6.Protocols & Packet Filtering - Part2
Summary
TLDRThis video covers essential networking protocols and their applications, focusing on email retrieval (IMAP), email sending (SMTP), remote management (Telnet and SSH), and secure communication (PPP and SMB). It delves into key protocols used for file sharing, system monitoring (SNMP), and point-to-point connections, as well as methods to secure networks with ACLs and port filtering. The video also highlights security mechanisms such as silent dropping and TCP resets, ensuring network communication remains efficient and protected. Whether you're managing a network or configuring security policies, this video provides an informative overview of modern network protocols.
Takeaways
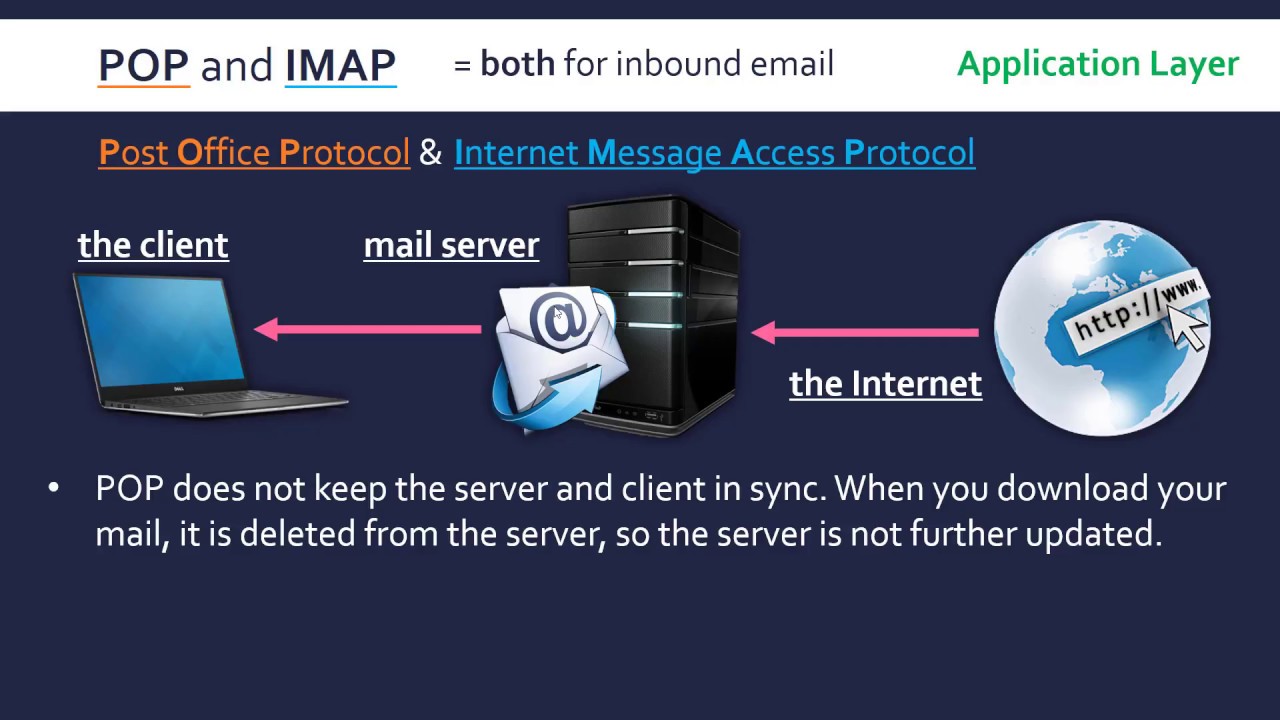
- 😀 IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) allows multiple devices to manage an email inbox without storing messages on the device, using servers for email retrieval and management.
- 😀 IMAP operates on ports 143 (unencrypted) and 993 (encrypted), and is supported by most modern email clients and services like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo.
