GCSE Biology - DNA Part 1 - Genes and the Genome #63
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the fundamental concepts of DNA, chromosomes, genes, and genomes. It explains that DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a polymer forming a double helix and is compacted into 46 chromosomes within each cell. Chromosomes are inherited in pairs, with the 23rd pair determining sex. Genes, which are segments of DNA, dictate the production of proteins that define cell types. The genome encompasses an organism's complete genetic material, and understanding it can aid in disease treatment and trace human ancestry.
Takeaways
- 🧬 DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid, which is the chemical substance that makes up all of our genetic material.
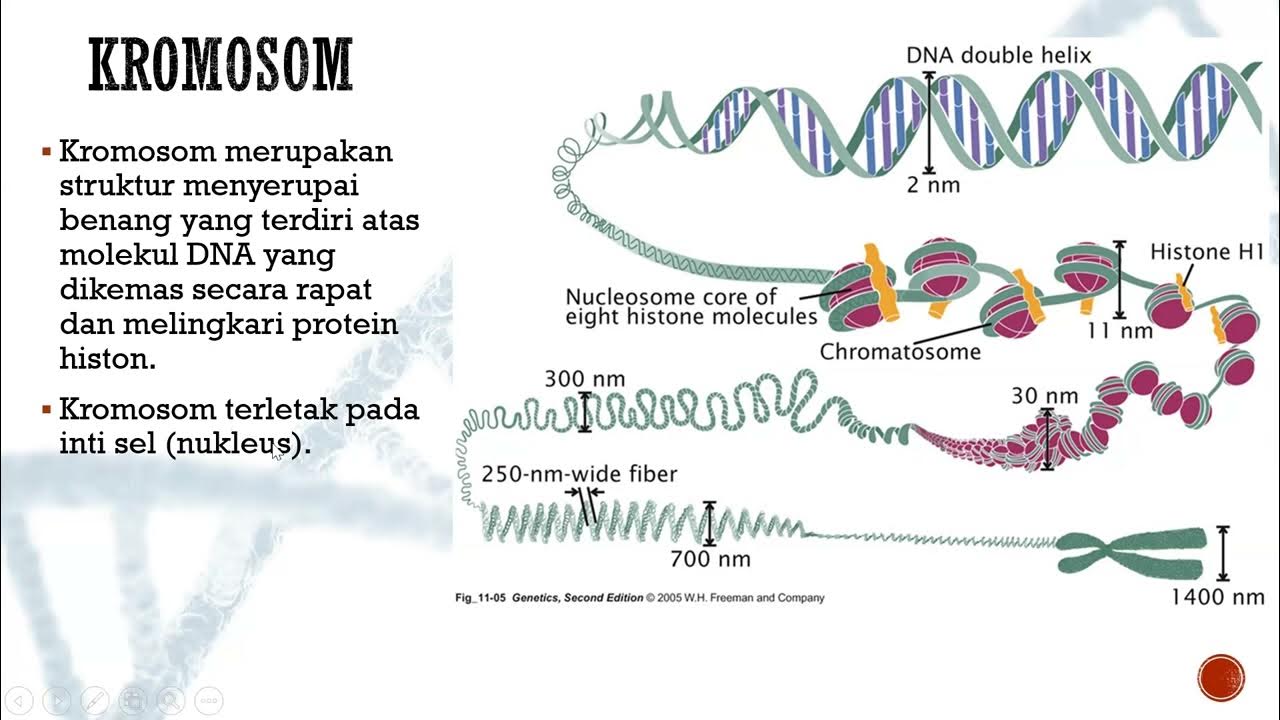
- 🌀 DNA is a polymer composed of many similar units, forming a double-stranded spiral known as the double helix.
- 🧬 If unraveled, the DNA from a single cell would be over two meters long, but it is compacted into chromosomes to fit within the cell nucleus.
- 🔍 Humans have 46 chromosomes in each cell, organized into 23 pairs, with one chromosome of each pair inherited from each parent.
- 🚹 The 23rd pair of chromosomes determines sex; females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome.
- 🧬 Chromosomes are typically depicted in an 'X' shape, but this is only accurate during cell division processes like meiosis or mitosis.
- 🧬 Genes are small sections of DNA that code for specific proteins, essentially being a code for a sequence of amino acids.
- 🌐 There are 20 different types of amino acids, which can combine in numerous ways to create thousands of different proteins.
- 🧬 The type of proteins a cell produces, determined by DNA, dictates the cell's function and characteristics.
- 🌐 The genome refers to the complete set of genetic material in an organism, with the human genome now fully mapped by scientists.
- 🧬 Understanding the genome allows for the identification of genes linked to diseases, which can inform treatment options and the development of new therapies.
- 🌐 Genomic data can also be used to trace human migrations and understand the genetic relationships between different populations.
Q & A
What does DNA stand for and what is its role in our cells?
-DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid, and it is the chemical that all of our genetic material is made of. It determines the traits and functions of our cells.
What is the structure of DNA described as in the script?
-DNA is described as a polymer made up of lots of similar units stuck together, forming a double-stranded spiral known as the double helix.
How long would a single cell's DNA be if unraveled?
-If you were to take all the DNA out of a single cell and unravel it into one long strand, it would be over two meters long.
How is DNA organized within a cell to fit inside the nucleus?
-DNA is separated into 46 different sections called chromosomes, which are tightly coiled to fit inside the nucleus.
What is the significance of having 46 chromosomes in human cells?
-Human cells have 46 chromosomes, with 23 different types, and each type exists in pairs, one from each parent, which is essential for inheritance.
What are the sex chromosomes, and how do they determine a person's sex?
-The 23rd pair of chromosomes are the sex chromosomes, which include an X and a Y chromosome. Women have two X chromosomes (XX), making them female, while men have one X and one Y chromosome (XY), making them male.
What is the typical appearance of chromosomes during cell division?
-Chromosomes typically appear as an 'X' shape just before cell division processes like meiosis or mitosis.
What is a gene and how does it relate to proteins?
-A gene is a small section of DNA that codes for a particular type of protein. It is a code for a sequence of amino acids that, when combined, form a protein.
How does the variety in amino acid combinations affect protein diversity?
-Although there are only 20 different types of amino acids, their various combinations can create thousands of different proteins, contributing to the diversity of cellular functions.
What is the genome and why is it significant for an organism?
-The genome is the entire set of genetic material in an organism. It is significant because it contains all the genetic information necessary for the organism's development and function.
How has the understanding of the human genome benefited medical science?
-Understanding the human genome allows scientists to identify genes linked to diseases, which can help in developing targeted treatments and understanding genetic predispositions.
What can genomes reveal about human ancestry and migrations?
-Genomes can reveal information about the migrations of our ancestors by showing similarities and differences in genetic material among different populations, such as when humans left Africa or first traveled to North America.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)