18 The Brain Part 2
Summary
TLDRThis lecture explores the limbic system, the brain's emotional center, and its key components. The thalamus serves as a sensory gateway, routing information to the appropriate brain areas. The hypothalamus maintains internal equilibrium, regulating hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sleep. The amygdala, often called the 'lizard brain,' processes primal emotions and the fight-or-flight response. The hippocampus handles memory and spatial navigation, while the basal ganglia control voluntary movement, and the cerebellum coordinates balance and movement. The video concludes with a teaser for the next lecture on the brain stem.
Takeaways
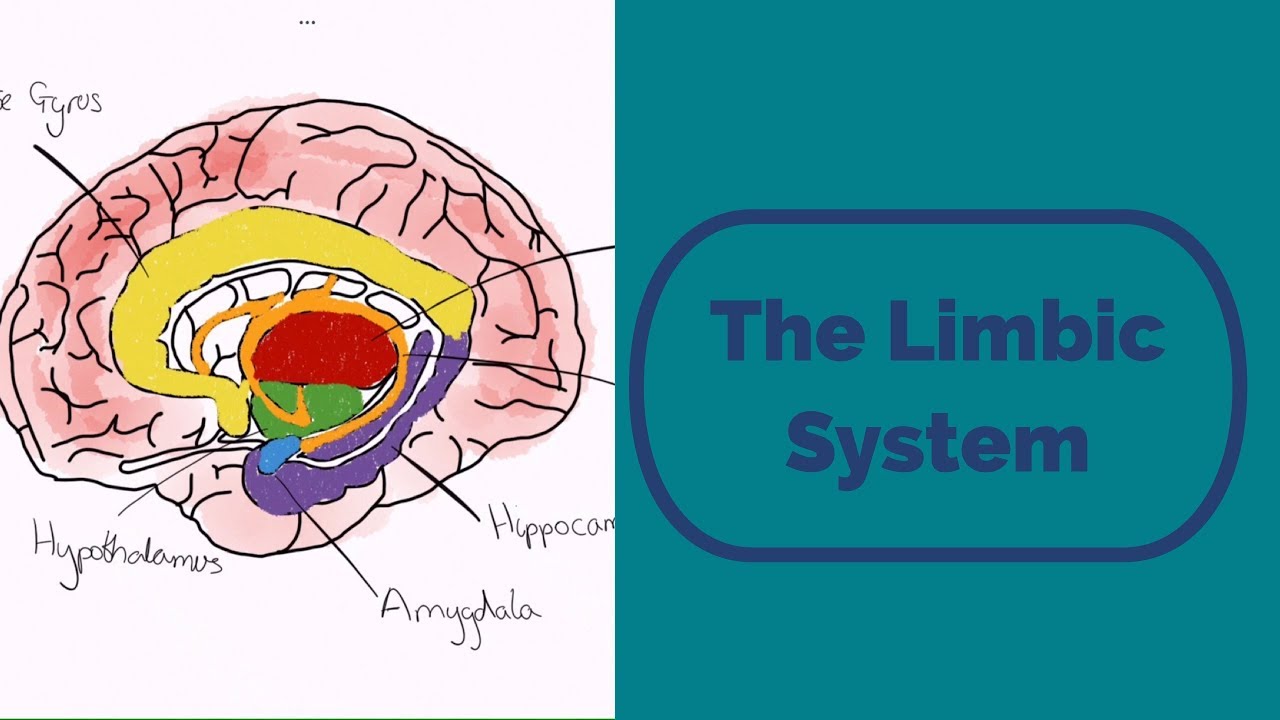
- 🧠 The limbic system is the brain's emotional center, with most parts associated with emotional functions.
- 👁️ The thalamus acts as a sensory gateway, routing information from sense organs to the appropriate sensory cortex areas.
- 🌡️ The hypothalamus maintains internal balance (equilibrium) and regulates functions like hunger, thirst, sex drives, body temperature, and sleep.
- ⏰ The hypothalamus also regulates circadian rhythms, helping manage sleep-wake cycles.
- 🧬 The hypothalamus links the central nervous system and the endocrine system, influencing hormone release through the pituitary gland.
- 🦎 The amygdala, often called the 'lizard brain,' processes emotions like excitement, arousal, and fear, and plays a role in the fight-or-flight response.
- 🧭 The hippocampus is crucial for memory, especially spatial memory, and transfers short-term memories into long-term storage.
- 🚖 Studies on London taxi drivers show they have larger hippocampi due to the need for navigating the city, demonstrating the role of spatial memory.
- 👁️🗨️ The basal ganglia control voluntary movement and eye movement, aiding in coordinated physical actions.
- 🎯 The cerebellum, or 'little brain,' is vital for balance and coordination, playing a key role in activities like dancing and sports.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the limbic system?
-The limbic system is the brain's emotional center, responsible for emotions and various functions related to emotions.
What is the role of the thalamus in sensory processing?
-The thalamus acts as a sensory relay, routing information from the sense receptors to the appropriate area in the brain for processing.
What does the term 'hypothalamus' mean and what is its main function?
-The term 'hypothalamus' means 'below the thalamus' and its main function is to maintain a constant internal state, also known as equilibrium.
How does the hypothalamus regulate our body's functions?
-The hypothalamus regulates our body's functions by influencing the autonomic nervous system or by sending signals to the pituitary gland to release or stop releasing certain hormones.
What is the amygdala and why is it referred to as the 'lizard brain'?
-The amygdala is a part of the brain involved in processing emotions, particularly those based on instinct or emotion rather than logical thought. It is called the 'lizard brain' due to its primitive nature and similarity to the emotional responses of animals.
What role does the hippocampus play in memory and learning?
-The hippocampus is involved in memory, particularly spatial memory, learning, and emotion. It holds short-term memory and transfers it into long-term storage.
How do London taxi drivers' hippocampi differ from non-taxi drivers'?
-London taxi drivers have larger hippocampi than non-taxi drivers due to the need for extensive spatial memory in navigating the city.
What is the function of the basal ganglia in the brain?
-The basal ganglia help control voluntary movement, including eye movements.
What does the cerebellum do and why is it important for athletes and performers?
-The cerebellum controls balance and coordination of movement, making it crucial for athletes, dancers, and performers who require precise and coordinated physical actions.
What happens when the hippocampus is damaged?
-Damage to the hippocampus can result in problems forming new memories, although older memories remain intact.
What will be discussed in the next lecture video following this one?
-The next lecture video will briefly discuss the brain stem.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Neurofisiología Sistema límbico Autor Dr Di Carlo #BarcelóLive

Neuroanatomy S1 E4: Hypothalamus and Limbic System #neuroanatomy #ubcmedicine

INTRODUCTION TO THE BRAIN by Professor Fink

Three Brains - Thinking to Doing to Being (Joe Dispenza)

Sistem Limbik si Pengatur Emosi dan Perilaku (Film Animasi)
The Limbic System
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)