Arithmetic Sequence vs Geometric Sequence
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial delves into the concepts of arithmetic and geometric sequences, explaining the common difference in arithmetic sequences and the common ratio in geometric ones. It illustrates how to find the nth term and the sum of the first n terms for both sequence types, using examples to demonstrate the calculation process. The script also offers tips for civil service exam preparation, emphasizing the importance of understanding these mathematical concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Arithmetic sequences involve a common difference between consecutive terms, while geometric sequences involve a common ratio.
- 📚 The common difference in an arithmetic sequence is found by subtracting a term from the previous term (e.g., 5 - 1 = 4).
- 📈 In a geometric sequence, the common ratio is found by dividing any term by the previous term (e.g., 3 ÷ 1 = 3).
- 🔍 To find the nth term in an arithmetic sequence, use the formula: nth term = first term + (n - 1) * common difference.
- 📐 For the nth term in a geometric sequence, the formula is: nth term = first term * common ratio^(n - 1).
- 🔑 The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic sequence is given by: Sum = (first term + nth term) / 2 * n.
- 🌟 The sum of the first n terms of a geometric sequence can be calculated using the formula: Sum = first term * (1 - common ratio^n) / (1 - common ratio).
- 📝 Example given for finding the 4th term in an arithmetic sequence: 1 + (4 - 1) * 4 = 13.
- 📉 Example provided for the 4th term in a geometric sequence: 1 * 3^(4 - 1) = 27.
- 📊 Sum of the first four terms in an arithmetic sequence is calculated as: (1 + 13) / 2 * 4 = 28.
- 📈 Sum of the first four terms in a geometric sequence is: 1 * (1 - 3^4) / (1 - 3) = 40.
Q & A
What are the two types of sequences discussed in the video?
-The two types of sequences discussed in the video are arithmetic sequences and geometric sequences.
What is the common difference in an arithmetic sequence?
-The common difference in an arithmetic sequence is the constant amount by which each term is greater than the previous term. For example, in the sequence 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, the common difference is 4.
How do you find the nth term of an arithmetic sequence?
-To find the nth term of an arithmetic sequence, you use the formula: nth term = first term + (n - 1) * common difference.
What is the common ratio in a geometric sequence?
-The common ratio in a geometric sequence is the constant factor by which each term is multiplied to get the next term. For example, in the sequence 1, 3, 9, 27, 81, the common ratio is 3.
How do you determine the nth term of a geometric sequence?
-The nth term of a geometric sequence is determined by the formula: nth term = first term * (common ratio)^(n - 1).
What is the formula for finding the sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic sequence?
-The formula for finding the sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic sequence is: sum = (n / 2) * (first term + nth term).
How do you calculate the sum of the first n terms of a geometric sequence?
-The sum of the first n terms of a geometric sequence is calculated using the formula: sum = first term * (1 - (common ratio)^n) / (1 - common ratio), provided the common ratio is not 1.
What is the difference between the operations used in arithmetic and geometric sequences?
-In arithmetic sequences, the operations used are addition and subtraction, while in geometric sequences, the operations are multiplication and division.
Can you provide an example of finding the fourth term of an arithmetic sequence given the first term and the common difference?
-Sure, if the first term is 1 and the common difference is 4, the fourth term is calculated as: 1 + (4 - 1) * 4 = 1 + 3 * 4 = 1 + 12 = 13.
How would you find the sum of the first four terms of a geometric sequence with a first term of 1 and a common ratio of 3?
-The sum of the first four terms of this geometric sequence is: 1 * (1 - 3^4) / (1 - 3) = 1 * (1 - 81) / (-2) = 40.
What is the significance of the common difference and common ratio in their respective sequences?
-The common difference in an arithmetic sequence determines the amount by which each term increases, while the common ratio in a geometric sequence determines the factor by which each term is multiplied. Both are essential for identifying the pattern and calculating future terms or sums in their respective sequences.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
MATH 10 : DIFFERENTIATING GEOMETRIC SEQUENCE FROM AN ARITHMETIC SEQUENCE (Taglish)

Introduction to Sequences

GCSE Maths - Types of Number Sequences - Arithmetic vs Geometric
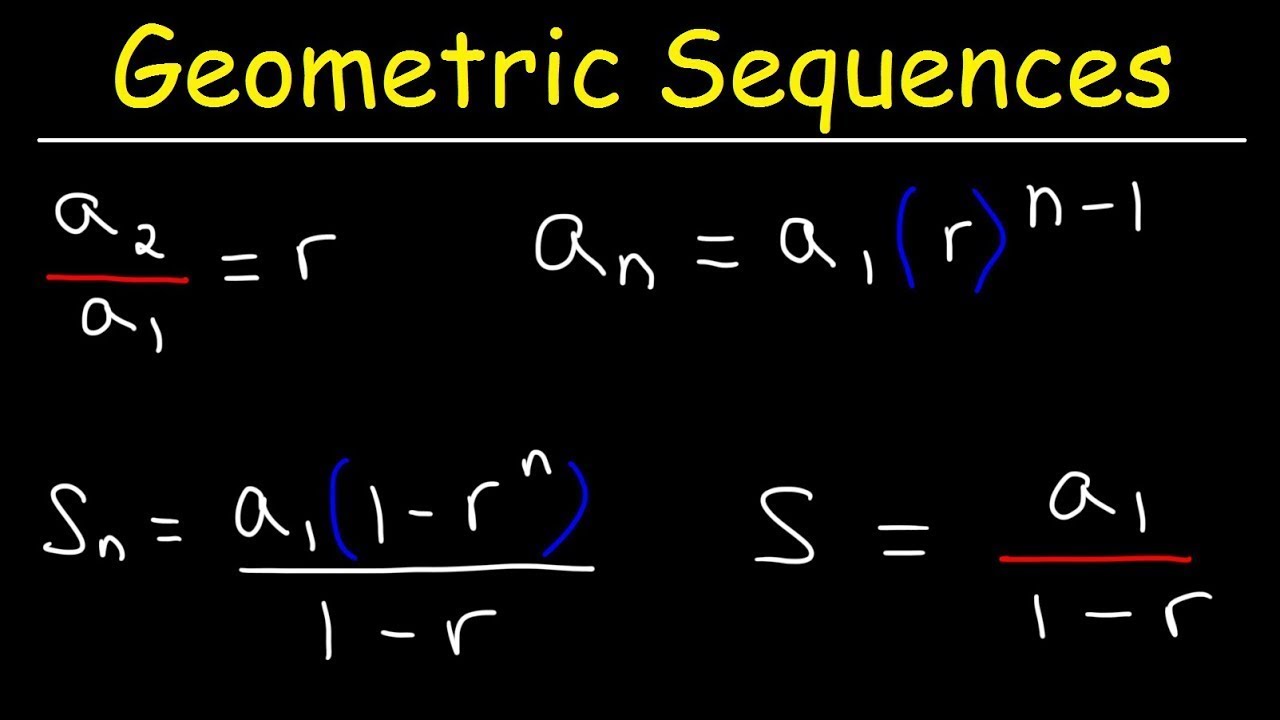
Geometric Series and Geometric Sequences - Basic Introduction

Pembahasan BARISAN DAN DERET (Aritmetika & Geometri) KELAS 11 | #MatematikAsik

Arithmetic vs Geometric Sequences
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
