Constant Velocity compared to Constant Acceleration
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the differences between constant velocity and uniform acceleration. Constant velocity means an object moves equal distances in equal amounts of time, resulting in a linear distance-time graph and zero acceleration. In contrast, uniform acceleration leads to increasing or decreasing distances over time, producing a quadratic distance-time graph and a linear velocity-time graph. The acceleration-time graph for constant velocity shows zero acceleration, while for uniform acceleration, it depicts a constant value. The video aims to clarify these key concepts graphically to resolve any lingering ambiguities.
Takeaways
- 🚶 Constant velocity means that an object moves equal distances in equal amounts of time.
- 📈 In a distance versus time graph for constant velocity, the relationship is linear, showing a straight line.
- 🏃 Uniform acceleration (constant acceleration) means that the velocity of an object increases at a constant rate over time.
- ⬆️ In a distance versus time graph for accelerating motion, the distance increases more significantly over time, creating a quadratic curve.
- 📏 Displacement vectors for constant velocity are equal in length, while for accelerating objects, the vectors grow larger over time.
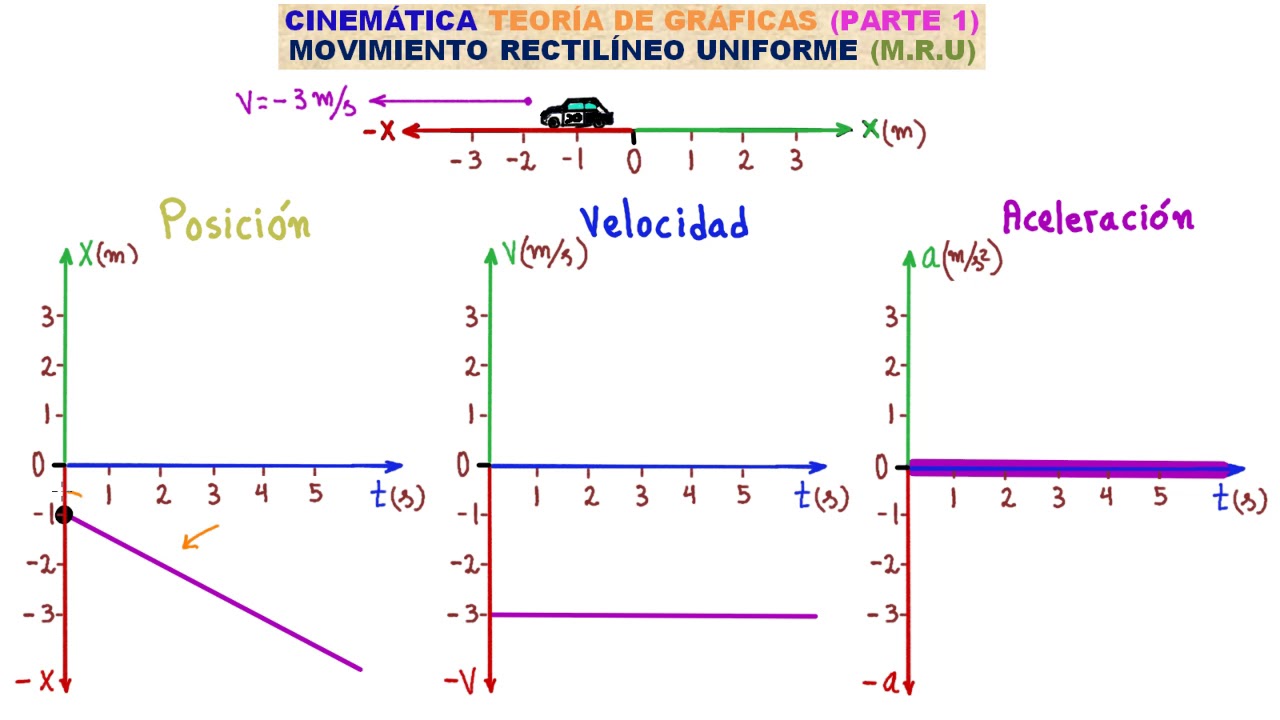
- 🕑 For velocity versus time graphs, constant velocity is represented as a horizontal line, indicating no change in speed.
- ⚖️ Constant acceleration results in a linear velocity versus time graph, showing that velocity increases steadily over time.
- 0️⃣ Acceleration is zero for constant velocity, meaning there's no change in the object's speed over time.
- 📉 For an object slowing down, displacement vectors in a distance versus time graph become shorter over time.
- 💡 An acceleration versus time graph for constant acceleration shows a flat horizontal line, indicating a steady rate of acceleration.
Q & A
What are the two types of motion discussed in the transcript?
-The two types of motion discussed are constant velocity and constant (or uniform) acceleration.
What does constant velocity mean?
-Constant velocity means that an object moves with the same speed and direction over time, without any changes in velocity.
How does a distance vs. time graph look for an object with constant velocity?
-For an object with constant velocity, the distance vs. time graph is a straight line, indicating a linear relationship where the object moves equal distances in equal amounts of time.
How is constant acceleration represented on a distance vs. time graph?
-Constant acceleration is represented as a curve on a distance vs. time graph, indicating that the object moves increasingly farther distances over equal time intervals.
What is a key characteristic of an object moving with constant velocity?
-A key characteristic is that the object moves equal distances in equal amounts of time, represented by displacement vectors of equal length on a distance vs. time graph.
What does the velocity vs. time graph look like for an object with constant velocity?
-The velocity vs. time graph for an object with constant velocity is a straight, horizontal line, indicating that the velocity remains constant over time.
How does the acceleration vs. time graph appear for an object with constant velocity?
-The acceleration vs. time graph for an object with constant velocity is a line along the time axis (zero acceleration), indicating that there is no change in velocity.
What does a velocity vs. time graph look like for an object with constant acceleration?
-For an object with constant acceleration, the velocity vs. time graph is a straight, diagonal line, showing that velocity increases at a constant rate over time.
How is the acceleration vs. time graph represented for an object with constant acceleration?
-The acceleration vs. time graph for constant acceleration is a horizontal line above the time axis, indicating that the acceleration remains constant over time.
What happens to the displacement vectors as time increases for an object with constant acceleration?
-For an object with constant acceleration, the displacement vectors get progressively longer, indicating that the object moves greater distances in equal time intervals.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Fisika - Penjelasan Perbedaan GLB dan GLBB
CINEMÁTICA. GRÁFICAS DEL M.R.U TEORÍA 1 [APRENDE LOS GRÁFICOS DE POSICIÓN, VELOCIDAD Y ACELERACIÓN]

Motion Class 9 One Shot in 10 mins | Best CBSE Class 9 Physics Revision Strategy | Abhishek Sir

Me Salva! CIN11 - MCU

FISIKA KELAS X | GERAK MELINGKAR (PART 1) - Besaran-besaran dalam Gerak Melingkar

Lecture3 part2 video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)