Pearson Correlation Analysis using SPSS - Running, Interpreting, and Reporting
Summary
TLDRThis session provides an overview of correlation analysis, explaining its significance, interpretation, and reporting using SPSS. It covers how correlation measures the relationship between two variables, with examples in business, HR, and research settings. The session distinguishes between Pearson and Spearman correlations, based on data type, and details how to run correlation analysis in SPSS. It also explains interpreting correlation coefficients and constructing a correlation matrix for multiple variables, emphasizing that correlation does not imply causation. The process is demonstrated through step-by-step instructions and reporting tips.
Takeaways
- 📊 Correlation analysis measures the relationship between two variables and is widely used in business and statistics.
- 📉 It helps assess the significance, strength, and direction of the relationship between two variables.
- 🎓 Examples of correlation use cases include exploring the link between social responsibility and university reputation or the effect of price hikes on sales.
- 🧑🤝🧑 There are two types of correlation: Pearson (for interval/ratio data) and Spearman (for ordinal data).
- 📈 Pearson correlation, denoted by R, measures relationships between continuous variables or between one continuous and one dichotomous variable.
- ➕ A positive correlation indicates that as one variable increases, the other increases, while a negative correlation means that as one increases, the other decreases.
- 🧮 Correlation coefficients range from +1 (perfect positive) to -1 (perfect negative) with values closer to 1 or -1 indicating stronger relationships.
- ❌ Correlation does not imply causation; it only shows how variables are related without determining cause-and-effect.
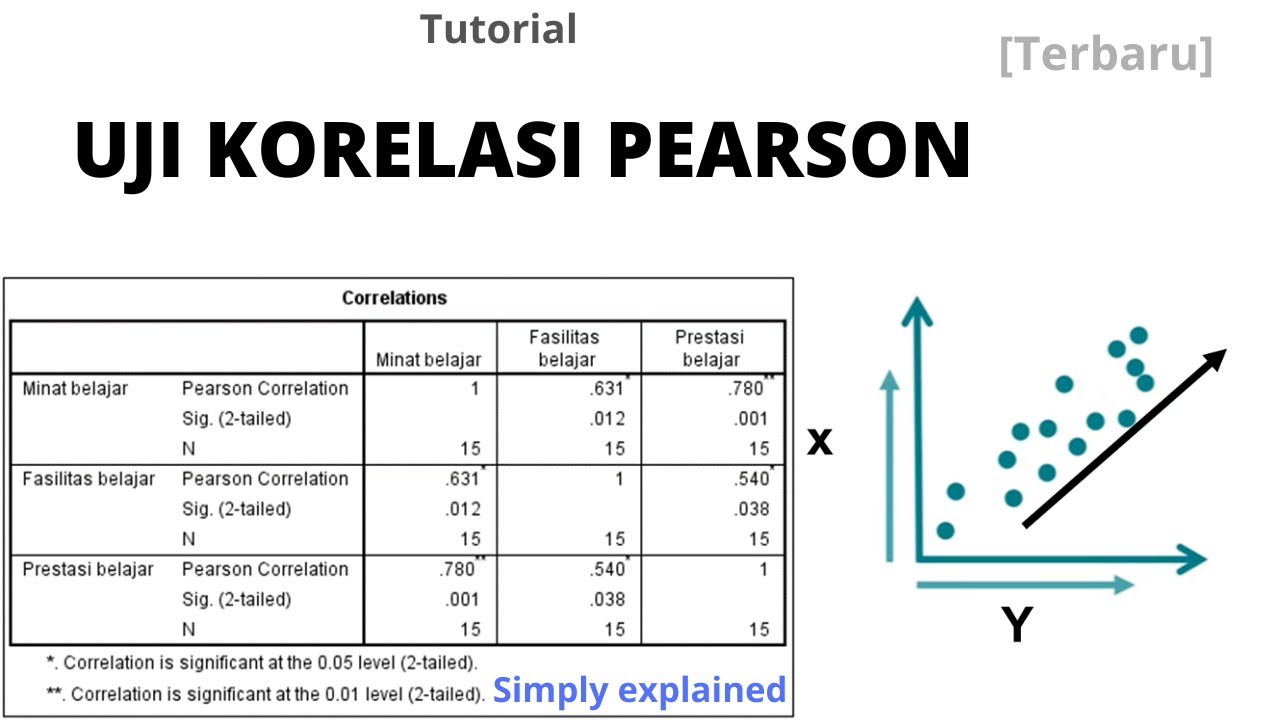
- 📑 Correlation can be analyzed with multiple variables using a correlation matrix, where SPSS helps produce a table showing relationships.
- ✍️ Reporting correlation analysis includes noting the R value (correlation coefficient) and P value (statistical significance) and formatting results appropriately.
Q & A
What is correlation analysis?
-Correlation analysis is a statistical method used to measure the relationship between two variables, determining whether there is an association, link, or bond between them.
When should correlation analysis be used?
-Correlation analysis should be used when you need to assess the relationship between two variables to understand the strength, significance, and direction of the relationship.
What are two types of correlation mentioned in the transcript?
-The two types of correlation mentioned are Pearson product-moment correlation (denoted by 'r') for interval or ratio data, and Spearman's rank correlation (denoted by 'rho') for ordinal data.
How do you choose between Pearson and Spearman correlation?
-Pearson correlation is used for continuous variables on an interval or ratio scale, especially when data is normally distributed. Spearman correlation is used for ordinal variables or when data does not meet the assumptions required for Pearson correlation.
What does a correlation coefficient (R) indicate?
-The correlation coefficient (R) indicates the strength and direction of a relationship between two variables. It ranges from +1 (perfect positive correlation) to -1 (perfect negative correlation), with 0 indicating no correlation.
What is the difference between positive and negative correlation?
-In a positive correlation, an increase in one variable leads to an increase in the other variable. In a negative correlation, an increase in one variable results in a decrease in the other variable.
What does it mean if the correlation coefficient is zero?
-A correlation coefficient of zero means there is no relationship between the two variables, meaning that knowing the value of one variable does not help predict the value of the other.
Can correlation analysis establish causation between variables?
-No, correlation analysis only shows the relationship between variables, but it does not establish a cause-and-effect relationship between them.
How is a correlation matrix used in SPSS?
-A correlation matrix in SPSS is used to explore the relationships between multiple variables. It displays the correlation coefficients between each pair of variables, allowing for the examination of relationships among several variables at once.
What should be reported after conducting correlation analysis?
-After conducting correlation analysis, you should report the strength and direction of the relationship (using the correlation coefficient R) and its significance (the p-value). If multiple variables are analyzed, a correlation matrix is often reported, typically with formatting to highlight key relationships.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)