Logistics Management - Internal Logistics
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the focus is on logistics management, specifically internal logistics. It covers key topics such as material flow planning, information flow planning, and storage conditions. The video discusses various tools for material handling like forklifts, trolleys, and human labor, and emphasizes the importance of effective information flow through methods like emails and ERP systems. It highlights best practices like FIFO (First-In, First-Out) for inventory management and ergonomically designed storage racks for human efficiency. Additionally, the video stresses the need for proper inventory levels, shelf-life management, and safety considerations, especially for hazardous materials and food items.
Takeaways
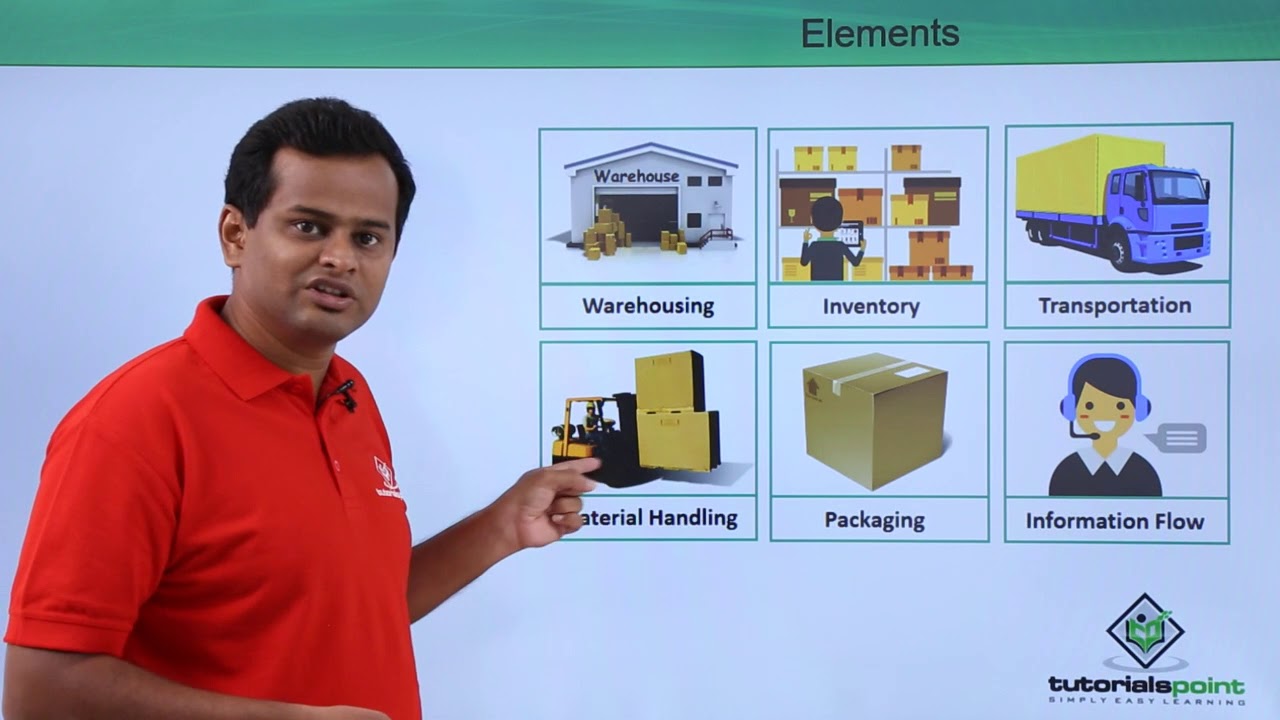
- 😀 Material flow planning involves using various assets like hands, forklifts, and trolleys depending on the material's weight and packaging.
- 😀 Information flow can be managed through human interaction, emails, portals, or ERP systems like SAP to reduce communication errors and facilitate decision-making.
- 😀 Storage conditions require an understanding of FIFO (First-In, First-Out) to manage inventory effectively and reduce waste.
- 😀 FIFO helps with complaint management, sorting, and shelf-life management, ensuring that older products are used first.
- 😀 Ergonomically designed racks and equipment improve efficiency and reduce strain on workers handling materials in logistics.
- 😀 Proper storage conditions are essential to prevent risks like fire or damage to materials, especially hazardous ones.
- 😀 Inventory management should involve setting both minimum and maximum levels to avoid stockouts or excess stock, which could lead to losses.
- 😀 Understanding inventory balance is key to ensuring customer satisfaction while minimizing losses.
- 😀 Shelf-life management is particularly important for products like food items, where expiration dates directly impact safety and quality.
- 😀 Failing to manage shelf-life can result in dangerous consequences, including harm to human and animal life due to expired products.
Q & A
What are the three key areas of logistics management discussed in the video?
-The three key areas of logistics management discussed are material flow planning, information flow planning, and storage conditions.
What are some examples of assets used for material handling in material flow planning?
-Examples of assets used for material handling include manual handling, forklifts, and trolleys, depending on the material's weight and packaging.
How can information flow be managed effectively in logistics?
-Information flow can be managed effectively through human interaction, emails, portals, or ERPs like SAP to ensure clear communication and reduce errors.
What is the advantage of using FIFO (First-In, First-Out) in storage management?
-FIFO ensures proper stock rotation, helps with shelf-life management, minimizes sorting effort, and reduces resource wastage during complaint management.
Why are ergonomically designed racks important in logistics?
-Ergonomically designed racks are important because they minimize physical strain on workers who may handle materials for long hours, improving efficiency and reducing fatigue.
What are the potential risks if hazardous materials are not stored properly?
-Improper storage of hazardous materials can lead to serious risks such as fires or other unintended safety issues, which can disrupt the value addition process.
What role does inventory play in logistics, and why are minimum and maximum levels important?
-Inventory plays a crucial role in ensuring that there is enough stock to meet demand. Maintaining minimum and maximum levels helps avoid customer shortages or excessive losses due to overstocking.
Why is shelf-life management critical in storage conditions?
-Shelf-life management is critical, especially for perishable items like food, because expired goods can become harmful or even dangerous, causing serious health risks to consumers.
What could happen if the basic minimum inventory level is not maintained?
-If the basic minimum inventory level is not maintained, customers may experience stockouts, leading to dissatisfaction or loss of business.
What consequences can occur if the maximum inventory level is not controlled?
-If the maximum inventory level is not controlled, it may lead to unnecessary costs, overstocking, and storage issues, resulting in financial losses.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Manajemen Logistik #1 Pengantar
Logistics Management - Introduction

PELAYANAN LOGISTIK DALAM MANAJEMEN PERKANTORAN DAN LAYANAN BISNIS (PART 1)

Manajemen Logistik

LOGISTICS VS. SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT| WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE?| COMPARISON| DEFINITION| EXPLANATION|

JENIS LAYANAN LOGISTIK (Materi Dasar Program Keahlian MPLB, Elemen 8 Bag. 2)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
