Motion Class 9 One Shot in 10 mins | Best CBSE Class 9 Physics Revision Strategy | Abhishek Sir
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses various fundamental concepts of motion, including distance, displacement, speed, average speed, velocity, and acceleration. It explains the differences between scalar and vector quantities, and covers the formulas of motion, such as s = ut + 1/2 at^2, which are essential for solving problems related to motion. The script also delves into graph analysis, explaining how to identify and interpret distance-time and velocity-time graphs, and their implications on understanding uniform and non-uniform motion. Additionally, it touches on uniform circular motion, highlighting the difference between constant speed and velocity due to changing direction. The session aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of motion, preparing viewers for exams and fostering a deeper knowledge of the subject.
Takeaways
- 😀 The session covers important topics within a 15-minute timeframe, including definitions and formulas related to motion concepts.
- 🎓 The instructor encourages reviewing the entire list of topics linked in the description for in-depth knowledge on each subject.
- 👉 It's recommended to watch the video during travel for a complete understanding before the exam.
- 📚 The video discusses the concepts of distance, displacement, speed, average speed, velocity, uniform motion, non-uniform motion, and acceleration.
- 📏 Distance is a scalar quantity that cannot be negative, while displacement, which is the shortest distance between the initial and final positions, can be negative, zero, or positive.
- 📐 Displacement is a vector quantity, differing from distance in that it accounts for direction.
- 🚀 Speed is a scalar quantity defined as the total distance traveled upon time, with units in meters per second.
- 🔍 Average speed is calculated as the total distance divided by the total time, and it cannot be negative.
- 📊 Velocity is defined as displacement divided by time, which can be negative, zero, or positive and is a vector quantity.
- 🔄 Average velocity is exactly the total displacement divided by the total time, which can also be negative, zero, or positive, and is a vector quantity.
- 📈 Graphs are used to store a lot of information in a small space, and the video explains how to identify distance-time graphs and velocity-time graphs.
- 📉 The slope of the curve in a distance-time graph represents speed, while in a velocity-time graph, it represents acceleration.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the session described in the script?
-The session focuses on covering important topics within a 15-minute timeframe from the 'Motion' chapter, including definitions and concepts such as distance, displacement, speed, average speed, velocity, acceleration, and graphical representations of these concepts.
What does the instructor recommend doing before the examination?
-The instructor recommends watching the video and revising all the concepts before the examination, especially if one has not learned the topics in depth yet.
What is the difference between distance and displacement as explained in the script?
-Distance is the total path covered by an object and can be zero or positive, whereas displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of the object and can be negative, zero, or positive.
How is speed defined in the script?
-Speed is defined as the rate of change of distance with respect to time, and its unit is meters per second. It is a scalar quantity.
What is the formula for average speed mentioned in the script?
-The formula for average speed is the total distance divided by the total time of an object, which is expressed as Total Distance / Total Time.
How is velocity described in the script?
-Velocity is described as the rate of change of displacement with respect to time, which can be negative, zero, or positive, and is a vector quantity.
What is the difference between uniform motion and non-uniform motion according to the script?
-Uniform motion is when an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, while non-uniform motion is when an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
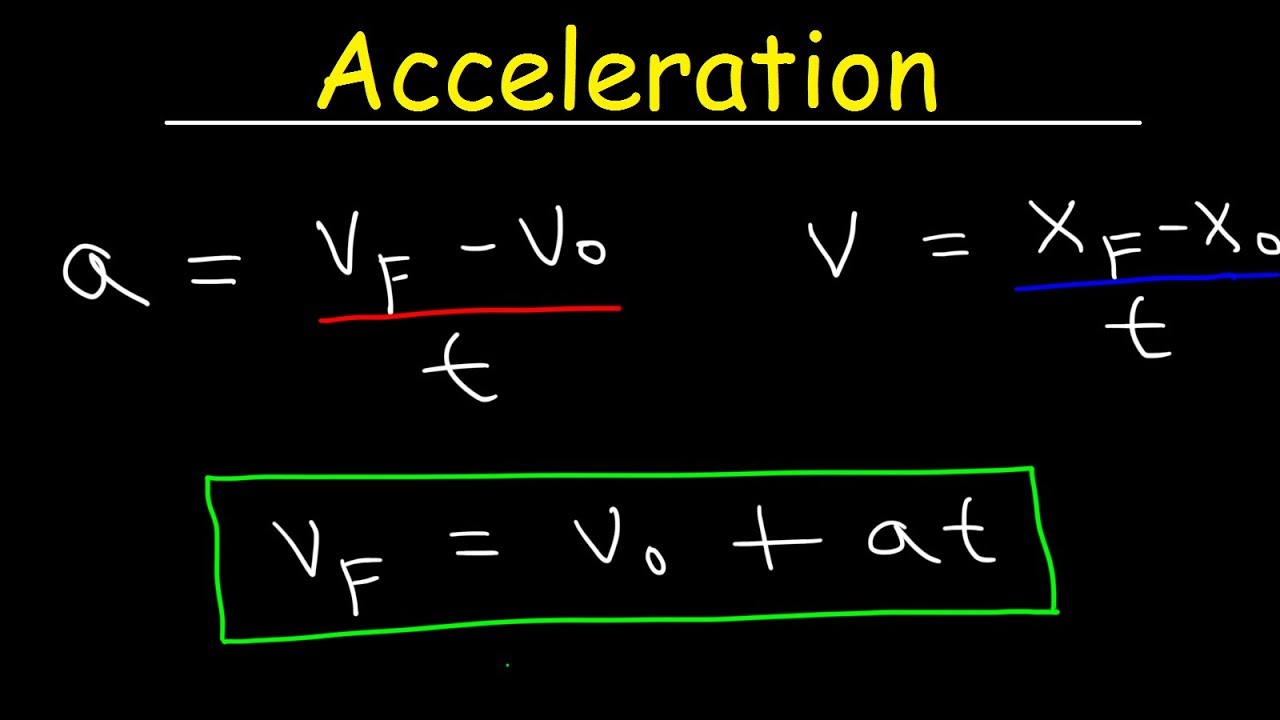
What is the unit of acceleration as mentioned in the script?
-The unit of acceleration is meters per second squared.
Why are graphs used in the context of motion as discussed in the script?
-Graphs are used to store a lot of information in a small space and to visually represent the concepts of motion, such as distance-time and velocity-time graphs.
What does the slope of the curve in a distance-time graph represent?
-The slope of the curve in a distance-time graph represents speed, as it is the change in distance with respect to time.
How does the script differentiate between a uniform circular motion and non-uniform motion?
-Uniform circular motion is characterized by constant speed, but the velocity is not constant due to the changing direction, making it a non-uniform motion because the velocity vector changes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Distance displacement speed velocity acceleration for IGCSE Physics, GCE O level Physics

FISIKA KELAS X: GERAK LURUS (PART 1) Jarak, Perpindahan, Kelajuan, Kecepatan, Percepatan
Physics - Acceleration & Velocity - One Dimensional Motion

Gerak Benda dan Makhluk Hidup di Lingkungan Sekitar

Kinematics in 1 dimension part 1

BAB 4 : GERAK DAN GAYA | Part 1 : GERAK BENDA | IPA SMP Kelas 7 Kurikulum Merdeka
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)