3 2 1 Basics of Cloud Storage
Summary
TLDRCloud storage offers scalable, on-demand data access via four types: Direct Attached (fast, ephemeral), File Storage (slower, shared, hierarchical), Block Storage (fast, reliable, volumes), and Object Storage (cheapest, slowest, scalable). Cloud providers manage infrastructure, ensuring data availability and charging per gigabyte used. Storage options vary in speed, cost, and persistence, with snapshots for backup and APIs for Object Storage access.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Cloud storage allows data and files to be saved and accessed remotely via the internet or private networks.
- 🔗 Certain storage types must be attached to a compute node to be accessed, while others can be accessed directly.
- 🛠️ Cloud providers are responsible for hosting, securing, managing, and maintaining the storage infrastructure.
- 📈 Cloud storage services enable scalability, meaning you only pay for the storage you provision, often on a per-gigabyte basis.
- 💰 The cost of cloud storage varies by type, with faster read/write speeds generally commanding higher prices.
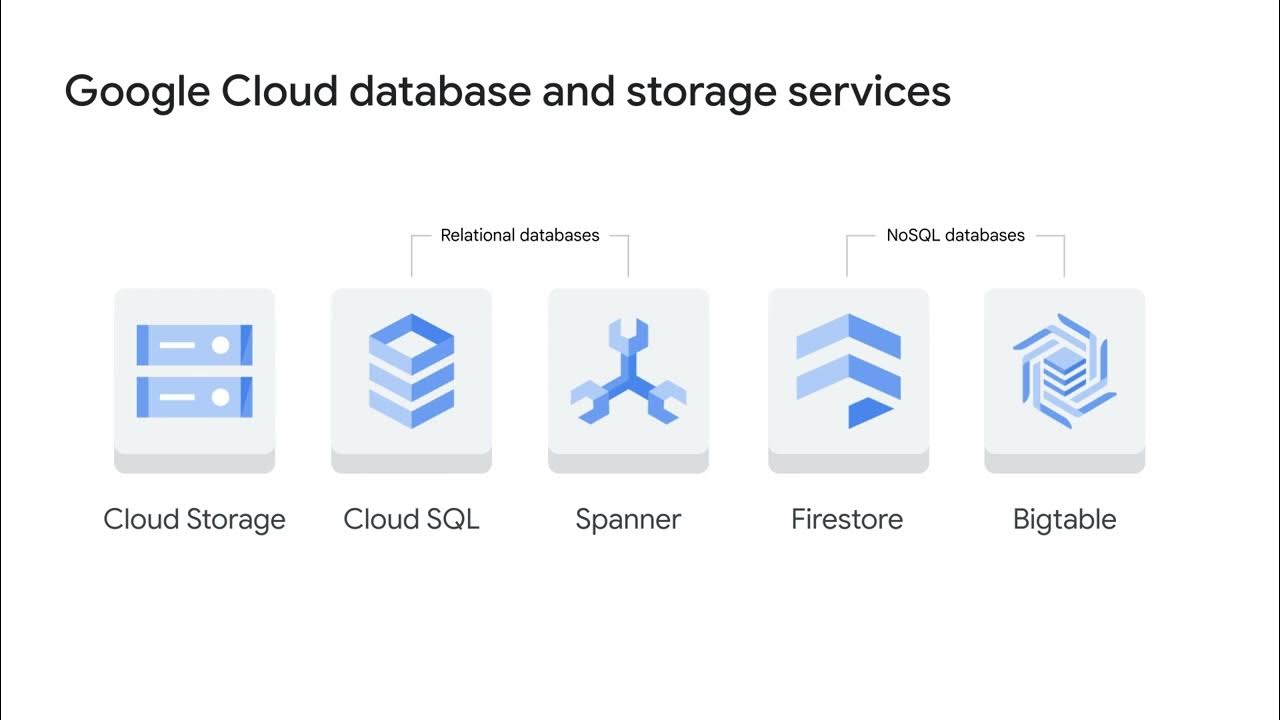
- 🗂️ There are four main types of cloud storage: Direct Attached, File Storage, Block Storage, and Object Storage.
- 💽 Direct Attached storage is fast and typically used for storing a server's operating system but is ephemeral and not shareable.
- 📁 File storage, often presented as NFS, is slower than direct-attached or block storage but can be mounted on multiple servers.
- 🔩 Block storage offers high-speed data access, making it suitable for databases and applications requiring fast disk speeds.
- 🔄 IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) is a term used to describe the speed of storage for File and Block storage.
- 🔒 Persistence determines whether storage is deleted when the compute node is terminated or if it remains available for mounting on another node.
- 📸 Snapshots are a way to back up both File and Block storage by creating a point-in-time image of the storage without downtime.
