Carbohydrates
Summary
TLDRThis podcast explores the diverse roles of carbohydrates, from energy provision to structural support in organisms. It delves into the classification of carbohydrates, from monosaccharides like glucose to complex polysaccharides like glycogen and cellulose. The script explains the biochemical processes of hydrolysis and dehydration reactions involved in carbohydrate metabolism, touches on the evolutionary significance of sugar, and cautions against excessive sugar consumption due to modern health concerns like heart disease and diabetes.
Takeaways
- 🍞 Carbohydrates are essential for both energy and structure in living organisms, with sugar being the basic building block.
- 🔬 The term 'saccharides' is used in science to describe sugars, which are the components of carbohydrates.
- 📊 Carbohydrates are categorized based on the number of sugar molecules they contain: monosaccharides (one), disaccharides (two), oligosaccharides (three to ten), and polysaccharides (many).
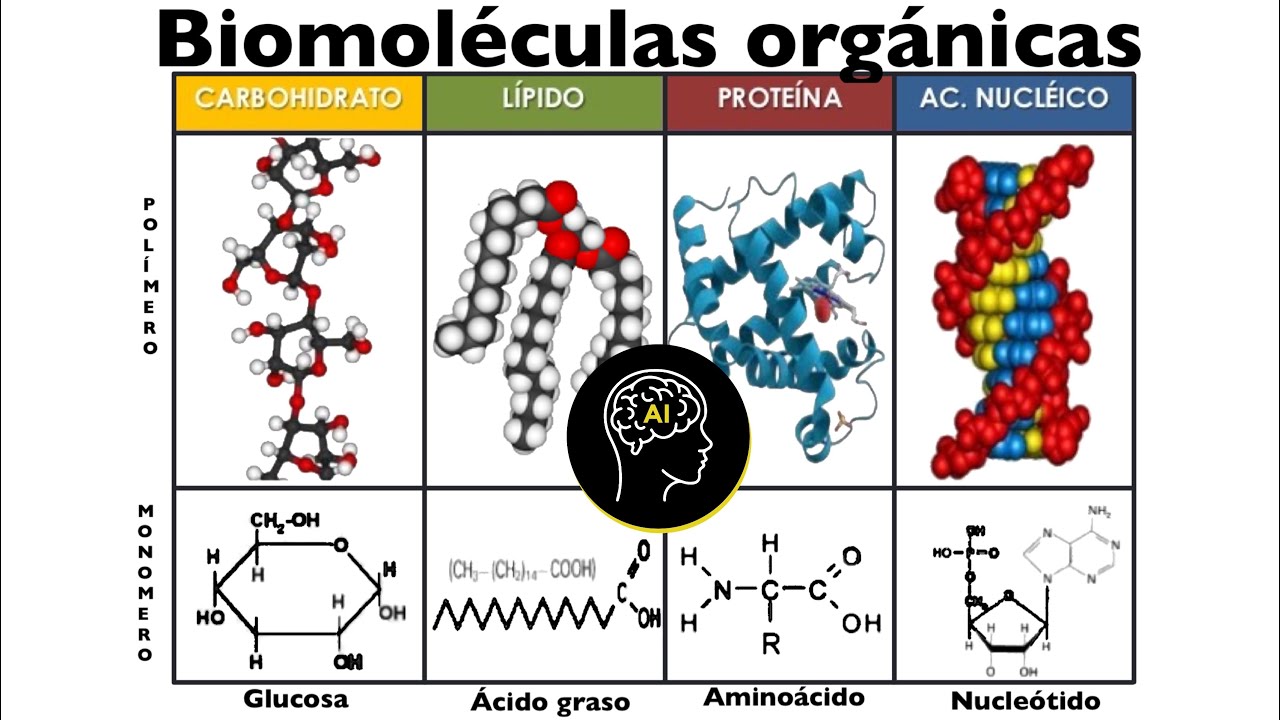
- 🌾 The empirical formula of all carbohydrates is the same, with a ratio of 1:2:1 of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, respectively.
- 🍇 Glucose, fructose, and galactose are the basic monosaccharides, each with different sweetness levels and found in various sources.
- 🍬 Disaccharides like sucrose (table sugar) and lactose (milk sugar) are made up of two monosaccharides and require specific enzymes for breakdown in the body.
- 🥕 Oligosaccharides are important in the formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids, which play a role in cell identification and extracellular matrix attachment.
- 🥔 Starch is a type of polysaccharide made up of hundreds of glucose molecules and serves as an energy storage molecule in plants.
- 🏋️ Glycogen is a large molecule with thousands of glucose units, stored in the liver and muscles for energy needs.
- 🌳 Cellulose, a structural polysaccharide in plants, is indigestible to humans without the help of microorganisms that can break it down.
- 🔄 Hydrolysis and dehydration reactions are the processes by which carbohydrates are broken down or built up, respectively.
- 🍭 While sugars are necessary for energy and have evolutionary benefits, excessive consumption, especially of high-fructose corn syrup, can lead to health issues like heart disease and diabetes.
Q & A
What is the primary building block of carbohydrates?
-The primary building block of carbohydrates is sugar, specifically monosaccharides like glucose, which are the simplest form of sugar.
Why are carbohydrates important for both energy and structure in living organisms?
-Carbohydrates are important for energy because they can be broken down to release glucose, a primary source of energy for cells. They are also crucial for structure, as seen in cellulose in plants and chitin in insect exoskeletons, providing rigidity and form.
What is the empirical formula of carbohydrates?
-The empirical formula of carbohydrates is C:H:O in a ratio of 1:2:1, which can be remembered as 'carbohydrates' with a carbon and water (H2O).
What is the difference between a monosaccharide and a disaccharide?
-A monosaccharide is a single sugar molecule, like glucose. A disaccharide is formed when two sugar molecules are joined together, such as sucrose which is composed of glucose and fructose.
How does the body process lactose found in milk?
-The body processes lactose through an enzyme called lactase, which breaks down lactose into its constituent monosaccharides, glucose and galactose, before they can be absorbed.
What is the significance of oligosaccharides in biological systems?
-Oligosaccharides, which consist of 3 to 10 sugar molecules, are significant in the formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids, playing important roles in cell membrane structure and function, including cell recognition and attachment to the extracellular matrix.
Why are glycogen and starch considered energy storage molecules?
-Glycogen and starch are considered energy storage molecules because they are composed of long chains of glucose molecules. When energy is needed, these chains can be broken down into monosaccharides that can be used by the body.
What is the role of cellulose in plants?
-Cellulose provides structural support in plants. It is a polysaccharide made up of many glucose units linked together with hydrogen bonds, making it extremely strong and durable.
How do the processes of hydrolysis and dehydration reactions relate to carbohydrates?
-Hydrolysis is the process of breaking down complex carbohydrates into simpler monosaccharides by the addition of water. Dehydration synthesis is the opposite process, where two monosaccharides combine to form a disaccharide or larger polysaccharide, with the removal of a water molecule.
What are the potential health risks associated with excessive sugar consumption?
-Excessive sugar consumption, particularly from sources like high fructose corn syrup, is associated with an increased risk of heart disease and diabetes. While sugars are necessary for energy, moderation is key to avoid health complications.
Why do humans have a natural preference for sugar?
-Humans have a natural preference for sugar because it is often an indicator of fruit, which is a source of essential vitamins. This preference has evolutionary roots, as sweet-tasting fruits were typically nutrient-rich and beneficial for survival.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)