V-I characteristics of ordinary p-n junction diode.
Summary
TLDRThis video demonstrates an electronics experiment involving the characteristics of a PN junction diode. The setup includes connecting a multimeter and power supply to measure voltage, current, and resistance across various circuit points. The script explores the process of identifying terminal connections, analyzing electrical behavior, and recording readings for different conditions. With references to power supply voltage, current measurement, and troubleshooting connections, this experiment provides hands-on insight into diode characteristics and their applications in electrical circuits. The content is technical, engaging users in learning how to interpret and measure key electronic parameters.
Takeaways
- 😀 The experiment involves working with a PN junction diode and examining its characteristics.
- 😀 Power supply connections are critical, and different terminal setups are used for measurements.
- 😀 Voltage and current measurements are taken using a multimeter, and these readings help analyze diode behavior.
- 😀 The experiment includes both DC and AC voltage supply setups, with specific voltages applied to test the diode.
- 😀 A detailed circuit diagram is referenced for setting up the experiment, with clear connections for power and measurement tools.
- 😀 The power supply voltage is varied, and its effect on current through the diode is measured at various points.
- 😀 Diode terminals are clearly identified, with positive and negative terminals connected according to the experiment's design.
- 😀 The script mentions several meter readings for voltage (e.g., 1.7 V, 14.5 V) and current (e.g., 5.9 mA, 21.63 mA) as part of the testing process.
- 😀 The diode is connected in a forward-biased configuration to observe the current flow, and the power supply is adjusted to different voltages.
- 😀 The script contains references to advanced electrical testing terms and concepts such as 'voltage drop', 'reverse bias', and 'forward bias'.
- 😀 The final phase of the experiment includes validating the power supply performance and the current flow at specific voltages, ensuring proper functioning of the circuit.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the experiment mentioned in the transcript?
-The experiment focuses on testing and analyzing the characteristics of a PN junction diode and its behavior when connected to different power supplies and measuring devices like multimeters.
What kind of measurements are discussed in the transcript?
-The transcript covers measurements of voltage, current (in milliamps), and frequency, taken using devices such as multimeters and voltmeters. These measurements are used to analyze the behavior of the PN junction diode.
What is a PN junction diode, as mentioned in the experiment?
-A PN junction diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction only. It consists of a region where p-type and n-type materials meet, forming a junction that controls current flow based on the applied voltage.
How is the power supply connected to the experiment setup?
-The power supply is connected with a specific positive and negative terminal arrangement to ensure the correct flow of current through the PN junction diode, with voltages being measured and adjusted throughout the experiment.
What is the significance of the 'positive terminal' and 'negative terminal' mentioned in the script?
-The positive and negative terminals determine the direction of current flow in the circuit. Correctly identifying and connecting these terminals to the PN junction diode is crucial for the accurate functioning of the experiment.
What role do multimeters play in this experiment?
-Multimeters are used to measure key electrical parameters such as voltage, current, and frequency in the circuit. They help in analyzing how the PN junction diode responds to varying conditions and power supplies.
What does the transcript mean by 'forward bias' and 'reverse bias' in relation to the diode?
-Forward bias occurs when the positive terminal is connected to the p-side of the diode and the negative terminal to the n-side, allowing current to flow. Reverse bias occurs when the polarity is reversed, preventing current flow through the diode.
What are the different power supply voltages mentioned in the experiment?
-Various power supply voltages are discussed in the transcript, including values such as 1.7 volts, 6.5 volts, and 12.2 volts. These voltages are used to test the diode’s response and to gather readings under different conditions.
What does the term 'circuit diagram' refer to in this context?
-A circuit diagram is a graphical representation of the electrical components and their connections in the experiment. It helps in visualizing how the diode, power supplies, and measuring devices are connected and interact with each other.
How does the diode's behavior change with different voltages?
-The diode's behavior changes depending on the applied voltage. At certain voltages, the diode allows current to flow (forward bias), while at others, it blocks current (reverse bias). The voltage levels and corresponding current readings help in characterizing the diode's performance.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
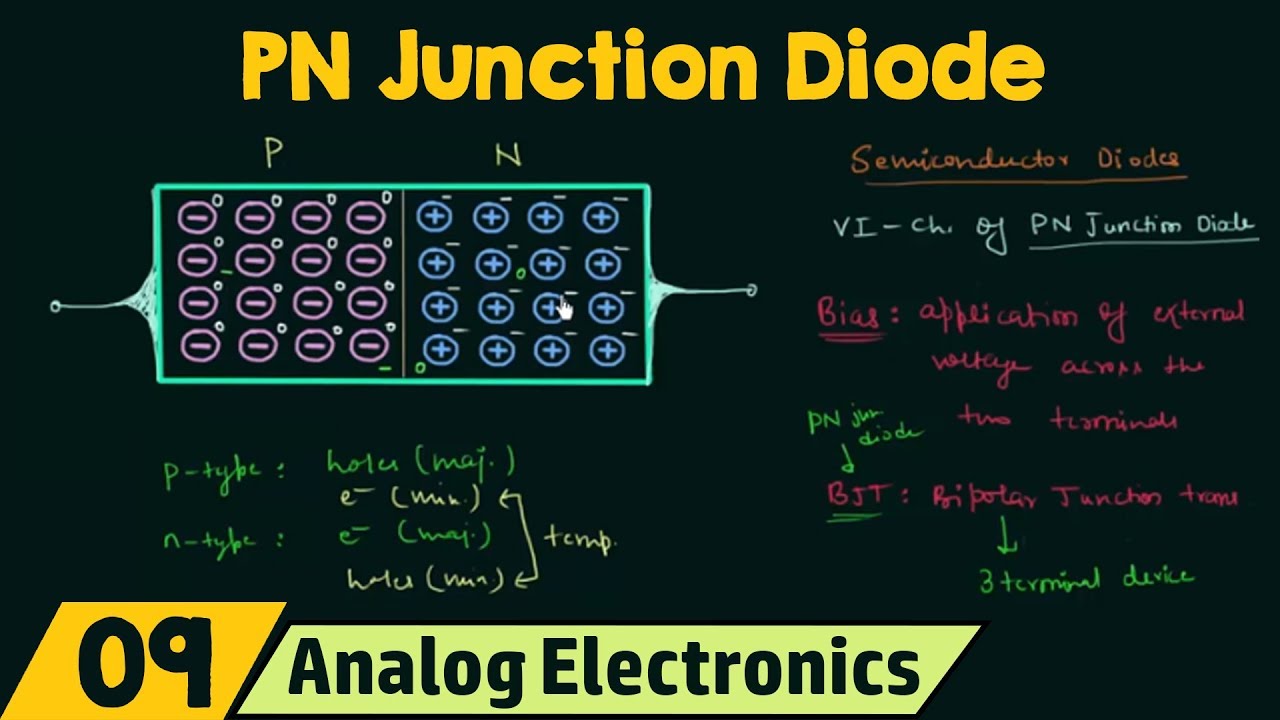
PN Junction Diode (No Applied Bias)
Basic Electronics: PN Junction Working Principle and V-I Characteristics of PN Junction Diode