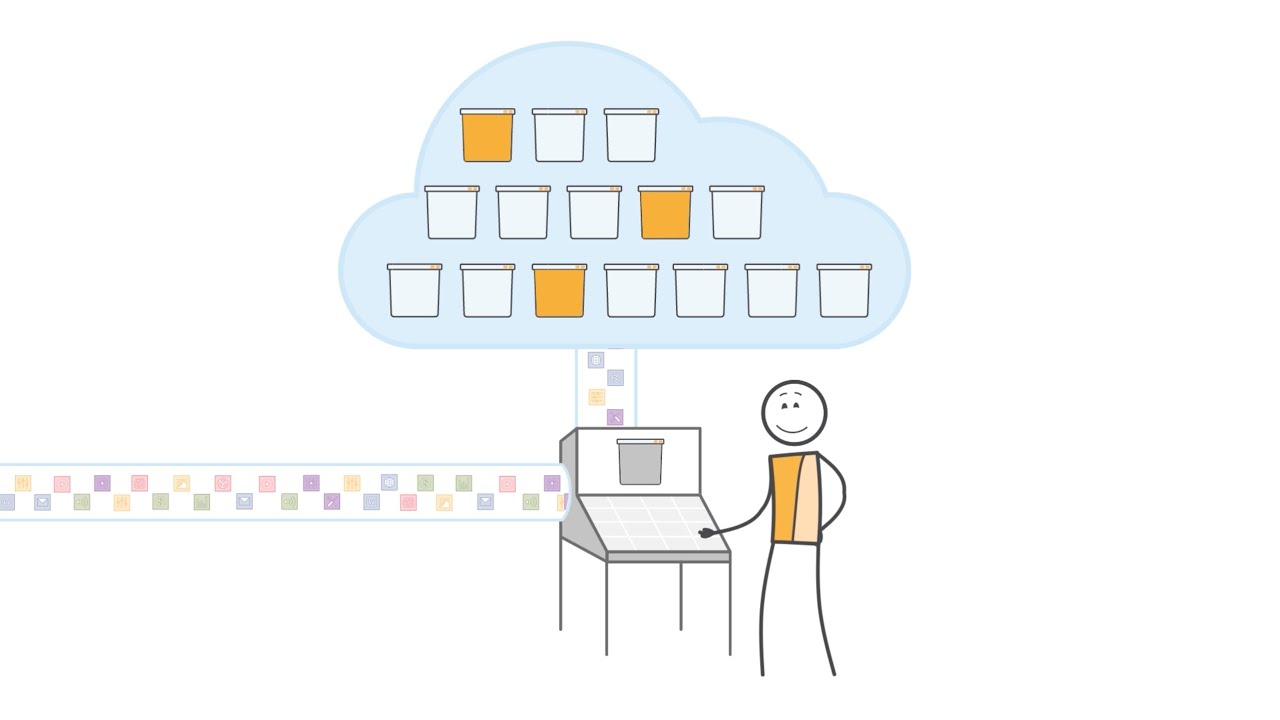
- 📦 Object Storage is accessed via an API, is the cheapest and slowest, and offers virtually unlimited size for storing unstructured data.
Q & A
What is cloud storage?
-Cloud storage is a service that allows you to save data and files over the internet, rather than on a physical device. It is hosted, secured, managed, and maintained by cloud providers.
What is the difference between storage that must be attached to a compute node and storage that can be accessed directly?
-Certain storage types must be attached to a compute node to be accessed, while others can be accessed directly either through the public internet or a private network. Direct access storage is more flexible in terms of accessibility.
How does cloud storage pricing typically work?
-Cloud storage services usually charge on a 'per gigabyte' basis, allowing you to scale your capacity as needed. You only pay for what you provision.
What factors affect the cost of cloud storage?
-The cost of cloud storage can vary by type, but generally, the faster the read/write speed, the higher the per gigabyte cost.
What are the four main types of cloud storage?
-The four main types of cloud storage are Direct Attached, File Storage, Block Storage, and Object Storage.
What is Direct Attached storage and what is it typically used for?
-Direct Attached storage, sometimes called 'Local Storage', is presented directly to a cloud-based server and is typically used to store a server's operating system due to its fast speed.
Why is Direct Attached storage considered Ephemeral?
-Direct Attached storage is considered Ephemeral because it lasts only as long as the compute resource it's attached to. It cannot be shared with other nodes and is not as resilient to failure.
How is File Storage typically presented to compute nodes?
-File Storage is typically presented to compute nodes as 'NFS Storage', which stands for Network File System, and is connected over a standard Ethernet network.
What is Block Storage and how is it different from File Storage?
-Block Storage is presented to compute nodes using high-speed fiber connections, offering faster and more reliable read/write speeds than file storage. It is suitable for databases and applications where disk speed is crucial.
What does the term 'IOPS' stand for and what does it measure?
-IOPS stands for 'Input/Output Operations Per Second' and measures the speed of storage, or how quickly data can be read from or written to the storage.
What is the difference between Persistent and Ephemeral storage?
-Persistent storage remains intact even after the compute node it is attached to is terminated, preserving its data. Ephemeral storage, on the other hand, is deleted along with the compute node, and data is lost unless backed up.
How can one back up data in cloud storage?
-One way to back up data in cloud storage is by taking a Snapshot, which is a point-in-time image of the storage. Snapshots are fast to create and record only changes to the data.
What is Object Storage and how does it differ from other storage types?
-Object Storage is accessed via an API and is not attached to a compute node. It is the cheapest and slowest in terms of read/write speeds but offers virtually unlimited size, charging only for what is used.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)