Rotational Motion: Crash Course Physics #11
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fundamentals of rotational motion, comparing it to translational motion. It introduces essential concepts like angular position, velocity, and acceleration, emphasizing the significance of radians for measuring angles. The discussion highlights the relationship between angular and tangential velocities and explains the unique phenomenon of rolling without slipping. Viewers learn how the velocity at different points on a rotating wheel varies, culminating in the intriguing idea that the point of contact with the ground has zero translational velocity. The video sets the stage for future exploration of momentum in rotational dynamics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Rotational motion is an important aspect of physics, alongside translational motion.
- 🔄 Both types of motion involve concepts like position, velocity, and acceleration.
- 📐 Angles are used to describe rotational motion, typically measured in radians rather than degrees.
- ⚖️ One full rotation corresponds to 2π radians, while half a rotation equals π radians.
- 🚴♂️ Angular velocity (ω) measures how quickly an object changes its angle over time.
- 📏 Tangential velocity (v_t) is the linear velocity of a point on a rotating object, dependent on the radius.
- 🚗 Rolling without slipping occurs when the bottom point of a wheel is momentarily at rest relative to the ground.
- ⏲️ Periodic motion repeats after a set time (T), with frequency (f) defined as 1/T.
- 📊 Angular acceleration (α) describes how angular velocity changes over time, related to radial and tangential acceleration.
- ⚙️ Understanding rotational motion is crucial for various applications, including sports, transportation, and engineering.
Q & A
What is the main focus of this episode of Crash Course Physics?
-The main focus is on rotational motion, explaining how it differs from translational motion and discussing key concepts related to rotation.
How is rotational motion defined in contrast to translational motion?
-Translational motion involves movement through space without rotation, while rotational motion involves points moving along circular paths and is measured in terms of angles.
What is the significance of radians in measuring angles?
-Radians are significant because they relate the angle to the radius of a circle, providing a natural way to measure angles based on the circle's circumference.
How is angular velocity represented and what does it signify?
-Angular velocity is represented by the Greek letter omega (Ω) and signifies the rate of change of angular displacement over time, analogous to linear velocity in translational motion.
What is the relationship between tangential velocity and angular velocity?
-Tangential velocity is the linear velocity of a point on a rotating object, calculated as the product of angular velocity and the radius of the circular path.
What does rolling without slipping mean in the context of rotational motion?
-Rolling without slipping refers to the condition where the bottom point of a wheel does not move relative to the ground, resulting in a total translational velocity of zero at that point.
What are the two types of acceleration associated with rotational motion?
-The two types of acceleration are radial (centripetal) acceleration, which acts inward, and tangential acceleration, which describes whether a point on the object is speeding up or slowing down.
How is periodic motion defined in relation to rotational motion?
-Periodic motion in rotational motion refers to when the rotation repeats after a set amount of time, represented by the period (T), and is linked to frequency and angular velocity.
What is the formula for converting frequency to angular velocity?
-To convert frequency (in revolutions per second) to angular velocity (in radians per second), multiply the frequency by 2π.
What is a practical example of rolling without slipping mentioned in the episode?
-A practical example is the motion of a car's tires or a train's wheels moving along a track without skidding.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

8.2. Rotational Kinematics
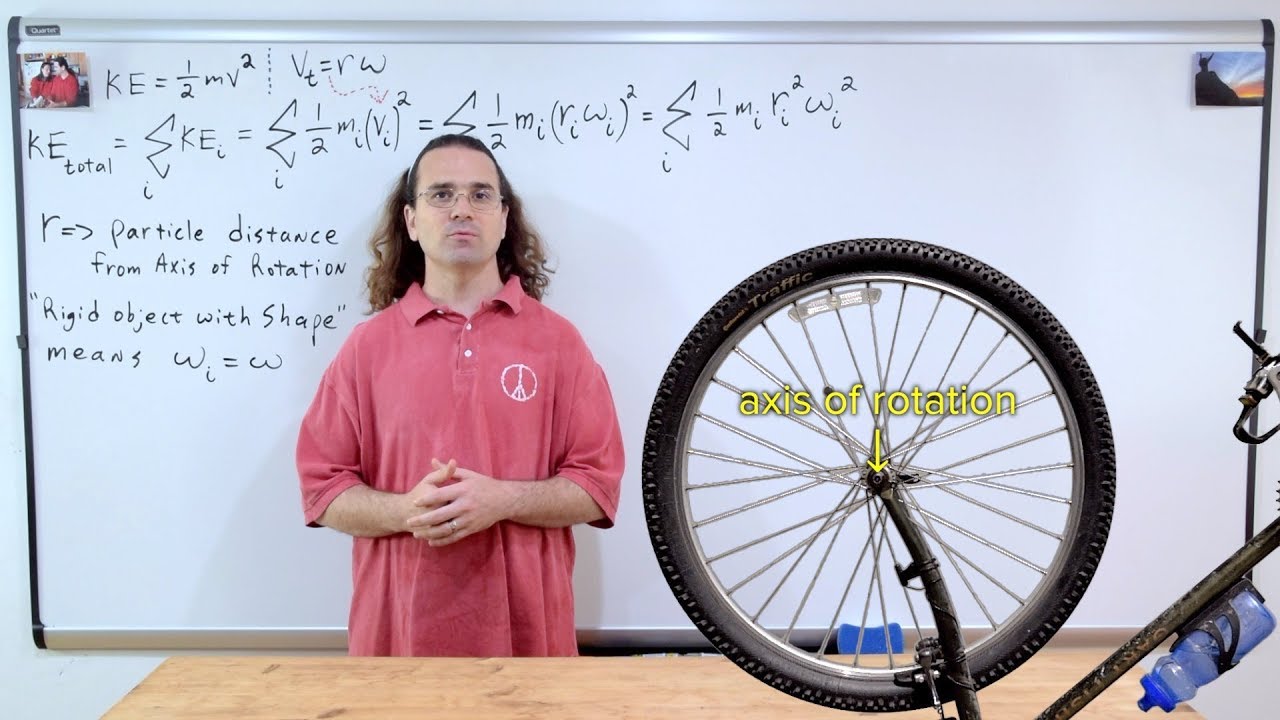

Moment of Inertia Introduction and Rotational Kinetic Energy Derivation

Torque Introduction

SK#2c: Pemodelan Sistem dengan Persamaan Differensial
Rotational Equilibrium Introduction (and Static Equilibrium too!!)

What are the Equations for Kinetic Energy & Angular Momentum of a Point Particle Moving in a Circle?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)