 POP is better for users who access email from a single device, as emails are removed from the server after download.
- 😀 IMAP is ideal for users who need multi-device access and want to keep their email organized and synchronized.
Q & A
What is SMTP and what role does it play in email communication?
-SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is an application layer protocol used for sending outbound email. It handles the process of sending emails from an email client to a mail server, and then further routing it to the recipient's mail server.
How does SMTP interact with DNS to route emails?
-SMTP relies on DNS (Domain Name System) to resolve email addresses and route emails. The domain part of an email address (e.g., '@gmail.com') is used to look up the corresponding mail server for the recipient's domain, ensuring the email is sent to the correct destination.
What is the difference between POP and IMAP?
-POP (Post Office Protocol) and IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) are both used to retrieve emails from a mail server. POP downloads emails to the client and removes them from the server, while IMAP keeps the email server and client in sync, retaining emails on the server unless explicitly deleted.
Why is IMAP more suitable for accessing email from multiple devices?
-IMAP is designed to keep the email server and client in sync. It allows users to access their emails from multiple devices, and any changes made on one device (such as moving an email to a folder) are reflected across all devices accessing the same account.
How does the behavior of POP differ when it comes to managing email on the server?
-With POP, once emails are downloaded to the client, they are deleted from the server. This means the email is only available on the device that downloaded it, and there is no synchronization between the server and other devices.
What happens when an email is retrieved using IMAP?
-When an email is retrieved using IMAP, only a copy of the email is downloaded to the client. The original message remains on the server until it is explicitly deleted by the user from the client.
Which protocol, POP or IMAP, is better for users who need to keep their inbox organized across multiple devices?
-IMAP is better for users who need to keep their inbox organized across multiple devices, as it ensures that any changes made to the email account (such as moving emails to folders) are synced across all devices.
Can POP and IMAP be used together for the same email account?
-No, POP and IMAP cannot be used together for the same email account. They are separate protocols and serve different purposes. POP downloads emails and removes them from the server, while IMAP keeps the server and client in sync.
How does IMAP keep track of changes made to emails on the client?
-IMAP tracks changes made to emails on the client by updating the server in real time. For example, if an email is moved to a different folder, this change is reflected on the server so that it is visible across all devices accessing the account.
What is the analogy used to explain the difference between POP and IMAP in the script?
-The script uses an analogy comparing POP to a post office that does not keep copies of parcels after they are delivered. In contrast, IMAP is compared to a service that keeps parcels (emails) stored and updated until the recipient decides to remove them.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)