DNA - Ácidos Nucleicos - Compostos Orgânicos - Aula Completa
Summary
TLDRIn this engaging DNA class by Samuel Cunha, the basics of nucleic acids, DNA, and RNA are explored. The video explains the structure and function of DNA, its relationship with chromosomes and genes, and the significance of nucleotides in the formation of DNA. Key concepts like purines and pyrimidines, the structure of the double helix, and the bonds between nitrogenous bases are covered. The lesson also dives into DNA replication, the semiconservative model, and the importance of enzymes like helicase and DNA polymerase. With practical tips for remembering key details, this class offers a clear and comprehensive introduction to molecular biology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Nucleic acids are large molecules that have an acidic character and were first discovered inside the nucleus. They play a key role in storing and transmitting genetic information.
- 😀 DNA and RNA are two types of nucleic acids, with DNA storing genetic information and RNA being involved in protein synthesis.
- 😀 DNA is a long molecule that coils into a double helix and can condense into chromosomes. Chromatin is the combination of DNA and histone proteins.
- 😀 A gene is a portion of DNA that stores the information required to produce a protein, and it consists of a specific sequence of nucleotides.
- 😀 DNA is a polymer made of smaller repeating monomers called nucleotides, which are made up of a phosphate group, a sugar (pentose), and a nitrogenous base.
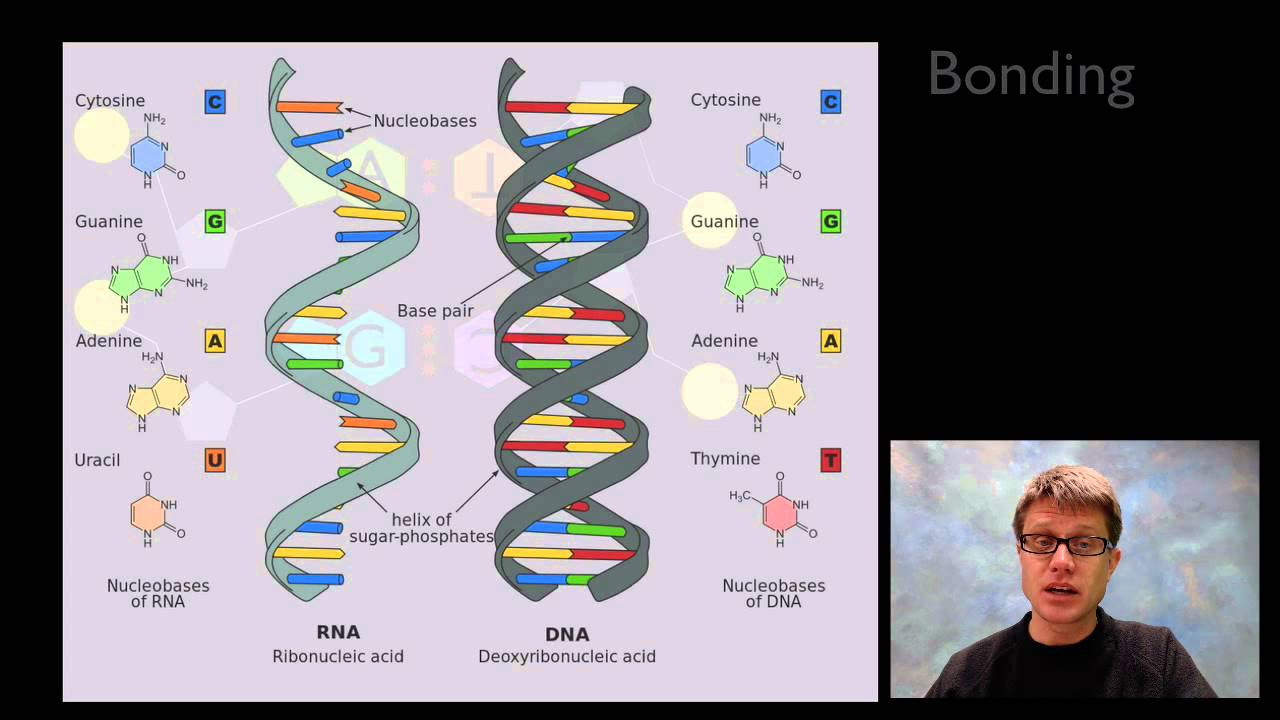
- 😀 The two main types of pentose sugars in nucleic acids are deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. This difference gives each molecule its respective name.
- 😀 There are five nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids: guanine (G), adenine (A), cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Thymine is found in DNA, while uracil is found in RNA.
- 😀 Nitrogenous bases are classified as purines (guanine and adenine) and pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, and uracil). Purines have two rings, while pyrimidines have one.
- 😀 In DNA, guanine pairs with cytosine (G-C), and adenine pairs with thymine (A-T), with hydrogen bonds connecting them. G-C pairs have three hydrogen bonds, making them stronger than the A-T pairs, which have two.
- 😀 DNA strands are antiparallel, meaning they run in opposite directions. The two strands are linked by phosphodiester bonds and hydrogen bonds between complementary nitrogenous bases.
- 😀 DNA replication is semiconservative, meaning each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. The process is facilitated by enzymes like helicase and DNA polymerase.
Q & A
What are nucleic acids and why are they called so?
-Nucleic acids, like DNA and RNA, are organic molecules that were first discovered inside the nucleus of cells. They are called 'nucleic' because they were found in the nucleus, and 'acids' because these molecules exhibit acidic properties.
What is the main function of nucleic acids?
-The main function of nucleic acids, such as DNA, is to store genetic information and transmit it. This information influences various traits such as muscle predisposition, hair color, height, and more.
How does DNA relate to chromosomes, genes, and chromatin?
-DNA is a long molecule that coils around proteins called histones to form chromatin. As DNA continues to condense, it forms chromosomes. A gene is a segment of DNA that contains the instructions to produce a protein.
What is a nucleotide and what components does it consist of?
-A nucleotide is the basic building block of DNA. It consists of three components: a phosphate group, a pentose sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA), and a nitrogenous base.
What are the differences between DNA and RNA in terms of structure?
-The main difference between DNA and RNA is the pentose sugar. DNA contains deoxyribose, while RNA contains ribose. Additionally, DNA uses the base thymine, while RNA uses uracil.
What are the nitrogenous bases in DNA and how are they classified?
-The nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). They are classified as purines (A and G) and pyrimidines (C and T), with purines having two rings and pyrimidines having one ring.
What is the significance of Chargaff's rule?
-Chargaff's rule states that in a DNA molecule, the amount of adenine (A) equals the amount of thymine (T), and the amount of cytosine (C) equals the amount of guanine (G). This is due to the base pairing rules of DNA.
How are the two strands of DNA held together?
-The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases: adenine bonds with thymine, and guanine bonds with cytosine. These bonds are crucial for the double-helix structure of DNA.
What is the significance of DNA replication and what process ensures it is accurate?
-DNA replication is crucial for cell division. The process is semiconservative, meaning that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. Enzymes like helicase and DNA polymerase play key roles in ensuring accuracy during replication.
What does it mean for DNA strands to be antiparallel?
-DNA strands are antiparallel, meaning that one strand runs in the 5' to 3' direction while the other runs in the 3' to 5' direction. This orientation is important for proper base pairing and replication.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)