Me Salva! CIT11 - Citologia - Substâncias orgânicas - Ácidos nucleicos
Summary
TLDRIn this biology class, the focus is on nucleic acids, specifically DNA and RNA molecules. The lesson explains the structure of DNA, composed of two polynucleotide chains, and RNA, which is single-stranded. Key concepts covered include nucleotides, their subunits (phosphate, sugar, nitrogenous base), and differences between the sugars in DNA (deoxyribose) and RNA (ribose). The script also explores the types of nitrogenous bases, their functions, and the roles of different RNA types (messenger RNA, transfer RNA, and ribosomal RNA) in protein synthesis. The overall theme centers on the relationship between DNA, RNA, and protein formation.
Takeaways
- 😀 DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, and RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. Both are types of nucleic acids with distinct structures and functions.
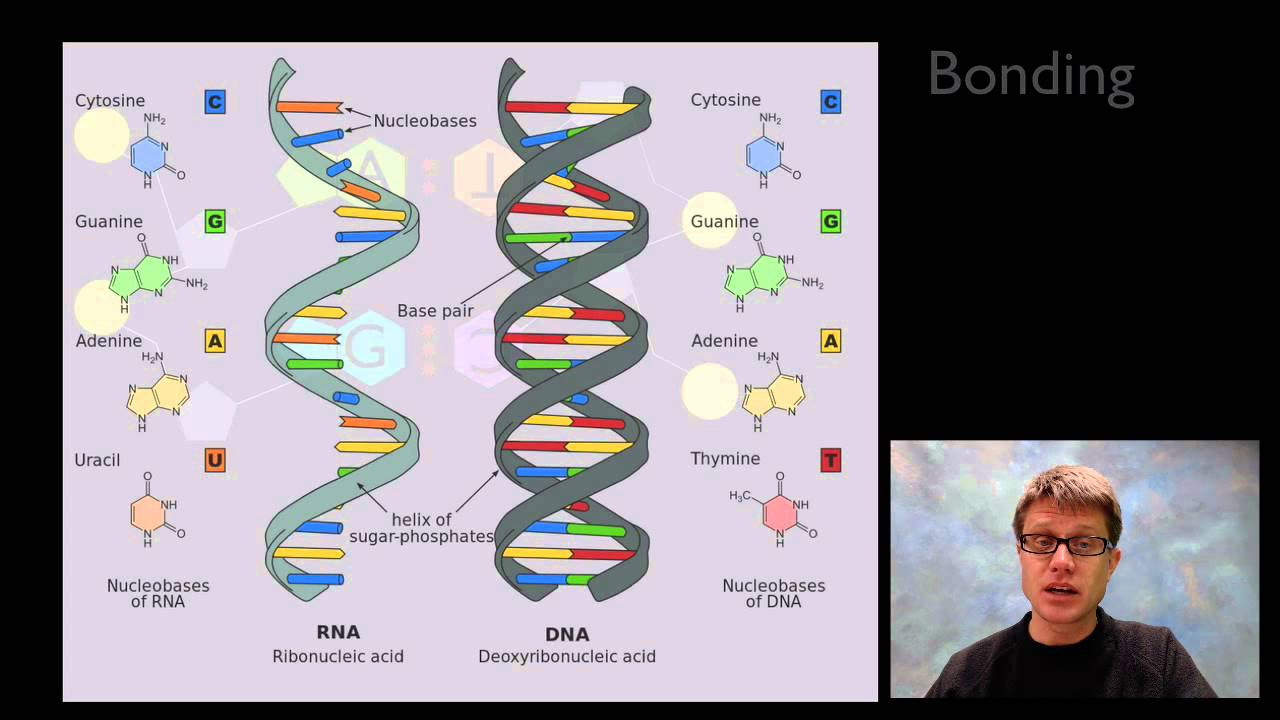
- 😀 DNA is double-stranded, forming a double helix, whereas RNA is single-stranded.
- 😀 Both DNA and RNA are polymers made up of smaller molecules called nucleotides, which consist of a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
- 😀 The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose (lacking one oxygen atom), whereas in RNA, the sugar is ribose.
- 😀 Nitrogenous bases in DNA include adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil.
- 😀 Nucleotides are made up of purine bases (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidine bases (thymine, cytosine, and uracil). Purine bases have two rings, while pyrimidine bases have one ring.
- 😀 The primary function of DNA is to store and retain the genetic information for the body.
- 😀 RNA plays a key role in transcription and translation, acting as an intermediary between DNA and the production of proteins.
- 😀 There are different types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), each with specific roles in protein synthesis.
- 😀 Messenger RNA carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where it is used to produce proteins. Transfer RNA helps deliver amino acids to the ribosome for protein assembly.
- 😀 Ribosomal RNA is a component of the ribosome and works with proteins to form the structure responsible for protein production.
Q & A
What are the two types of nucleic acids discussed in the class?
-The two types of nucleic acids discussed are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
What is the difference between the structure of DNA and RNA?
-DNA is double-stranded, with two polynucleotide chains, while RNA is single-stranded.
What is a polymer, and how is it related to DNA and RNA?
-A polymer is a large molecule made up of smaller units called monomers. DNA and RNA are polymers made up of nucleotides.
What are nucleotides composed of?
-Nucleotides are composed of three subunits: a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA), and a nitrogenous base.
What is the main difference between the sugars in DNA and RNA?
-The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, which lacks one oxygen atom compared to the sugar in RNA, which is ribose.
What are the nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA, and how do they differ?
-In DNA, the nitrogenous bases are adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil, so the nitrogenous bases are adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine.
What are purine and pyrimidine bases, and how do they differ?
-Purine bases (adenine and guanine) have two rings, while pyrimidine bases (thymine, cytosine, and uracil) have a single ring.
What is the function of DNA in the body?
-The function of DNA is to store and retain all the genetic information necessary for the body's characteristics and functions.
What is the role of RNA in the body?
-RNA plays a crucial role in transcription and translation, acting as an intermediary between DNA and protein synthesis.
What are the different types of RNA, and what are their functions?
-The different types of RNA include messenger RNA (mRNA), which carries the genetic code for protein synthesis; transfer RNA (tRNA), which transports amino acids to the ribosome; and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), which helps form the ribosome itself.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

DNA e RNA (Ácidos Nucleicos) - LEIA A DESCRIÇÃO

Biologia Molecular – Ácidos Nucleicos - Biologia Básica - Me Salva! Saúde

6-1 Nucleic Acids and Nucleotides (Cambridge AS & A Level Biology, 9700)

Types of Organisms, Cell Composition, excerpt 2 | MIT 7.01SC Fundamentals of Biology
Biologia Molecular - Introdução - Biologia Básica - Me Salva! Saúde
Nucleic Acids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)