Planejamento e Controle da Produção # 15 – Implantação do MRP
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the Material Requirements Planning (MRP) system, which helps manage production and inventory by calculating material needs and scheduling orders. It covers how MRP uses the Master Production Schedule (MPS) to forecast demand, breaks down the requirements into component parts using the Bill of Materials (BOM), and determines when materials need to be ordered or produced. The video also highlights the importance of inventory management, lead times, and backward scheduling in ensuring timely production and minimizing costs, making MRP essential for efficient manufacturing operations.
Takeaways
- 😀 The MRP system calculates the necessary production and purchasing actions for each week based on stock levels, demand, and product structure.
- 😀 MRP 'explodes' the product structure from the final product down to individual components, calculating material requirements at each level.
- 😀 Work orders and purchase orders are generated for each component at different levels based on the material requirements and available stock.
- 😀 Stock levels are updated continuously as components are produced or purchased, ensuring material availability for production.
- 😀 The MRP system takes input from the Master Production Schedule (MPS), which specifies the required quantities of finished products.
- 😀 The system calculates net material requirements by subtracting available stock from the gross requirements.
- 😀 Lead times are a crucial factor in determining when orders must be placed to ensure materials are available on time.
- 😀 MRP uses backward scheduling, determining when to place orders based on the required final product date and the lead time for each component.
- 😀 When a component is required, MRP ensures that purchase orders are made in advance, considering the lead time of suppliers.
- 😀 The MRP process repeats at each level of the BOM, ensuring that each material requirement is met in the production process.
- 😀 The next video will cover a practical example of how MRP works in real-world scenarios, demonstrating its dynamic application.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of Material Requirements Planning (MRP)?
-The main purpose of MRP is to ensure that the right materials and components are available for production at the right time, and in the right quantities, so that products can be completed by the promised delivery date.
How does the MRP system determine production and purchase actions?
-The MRP system calculates production and purchase actions based on the demand for finished products, the available inventory, and the bill of materials (BOM) that lists all required components for production.
What role does the bill of materials (BOM) play in the MRP process?
-The BOM is essential in MRP as it helps 'explode' the product structure, identifying the quantities of each component needed at different production levels, which drives the calculations for purchasing and production orders.
What does it mean for MRP to 'explode' materials?
-When MRP 'explodes' materials, it breaks down the requirements for a finished product (level 0) into the components needed at each subsequent level, from level 1 to the final level, determining the quantity and timing of each item.
How are the 'gross requirements' and 'net requirements' calculated in MRP?
-Gross requirements are the total quantity needed for a product or component, and net requirements are calculated by subtracting the available stock from the gross requirements, showing the actual amount that needs to be produced or purchased.
What types of orders are generated by the MRP system?
-The MRP system generates purchase orders for materials that need to be bought and work orders for items that need to be produced or assembled within the organization.
How does MRP handle inventory updates during the production process?
-As production and purchasing orders are completed, the inventory levels are updated. Stock increases when materials are received or produced, and it decreases when materials are used in production.
Why is lead time important in the MRP system?
-Lead time is important in MRP because it helps determine when orders should be placed. By knowing the lead time, MRP ensures that components are ordered in advance and arrive at the right time to meet production schedules.
What is the function of the Master Production Schedule (MPS) in MRP?
-The Master Production Schedule (MPS) sets the production requirements for finished goods, which are then used by MRP to calculate the gross requirements and generate the necessary orders for components at each level.
How does the MRP system ensure that production meets customer demand?
-The MRP system ensures that production meets customer demand by accurately calculating when and how much of each component is needed, considering existing stock and the lead times for both purchases and manufacturing.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What is the Material Requirement planning (MRP)? | MRP Process
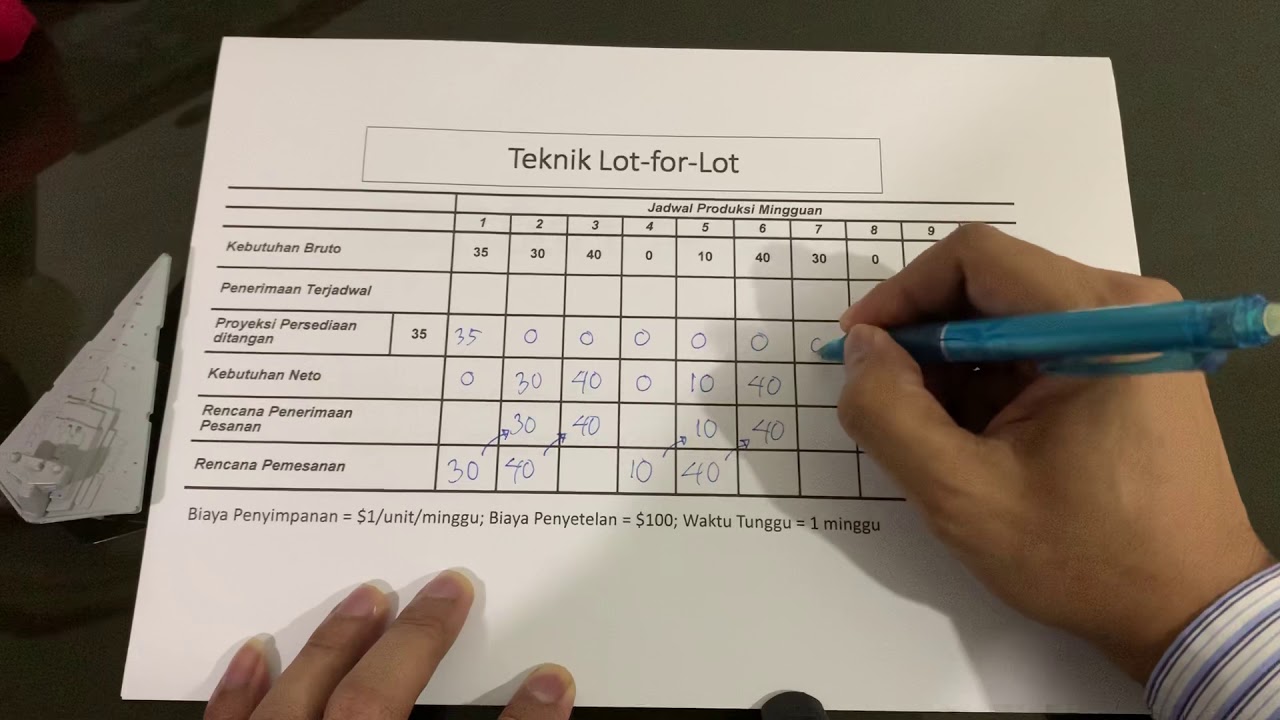
Teknik Lot for Lot pada Lot Sizing (Penentuan Ukuran Lot) dalam Sistem MRP

Chapter 14. Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and ERP - Part 3

Memahami Perencanaan Kebutuhan Material untuk proses produksi ...

Explicación MRP

Materi kuliah Pengantar Bisnis, Pertemuan Ke-5
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)