What is Object Storage?
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the concept of object storage, ideal for low-cost, low-performance storage needs, particularly for internet workloads like web applications and content delivery. It explains the fundamental components of an object, including its unique ID, data, metadata, and attributes, and how they are organized into scalable 'buckets.' The script also highlights the benefits of object storage, such as global replication for improved latency in video streaming, efficient file sharing for global collaboration, and secure hosting for web assets and regulatory data.
Takeaways
- 💾 Object storage is designed for low-cost, low-performance storage suitable for Internet workloads, including web applications and hosting.
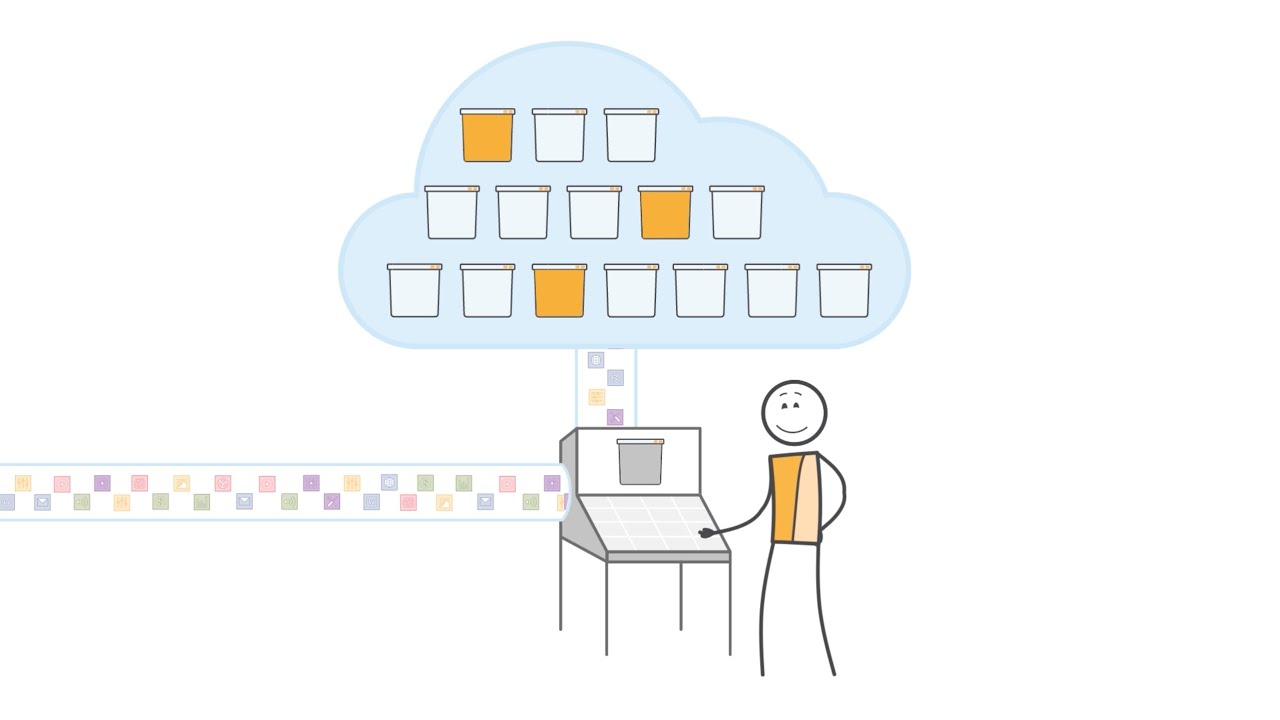
- 🗂️ The term 'object' in object storage refers to any kind of file, which can be stored without file restrictions, but requires certain characteristics.
- 🔑 Every object in object storage must have a unique identifier (ID) for retrieval, along with the actual data, metadata, and attributes.
- 📁 Metadata is crucial for object storage as it provides information about the file, such as creation date, file type, and size, enabling search and indexing.
- 🛡️ Attributes in object storage define permissions and access rights, such as who can override, download, or delete the object.
- 🗑️ Objects are stored in 'buckets' which can scale to hold billions of objects and are virtual constructs in the storage system.
- 🔄 The replication of objects across multiple physical devices ensures data integrity and security, providing redundancy in case of hardware failure or network issues.
- 📈 Object storage pricing and metering are unique and can vary based on performance needs, with different tiers for 'cold' and 'cold-ish' storage.
- 🌐 Object storage is ideal for global use cases like video streaming, where replication across different geographical locations can reduce latency.
- 🤝 It supports file sharing and collaboration across the globe, allowing for version control and easy access for distributed teams.
- 🏛️ Suitable for regulatory data and digital archiving, object storage provides a secure and cost-effective solution for long-term data retention.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of object storage?
-The primary purpose of object storage is to provide a low-cost, low-performance storage solution designed for Internet workloads, such as web applications and hosting, as well as a secure and durable place for data that needs to be retained for long periods due to regulatory or legal reasons.
What are the four essential components of an object in object storage?
-The four essential components of an object in object storage are: 1) A unique identifier (ID) for the object, 2) The actual data content of the object, 3) Metadata that provides information about the object, and 4) Attributes that define permissions and other properties of the object.
How does object storage handle data replication for data integrity and security?
-Object storage replicates the data across multiple physically separated devices. This ensures that even if one device fails or there is a network outage, the data remains accessible from the other replicated locations, thus maintaining data integrity and security.
What is a 'bucket' in the context of object storage?
-In object storage, a 'bucket' is a virtual container where objects are stored. Buckets can scale to hold billions of objects and are a fundamental part of organizing data in object storage systems.
How does object storage pricing and metering work?
-Object storage pricing and metering are based on factors such as the number of 'gets' (data retrievals), 'puts' (data uploads), and the amount of storage used. Different providers may have unique metrics for billing, but performance level and data access frequency are key considerations that affect cost.
What are the different storage tiers mentioned in the script, and how do they differ in cost and use case?
-The script mentions 'cold times 10' as the coldest and least expensive tier, suitable for data archived for long periods. 'Cold' is the next tier, slightly more expensive, for data accessed occasionally. 'Cold-ish' is for more frequently accessed data, like website assets, and is more costly than the colder tiers.
How can object storage be used for video streaming?
-Object storage can be used for video streaming by replicating video files globally across different locations. This reduces latency and improves the streaming experience for users by hosting the content closer to them geographically.
What benefits does object storage offer for file sharing and collaboration?
-Object storage facilitates file sharing and collaboration by allowing multiple versions of a file to be uploaded and stored with metadata tracking changes. This enables secure, low-cost, and efficient global collaboration on documents, spreadsheets, and other files.
How is object storage useful for web hosting and digital archiving?
-Object storage is useful for web hosting as it can host website assets at a lower cost and with high availability. For digital archiving, it provides a secure and durable place to store and access large volumes of data that are not frequently accessed, such as digital photographs of manuscripts.
What is the role of APIs in interacting with object storage?
-APIs are the primary method of interaction with object storage. Users perform operations such as uploading, downloading, and managing objects through API calls, which allows for automation and integration with other systems.
How can object storage help with regulatory data and cold storage requirements?
-Object storage can store large volumes of data securely and durably, making it suitable for regulatory data that must be retained for long periods. The ability to replicate data across devices ensures that the data is protected against hardware failures or other issues.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Why Your Backend Shouldn't Serve Files

Block Storage vs. File Storage

Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) Overview
Introduction to Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) - Cloud Storage on AWS

What is Content Delivery Network (CDN) | Content Delivery Network Explained | How CDN Works

Parquet File Format - Explained to a 5 Year Old!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)