Semiconductor Diode
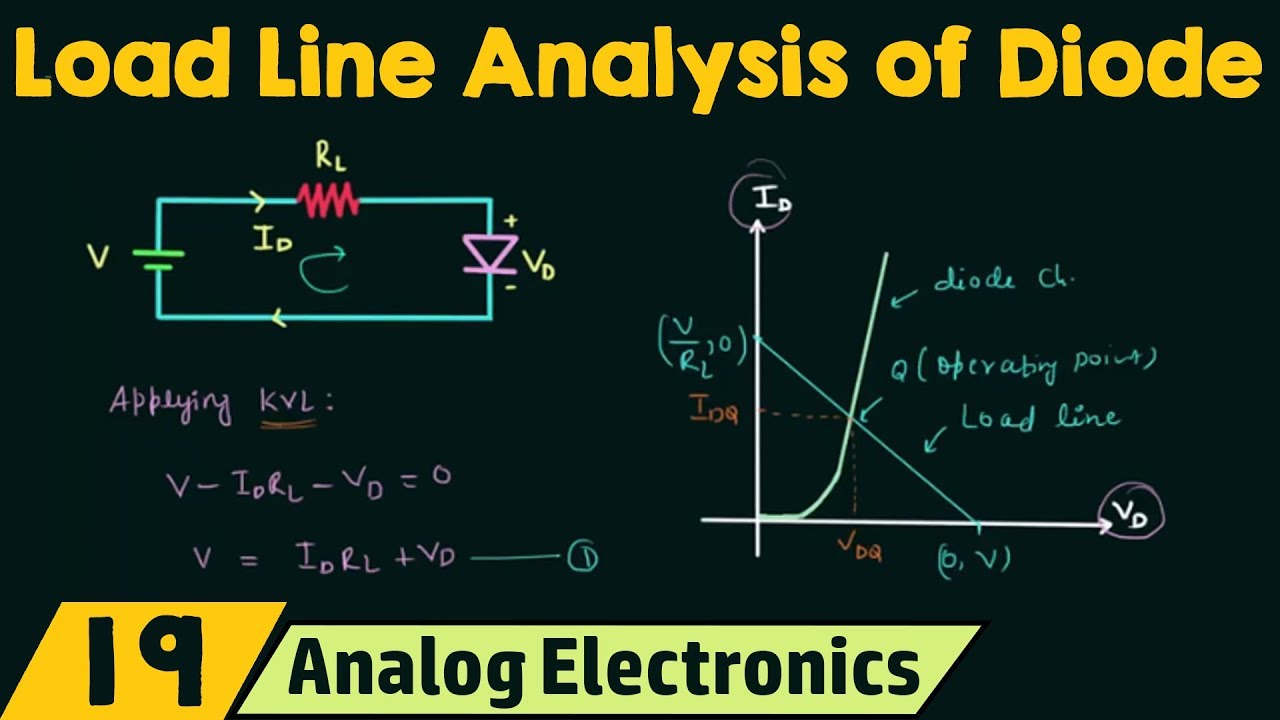
Load Line Analysis of Diode

Schottky Diode (Construction & Working) Special Purpose Diodes (Basics Electronics)

Cara Kerja Dioda PN Junction | Kuliah Fisika Semikonduktor
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)