Kromosom
Summary
TLDRThis video script covers the basics of chromosomes, genes, and genetics, explaining key concepts like genomes, alleles, genotypes, and phenotypes. It delves into how chromosomes, composed of DNA, are structured and compacted with the help of histone proteins to fit into the small cell nucleus. The script also explores the different types of chromosomes, their roles during cell division, and how they ensure accurate genetic material distribution. A focus on human chromosomes is presented, with emphasis on the 23 pairs, including the autosomes and sex chromosomes, and their structural details like centromeres and arms.
Takeaways
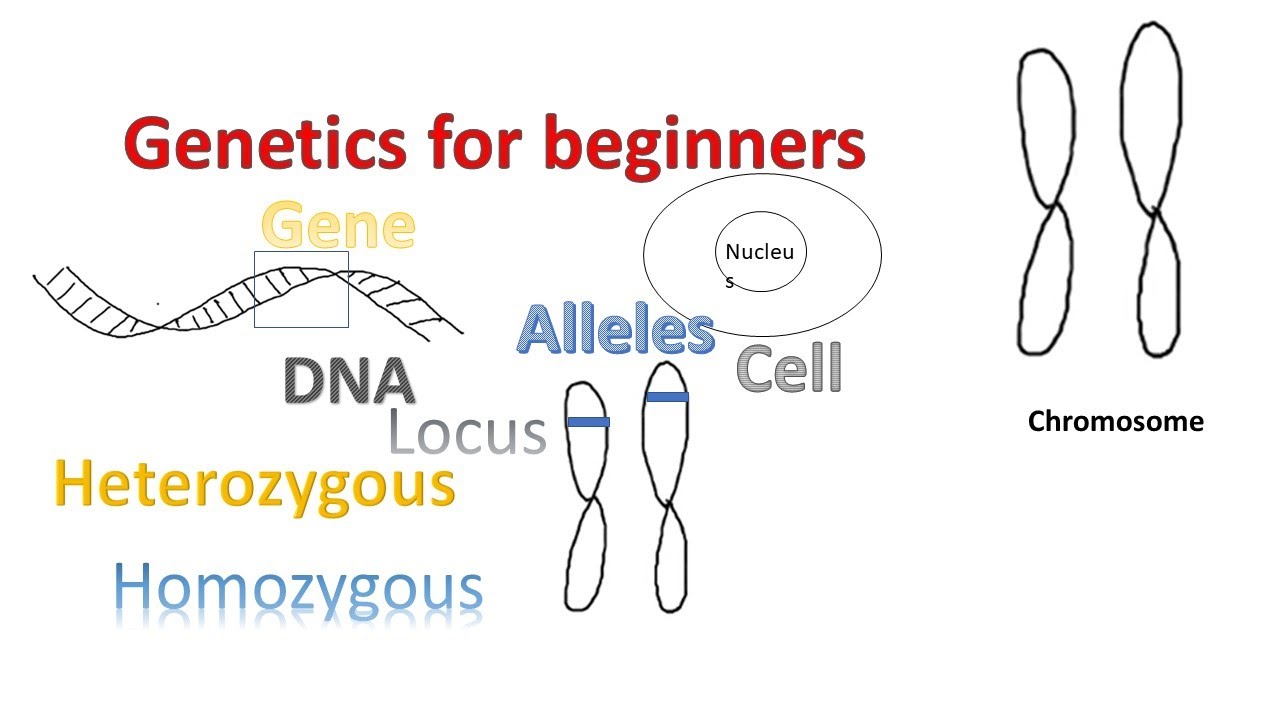
- 😀 The gene is the basic unit of genetic information, made up of DNA, and determines inherited characteristics.
- 😀 The genome refers to the total genetic information in an organism, consisting of both coding and noncoding regions.
- 😀 Coding regions of the genome are involved in protein synthesis, while noncoding regions often function as regulatory elements.
- 😀 Human genomes contain approximately 6.37 GB of DNA for females and 6.27 GB for males, measured in base pairs (GB/GBP).
- 😀 Alleles are different versions of the same gene; they can be homozygous (identical) or heterozygous (different).
- 😀 The phenotype refers to observable traits, such as physical characteristics, that result from the expression of the genotype.
- 😀 Chromosomes are long DNA molecules compressed into compact X-shaped structures, aided by histone proteins.
- 😀 Chromosomes help protect genetic material and ensure proper distribution during cell division.
- 😀 Human cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes: 22 pairs are autosomes, and 1 pair determines sex (haploid).
- 😀 Chromosomes are categorized by the position of the centromere: metacentric, submetacentric, acrocentric, and telocentric.
- 😀 Chromosomes have distinct arms, labeled P (upper) and Q (lower), and are analyzed by specific banding patterns for identification.
Q & A
What is a gene and what is its role in genetics?
-A gene is the basic unit of genetic information, made up of DNA. It determines inherited characteristics by encoding the instructions to create proteins.
What is the difference between coding and non-coding DNA?
-Coding DNA is the part of the genome that is translated into proteins, while non-coding DNA does not directly code for proteins but can have regulatory functions, controlling gene expression.
What is the human genome size and how is it measured?
-The human genome size for each cell is about 6.37 GB for women and 6.27 GB for men. It is measured in gigabytes (GB) or megabytes (MB) based on the number of base pairs in the DNA sequence.
How do alleles affect genetic traits?
-Alleles are different versions of the same gene. If the alleles are identical (homozygous), the individual has two copies of the same gene. If the alleles are different (heterozygous), the individual has two different versions of the gene, which can affect the traits expressed.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
-Genotype refers to the specific genetic makeup of an individual, while phenotype is the observable physical or behavioral traits that result from the expression of the genotype.
What is a chromosome and why is it compacted into an X-shape?
-A chromosome is a long DNA molecule that carries genetic information. It is compacted into an X-shape to fit inside the cell nucleus, allowing for efficient storage and protection of genetic material.
What role do histone proteins play in the structure of chromosomes?
-Histone proteins help compact DNA into a dense structure, allowing it to fit inside the small cell nucleus. They also protect the genetic material and regulate its accessibility during processes like cell division and protein synthesis.
How do centromeres function during cell division?
-Centromeres are the regions on chromosomes that play a crucial role during cell division. They help attach the chromosomes to spindle fibers, ensuring that the genetic material is evenly distributed between the daughter cells.
How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have and what are autosomes?
-Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. The first 22 pairs are autosomes, which are chromosomes that do not determine the sex of an individual. The 23rd pair are sex chromosomes that determine the biological sex of the individual.
What are the different types of chromosomes based on the position of the centromere?
-Chromosomes are classified into different types based on the position of the centromere: metacentric (centrally located), submetacentric (slightly off-center), acrocentric (near one end), and telocentric (at the very end). These types affect how chromosomes are distributed during cell division.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Pewarisan Sifat Kelas 9 SMP (Part-1)

Genetics vocabulary | Inheritance and variation | Middle school biology | Khan Academy

Punnett Squares - Basic Introduction
Genetics for beginners | Genes Alleles Loci on Chromosomes |

Genetika Bakteri | Pertukaran Materi Genetik | Transposisi Konjugasi Transduksi Transformasi Plasmid

Pendahuluan Pola Hereditas (Istilah Penting dalam Hereditas)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)