Variabel #5 | C++ | Bahasa Indonesia
Summary
TLDRIn this video, viewers are introduced to the fundamental concepts of data types and variables in C++ programming. The script covers the purpose of variables in storing data and explains the four basic data types in C++: char, int, float, and bool. Practical examples demonstrate how to declare, initialize, and use variables in C++ for tasks like calculating the area of a rectangle. The video is aimed at beginners, providing clear, hands-on guidance for understanding key programming concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 **Understanding Variables in C++**: Variables are used to store data in memory, and each variable has a specific data type.
- 😀 **Types of Data in C++**: There are several fundamental data types, including `char`, `int`, `float`, and `bool`.
- 😀 **char**: A data type used for storing characters, such as letters or symbols.
- 😀 **int**: Used to store integer values (whole numbers), including both positive and negative values.
- 😀 **float**: A data type used to store real numbers (decimals), which is useful for calculations requiring precision.
- 😀 **bool**: Represents boolean values (true or false), typically used in conditional statements and logic operations.
- 😀 **Declaring Variables**: To use a variable, it must first be declared with a specific type and a unique identifier (name).
- 😀 **Initializing Variables**: Variables can be initialized by assigning a value to them at the time of declaration.
- 😀 **Example of Variable Initialization**: `int length = 20; int width = 10;` is an example of declaring and initializing integer variables.
- 😀 **Performing Operations with Variables**: Once variables are initialized, they can be used in arithmetic operations, such as multiplying length and width to calculate area.
- 😀 **Real-life Example**: In a program calculating the area of a rectangle, variables for length and width are declared, and the area is calculated by multiplying them.
- 😀 **Using Different Data Types for Different Operations**: The choice of data type impacts what operations can be performed on variables. For example, `int` is used for whole numbers, while `float` is used for decimals.
Q & A
What are data types in C++?
-In C++, data types define the kind of data a variable can store. The main data types include `char` for characters, `int` for integers, `float` for floating-point numbers, and `bool` for Boolean values (true or false).
What is a variable in C++?
-A variable in C++ is a named storage location in memory where data is held. Each variable must be declared with a specific data type to indicate the kind of data it will store.
How do you declare a variable in C++?
-To declare a variable in C++, you specify the data type followed by the variable's name. For example: `int length;` or `char character;`.
What is the significance of a variable's data type?
-The data type of a variable determines the kind of data it can hold and what operations can be performed on it. For example, a `float` can hold decimal numbers, whereas a `char` can only hold single characters.
Can you declare multiple variables of the same type in C++?
-Yes, you can declare multiple variables of the same type in C++ by separating them with commas. For example: `int length, width, height;`.
What is initialization in C++?
-Initialization in C++ refers to the process of assigning an initial value to a variable when it is declared. For example: `int length = 10;`.
What happens if you don't initialize a variable in C++?
-If a variable is not initialized, it contains a garbage value, which can lead to unpredictable behavior or errors in your program. It's always best to initialize variables before using them.
How do you perform arithmetic operations with variables in C++?
-You can perform arithmetic operations directly on variables by using standard operators like `+`, `-`, `*`, and `/`. For example, to calculate the area of a rectangle, you might write `int area = length * width;`.
What is the difference between `int` and `float` data types?
-The `int` data type is used for whole numbers (without decimals), while the `float` data type is used for numbers that may have decimal points. For example, `int x = 10;` and `float y = 3.14;`.
Why can’t you store a number with a decimal in a variable declared as `int`?
-The `int` data type can only store whole numbers, so attempting to store a decimal number would result in a loss of data or an error. To store numbers with decimals, you need to use a `float` or `double`.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

VARIABEL dan TIPE DATA dalam pemrograman yang penting untuk diketahui

C++ 03 | Tipe Data pada Pemrograman C++ | Tutorial Dev C++ Indonesia
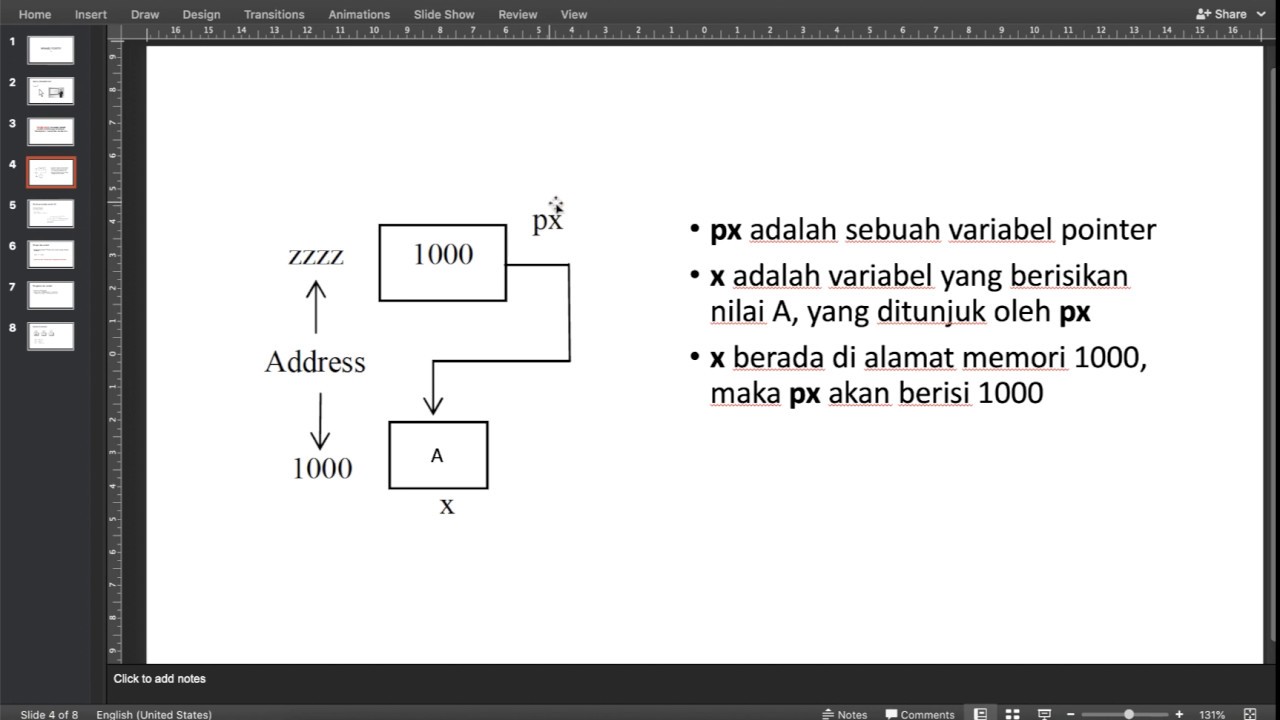
Variabel Pointer

C_08 Variables in C Programming | C Programming Tutorials

#2 Tipe Data, Variabel, dan Operator

Introduction to C++, The Parts of a C++ Program, Identifier Naming Rules, output statements
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)