Neuroanatomy S1 E4: Hypothalamus and Limbic System #neuroanatomy #ubcmedicine
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the brain's higher cortical functions, focusing on the limbic system and hypothalamus. The hypothalamus, a small yet vital structure, maintains homeostasis by responding to internal and external environments. The limbic system, evolutionarily ancient, links the hypothalamus and neocortex, facilitating emotional responses and memory. Core structures like the hippocampus and amygdala play key roles in memory and emotion, respectively. The script delves into their anatomy and interconnectedness, highlighting the Papez circuit's role in learning, memory, and emotion, and the amygdala's connection to the hypothalamus for fear responses.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The brain's sensory and motor systems allow us to detect and respond to our environment.
- 💖 Higher cortical functions like love and importance determination involve complex interactions between neurotransmitters and hormones.
- 🌐 The limbic system and hypothalamus are two major structures influencing these behaviors.
- 🔍 The hypothalamus is crucial for responding to both internal and external environments and maintaining homeostasis.
- 📚 The limbic system is vital for learning, memory, and emotional aspects of behavior.
- 🔄 These structures are interconnected, with the hypothalamus influencing the endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system.
- 🧬 The limbic system is evolutionarily old and acts as a bridge between the hypothalamus and the neocortex.
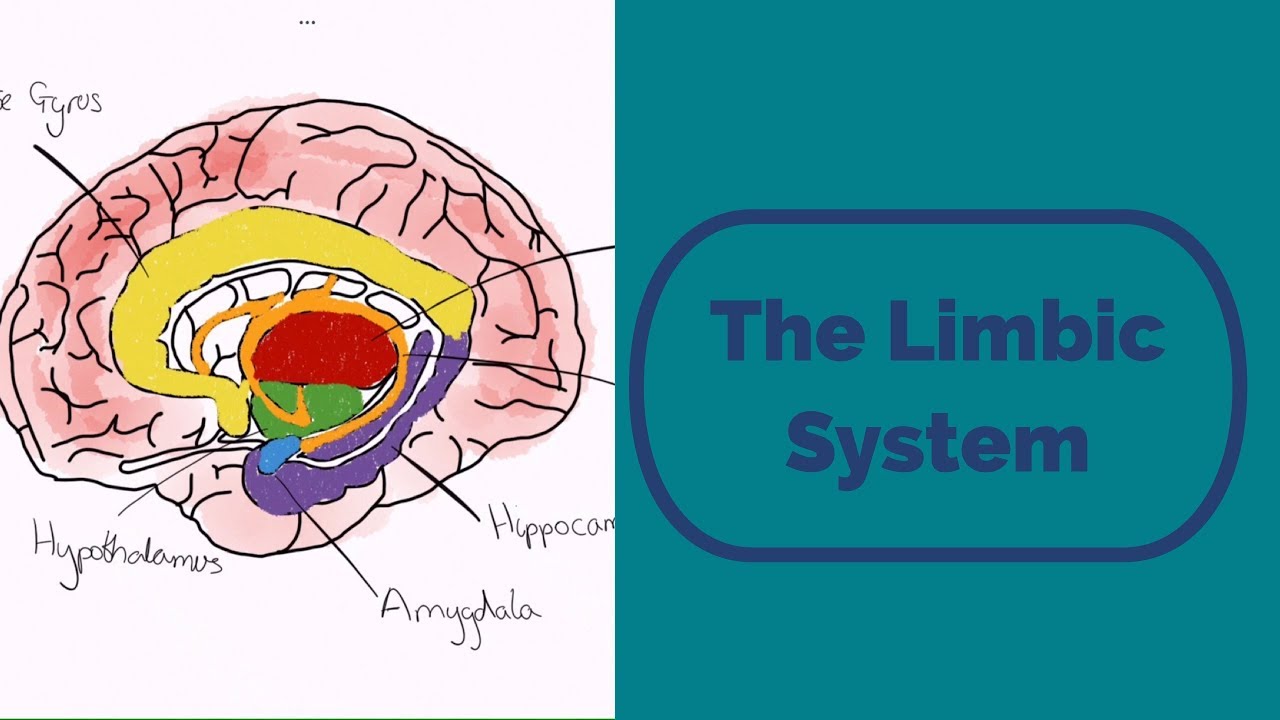
- 🧭 Key structures of the limbic system include the hippocampus, amygdala, and the limbic lobe of the brain.
- 🗺️ The hippocampus is involved in memory, and the amygdala is responsible for emotional processing.
- 🔗 The Papez circuit, involving the hippocampus, fornix, mammillary bodies, and thalamus, is crucial for learning, memory, and emotion.
- 🔄 The amygdala and hypothalamus are linked, playing a significant role in fear responses and salience filtering.
Q & A
How do sensory and motor systems work together to allow us to interact with our environment?
-Sensory and motor systems work together by transmitting sensory information to the brain and motor information to muscles, enabling us to detect and respond to our surroundings.
What is the role of neurotransmitters and hormones in higher cortical functions?
-Neurotransmitters and hormones play a crucial role in higher cortical functions by facilitating complex interactions throughout the nervous system, influencing behaviors such as engagement with the world, determining importance, and emotional responses like falling in love.
What are the two major anatomical substrates that influence higher cortical functions?
-The two major anatomical substrates that influence higher cortical functions are the limbic system and the hypothalamus.
Why is the hypothalamus critical for life?
-The hypothalamus is critical for life as it allows us to respond to both internal and external environments and helps maintain homeostasis.
How does the limbic system contribute to learning and emotional behavior?
-The limbic system contributes to learning and emotional behavior by being important for memory and all emotional aspects of behavior, and it is interconnected with the hypothalamus.
What is the anatomical relationship between the hypothalamus and the thalamus?
-The hypothalamus can be delineated from the thalamus via the hypothalamic sulcus in a mid sagittal section of the brain.
What is the function of the hypothalamus in relation to the endocrine system?
-The hypothalamus functions as part of the limbic system and helps maintain homeostasis in the entire body through influences on the endocrine system and its primary influence on both the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
What are the core structures of the limbic system?
-The core structures of the limbic system include deep forebrain nuclei and cortical areas, with the key cortical area being the limbic lobe, which spans the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes.
What are the primary functions of the hippocampus and the amygdala?
-The hippocampus is primarily involved in memory, while the amygdala is primarily responsible for emotional processing.
What is the Papez circuit and its significance?
-The Papez circuit is a classic circuit involved in learning, memory, and emotion, connecting structures such as the hippocampus, mammillary bodies, and the anterior nucleus and dorsal medial nucleus of the thalamus.
How is the amygdala connected to the hypothalamus and what is its significance?
-The amygdala is connected to the hypothalamus, which is an important connection for fear responses and salience filtering, playing a key role in the expression of emotion, emotional memory, and basic drives.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)