Percentiles, Quantiles and Quartiles in Statistics | Statistics Tutorial | MarinStatsLectures
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the concepts of percentiles, quantiles, and quartiles, explaining their significance in data analysis. It emphasizes the median as the 50th percentile and introduces the first (25th percentile) and third (75th percentile) quartiles, highlighting their roles in dividing data into quarters. The video also touches on how percentiles can be used to interpret individual data points within a dataset. The speaker advises focusing on understanding these concepts rather than the calculation methods, which are typically handled by statistical software like R. The video concludes with a mention of other divisions like terciles, quintiles, and deciles, suggesting their utility in different analytical scenarios.
Takeaways
- 📊 Percentiles and quantiles are measures used to divide a dataset into 100 equal parts, with each part representing a percentage of the data.
- 🔄 The terms 'percentile' and 'quantile' are often used interchangeably, although there is a slight difference between them.
- 📈 Quartiles are specific types of percentiles or quantiles that divide the data into four equal parts, with the first quartile (Q1) representing the 25th percentile, the median (Q2) the 50th percentile, and the third quartile (Q3) the 75th percentile.
- 🎯 The median, or 50th percentile, is a special case where 50% of the data points fall below this value and 50% above.
- 📉 The first quartile (Q1) divides the dataset so that 25% of the data points are below it and 75% are above.
- 📈 The third quartile (Q3) is where 75% of the data points are below this value and 25% are above, often considered the upper quartile.
- 📊 Box plots are a graphical representation of the median, first quartile, third quartile, minimum, and maximum values of a dataset.
- 🔢 Percentiles and quantiles can be calculated for any percentage, not just the common quartiles, to provide a detailed understanding of data distribution.
- 🔄 Understanding the percentile a specific value falls into can help interpret how that value compares to the rest of the dataset.
- 📊 Beyond quartiles, other divisions of data such as tertiles (thirds), quintiles (fifths), and deciles (tenths) can be used to analyze and summarize data.
Q & A
What is the difference between percentiles and quantiles?
-While there is a slight subtle difference between the two, they can be used interchangeably for the most part. Percentiles and quantiles are measures that divide a dataset into 100 equal parts, with each part representing a percentage of the dataset.
What is the median in the context of percentiles?
-The median is the 50th percentile, which means it has 50% of the ordered observations below it. It is the value that cuts the dataset in half.
What is the first quartile (Q1) and how is it calculated?
-The first quartile, or Q1, is the 25th percentile, which has 25% of the observations below it. It divides the dataset into quarters, with one quarter below and three quarters above this value.
What does the third quartile (Q3) represent?
-The third quartile, or Q3, represents the 75th percentile, having 75% of the observations below it. It divides the dataset so that three-quarters of the data are below this value.
How are quartiles used to divide a dataset?
-Quartiles divide the dataset into four equally sized quarters. The first quartile (Q1) is the 25th percentile, the second quartile (the median) is the 50th percentile, and the third quartile (Q3) is the 75th percentile.
What is a box plot and how does it relate to quartiles?
-A box plot is a graphical visualization that displays the median, first quartile (Q1), and third quartile (Q3), as well as the minimum and maximum values of a dataset. It provides a quick summary of the data's distribution.
Can percentiles or quantiles be used to determine how an individual data point ranks within a dataset?
-Yes, percentiles or quantiles can be used to determine the rank of an individual data point within a dataset by identifying what percentage of observations fall below that specific value.
What is the purpose of calculating percentiles or quantiles?
-Percentiles and quantiles are useful for summarizing the distribution of a dataset and for comparing individual data points to the overall dataset, providing insights into the relative standing of those points.
What are some other types of divisions of a dataset besides quartiles?
-Besides quartiles, datasets can be divided into tertiles (three equal parts), quintiles (five equal parts), or deciles (ten equal parts), depending on the level of detail required for analysis.
Why might one use statistical software like R for calculating percentiles or quantiles?
-Statistical software like R is used for calculating percentiles or quantiles because it can handle the complexity and variations in calculation methods, and it can process large datasets efficiently.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

CARA MENCARI NILAI KUARTIL DESIL PERSENTIL UKURAN LETAK II DATA TUNGGAL
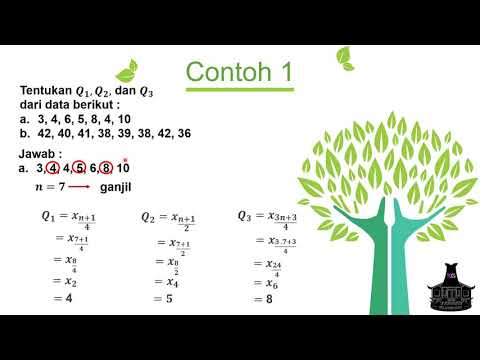
Ukuran Penyebaran Data : Kuartil, Desil dan Persentil + Contoh Soal

Ukuran Letak Data Tunggal (Kuartil, Desil dan Persentil)
MEASURES OF POSITION OF GROUPED DATA | MATHEMATICS IN THE MODERN WORLD

Statistika - Ukuran Letak Data (Kuartil, Desil, Persentil)
QUARTILES, DECILES AND PERCENTILES OF UNGROUPED DATA || GRADE 10 MATHEMATICS Q4
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)