WCLN - Hydrolysis of Polysaccharides - Biology
Summary
TLDRThe video script explains the biochemical processes of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis, focusing on the formation and breakdown of carbohydrates. Dehydration synthesis is used to create disaccharides from monosaccharides and polysaccharides from these disaccharides. Conversely, hydrolysis breaks down polysaccharides into disaccharides and then into monosaccharides, such as glucose. Key enzymes like salivary amylase and those in the small intestine facilitate these processes, which are crucial for energy production, with the exception of cellulose, which humans cannot digest.
Takeaways
- 💧 Hydrolysis is the process of breaking down complex molecules by adding water.
- 🔗 Dehydration synthesis is the process of forming larger molecules from smaller ones by removing water.
- 🍬 Monosaccharides can be joined to form disaccharides through dehydration synthesis.
- 🌐 Polysaccharides are formed by joining many monosaccharide or disaccharide units via dehydration synthesis.
- 🔄 Hydrolysis breaks down polysaccharides into disaccharides and further into monosaccharides.
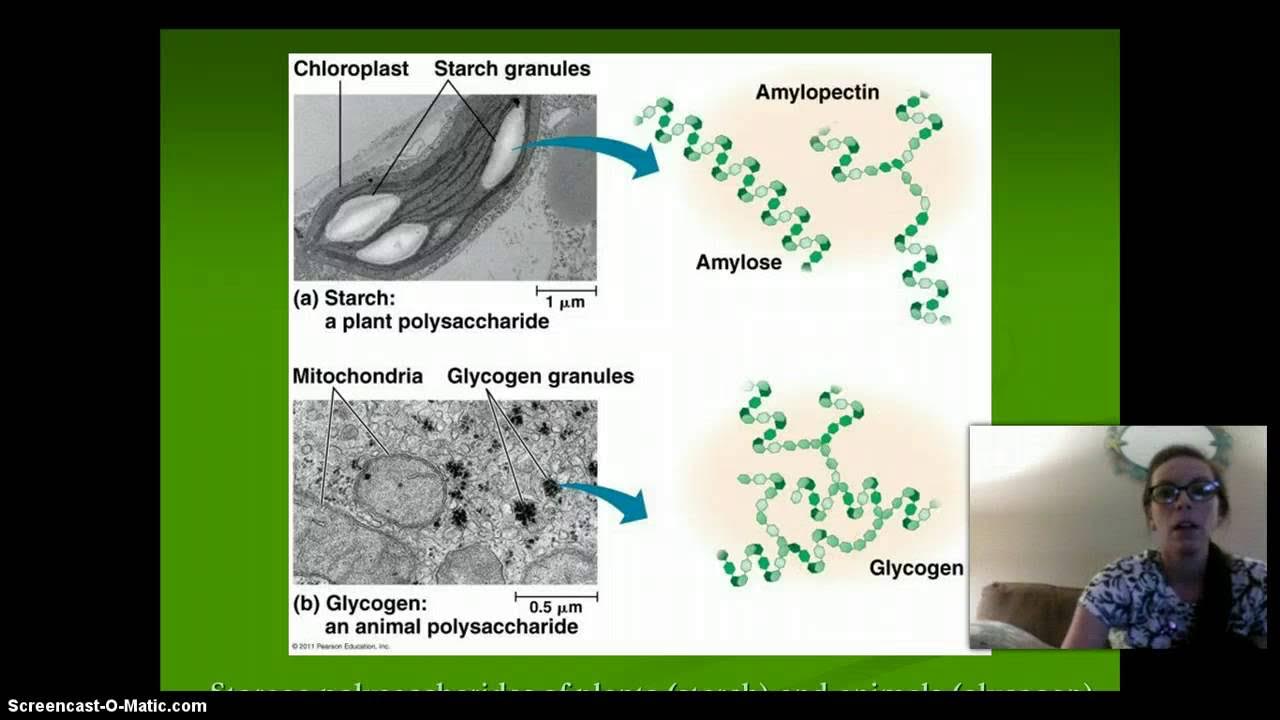
- 🌾 Starch, a polysaccharide, is broken down into maltose through hydrolysis in the mouth with salivary amylase.
- 🍯 Maltose, a disaccharide, can be hydrolyzed into two glucose molecules in the small intestine.
- 🏃 Glycogen is broken down into glucose for quick energy through hydrolysis, especially for muscles.
- 🚫 The human body lacks enzymes to hydrolyze cellulose into glucose, unlike some microorganisms.
- 🔑 Enzymes play a crucial role in the hydrolysis process, facilitating the breakdown of complex carbohydrates.
Q & A
What is hydrolysis?
-Hydrolysis is the process of breaking down larger molecules into smaller units by adding water.
How does hydrolysis relate to the breakdown of polysaccharides?
-Hydrolysis is used to break down polysaccharides into disaccharides and further into monosaccharides by adding water.
What is the opposite process of hydrolysis?
-The opposite process of hydrolysis is dehydration synthesis, which is used to build larger molecules from smaller ones.
How are disaccharides formed from monosaccharides?
-Disaccharides are formed from monosaccharides through the process of dehydration synthesis, where a water molecule is removed.
What is starch and how is it broken down?
-Starch is a polysaccharide that can be broken down into maltose using hydrolysis with the help of enzymes like salivary amylase.
What enzyme is responsible for breaking down starch into maltose?
-Salivary amylase is the enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose during the hydrolysis process in the mouth.
How is maltose further broken down in the body?
-Maltose is further broken down into two molecules of glucose through hydrolysis in the small intestine.
What is glycogen and how does its breakdown relate to energy production?
-Glycogen is a storage form of glucose in the body and is broken down into glucose through hydrolysis when a quick energy source is needed for muscles.
Why can't the human body break down cellulose into glucose?
-The human body does not possess the enzymes necessary to break down cellulose into glucose, which is a component of plant cell walls.
What is the role of hydrolysis in the digestion of carbohydrates?
-Hydrolysis plays a crucial role in the digestion of carbohydrates by breaking down complex carbohydrates into simpler forms that can be absorbed and used by the body.
How does the process of hydrolysis differ for different types of carbohydrates?
-The process of hydrolysis can differ for different carbohydrates based on the specific enzymes and conditions present, such as pH and temperature, which affect the efficiency of the breakdown.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)