Storage options in the cloud
Summary
TLDRGoogle Cloud offers a range of scalable and reliable storage solutions, including Cloud Storage, Cloud SQL, Spanner, Firestore, and Bigtable. These services are designed to meet diverse business needs, whether for content delivery, data analytics, or backup storage. The right choice of storage depends on the data type and business requirements. Google Cloud also supports seamless migration of databases, helping businesses move to the cloud and innovate for future growth. With global infrastructure and managed services, Google Cloud simplifies data storage and management, enabling faster deployments and better cost efficiency.
Takeaways
- 😀 Google Cloud offers a variety of storage options, including relational and non-relational databases, and object storage for different data types and workloads.
- 😀 Google Cloud’s storage solutions are designed to be scalable, reliable, and easy to operate, helping businesses reduce costs and save time.
- 😀 Key Google Cloud storage products include Cloud Storage, Cloud SQL, Spanner, Firestore, and Bigtable, each catering to specific use cases.
- 😀 Cloud Storage is ideal for storing and delivering content like images and videos to users globally, providing fast and reliable access.
- 😀 Google Cloud supports data analytics and general compute needs, allowing businesses to process and analyze large datasets for tasks like genomic sequencing or IoT data analysis.
- 😀 Backup and archival storage is a major use case in Google Cloud, offering lower-cost storage solutions for infrequently accessed data and ensuring disaster recovery.
- 😀 Google Cloud helps users migrate existing databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL) to the cloud, easing the transition to cloud-native solutions.
- 😀 Cloud SQL is the go-to service for migrating traditional relational database workloads to the cloud, providing a managed environment for MySQL and PostgreSQL databases.
- 😀 Spanner offers globally distributed relational databases for applications requiring scalability and high availability.
- 😀 Firestore provides a NoSQL database solution for web and mobile applications, suitable for real-time applications and scaling effortlessly.
- 😀 Google Cloud’s storage solutions and database services enable businesses to innovate, build, and plan for future growth, especially in mobile app development and cloud-native solutions.
Q & A
What are the different storage options available in Google Cloud?
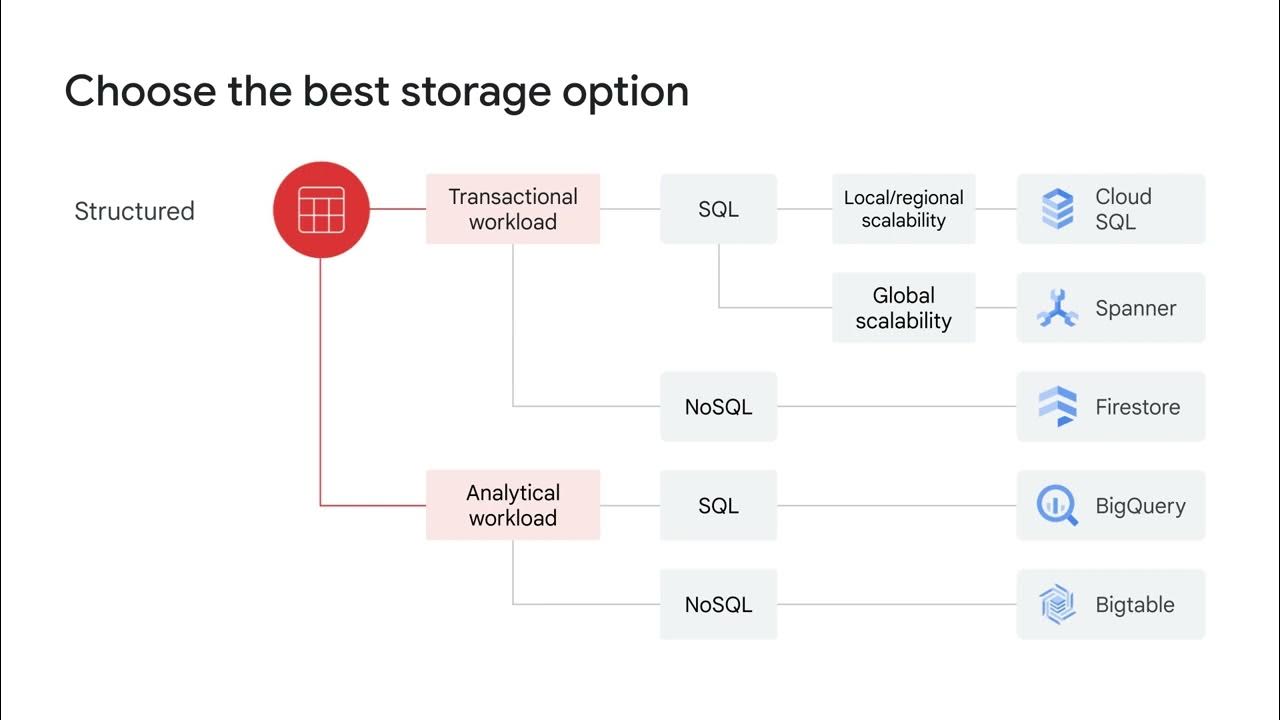
-Google Cloud offers various storage options including Cloud Storage, Cloud SQL, Spanner, Firestore, and Bigtable. These services are designed to support different types of data storage and processing needs, ranging from media delivery to data analytics and backups.
What types of databases does Google Cloud provide?
-Google Cloud provides both relational and non-relational databases. The main options include Cloud SQL (for relational databases), Firestore (for NoSQL databases), Bigtable (for large-scale NoSQL databases), and Spanner (for globally distributed relational databases).