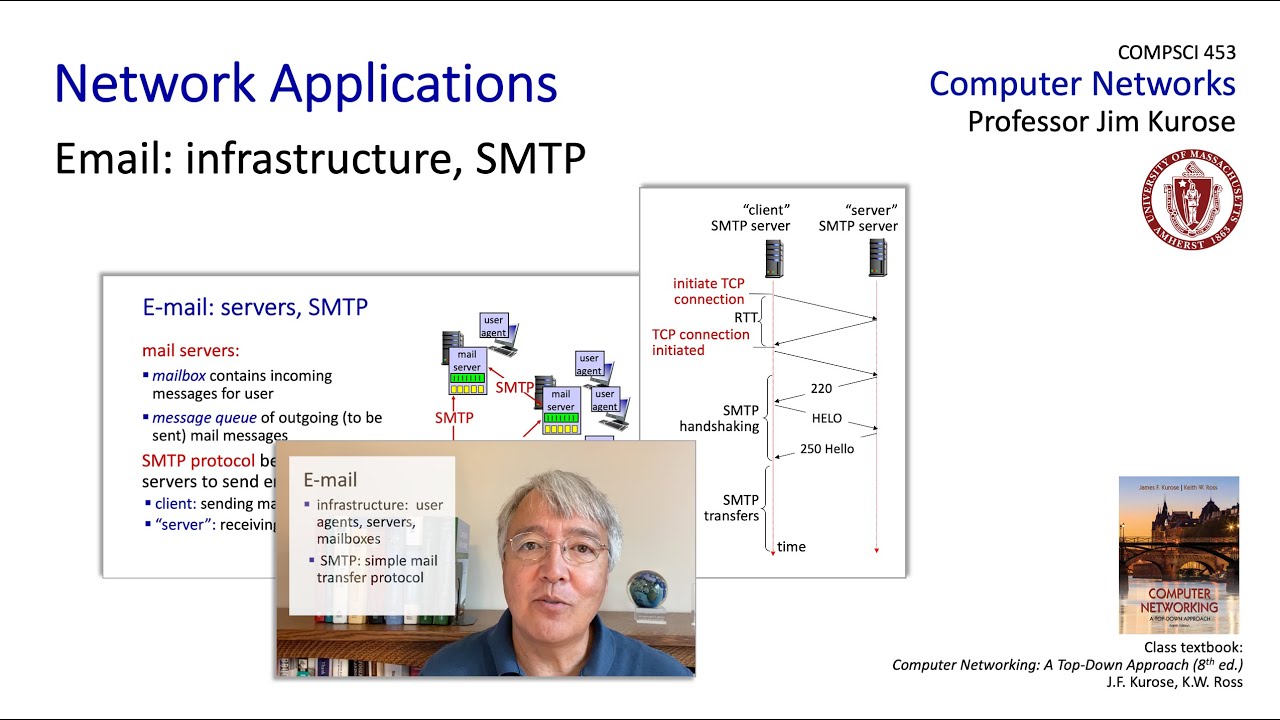
- 😀 SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is used to send emails between servers and from email clients to mail servers, typically using port 25.
- 😀 PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a data link layer protocol used for transmitting multi-protocol data across point-to-point connections, often in DSL setups.
- 😀 PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) is a common method used by ISPs for DSL connections, involving authentication protocols like PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) and CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol).
- 😀 PPP supports compression, error detection, and multi-link, improving throughput and reliability on point-to-point links.
- 😀 SMB (Server Message Block) is a client-server protocol used for sharing files, printers, and other resources over a network, commonly seen in Windows networks.
- 😀 SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) allows devices to share information about their current state, with SNMP agents gathering and organizing data from hardware devices.
- 😀 Telnet and SSH are protocols for remote administration of network devices, with SSH being the more secure option due to encryption and authentication, using port 22.
- 😀 SSH employs both symmetric and asymmetric encryption, alongside cryptographic hashing, to ensure secure data transmission across the internet.
- 😀 Network security relies on packet filtering, using access control lists (ACLs) to control traffic flow based on five-tuple information (source/destination IPs, ports, and protocols).
Q & A
What is the IMAP protocol and how does it function?
-IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) is a protocol used for managing email messages on a server. It allows users to access and manage their email from multiple devices without downloading messages. Emails typically stay on the server unless the user deletes them, and the protocol supports encrypted (port 993) and non-encrypted (port 143) communication.
How does IMAP differ from POP3?
-IMAP is designed to allow email to remain on the server and be accessed by multiple devices, whereas POP3 (Post Office Protocol) downloads email from the server to a single device. IMAP provides more flexibility for accessing and managing email across multiple devices, while POP3 is limited to a single device.
What role does SMTP play in email communication?
-SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is used for sending email messages between servers and from a mail client to a mail server. It operates over TCP port 25 and is responsible for transmitting emails across the internet.
What is the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) and how is it used?
-PPP is a data link layer protocol that provides a standard for transmitting multi-protocol data over point-to-point connections. It is commonly used to establish DSL connections between internet service providers and customers, and it can handle authentication, error detection, and compression of data.
What are the two types of PPP authentication?
-PPP supports two types of authentication: PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) and CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol). PAP is simpler and less secure, while CHAP offers more security by periodically verifying the identity of the connection.
How does the SMB protocol work?
-SMB (Server Message Block) is a client-server protocol used to share resources like files and printers over a network. It enables applications to access files on remote servers and communicate with server programs to manage resources. SMB runs over TCP ports 445 and 139.
What is the purpose of SNMP in network management?
-SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is used to monitor and manage network devices. It uses agents to collect information about the device’s state and stores it in a Management Information Base (MIB). The SNMP manager then queries the agents for information about the device's performance and status.
What is the difference between Telnet and SSH?
-Telnet and SSH are both used for remote administration of network devices. However, Telnet is insecure as it transmits data in plaintext, making it vulnerable to interception. SSH (Secure Shell) uses encryption to secure data transmission, making it a more secure choice for remote access.
What is the significance of public and private keys in SSH?
-In SSH, asymmetric encryption is used, which involves a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The public key can be freely shared to encrypt data, but only the corresponding private key can decrypt it. This ensures secure communication where only the holder of the private key can access the information.
How can access control lists (ACLs) be used for network security?
-ACLs (Access Control Lists) are used to filter network traffic based on parameters like source IP, destination IP, ports, and protocols. They can permit or deny traffic and are a common method for controlling access to resources. ACLs can also block specific ports to restrict unwanted traffic, such as gaming applications or unauthorized access.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)