How do the different Google Cloud storage options help with cost reduction and time savings?
-These storage options help reduce costs by offering scalable solutions where users only pay for what they use. They also accelerate the time it takes to launch applications, as Google Cloud provides managed services that eliminate the need for manual configuration and maintenance.
What is the significance of choosing the right storage solution based on data type and business need?
-The right storage solution is critical to optimize data processing, performance, and cost-efficiency. Different types of data—like media, sensor data, or transactional information—have different requirements in terms of structure, scalability, and access speed, which influences the choice of storage.
What are the key use cases for Google Cloud storage services?
-There are three primary use cases for Google Cloud storage: 1) Content storage and delivery, where media like images or videos are served globally. 2) Storage for data analytics and general compute, used for tasks like genomic sequencing or IoT data analysis. 3) Backup and archival storage, where infrequently accessed data is moved to cheaper storage solutions and kept for disaster recovery purposes.
What is the advantage of using Google Cloud’s global network for content storage and delivery?
-Using Google Cloud's global network ensures that content is delivered quickly and reliably to users, regardless of their location. This leads to better user experience, as media like images or videos are accessed faster from geographically distributed servers.
How does Google Cloud support data analytics and compute tasks?
-Google Cloud allows users to store and process data through various analytics tools, including Google Cloud's analytics stack. This is useful for tasks such as genomic sequencing or processing IoT data, which require large-scale data storage and analysis.
What role does backup and archival storage play in Google Cloud’s storage solutions?
-Backup and archival storage allow users to store data that is infrequently accessed at a lower cost. It is also critical for disaster recovery, ensuring that there is a secure copy of data in the cloud in case something happens to the on-premises data.
How does Google Cloud assist users in migrating existing databases?
-Google Cloud helps users migrate their existing databases, such as MySQL or PostgreSQL, to the cloud, typically by moving them to Cloud SQL. The goal is to simplify the migration process while ensuring that databases remain scalable and reliable.
What is the focus of Google Cloud when helping businesses innovate or scale their applications?
-Google Cloud’s focus is to support businesses in rebuilding or developing applications for the cloud, particularly for mobile applications. It also helps companies plan for future growth by providing scalable storage and database services that can adapt as their needs expand.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)