ATP-ADP ENERGY CYCLE
Summary
TLDRThis video by Seher from Easy Peasy explores the ATP-ADP energy cycle, detailing how ATP is produced in mitochondria and utilized in the cytoplasm. It explains the processes of phosphorylation, highlighting oxidative phosphorylation as the primary method of ATP production, and substrate-level phosphorylation as a secondary method. The video also covers the hydrolysis of ATP, its conversion into ADP and inorganic phosphate, and the factors influencing energy release. Through engaging visuals and examples, the video underscores the significance of the ATP-ADP cycle in cellular metabolism and energy management.
Takeaways
- 🔋 ATP is produced in the mitochondria and serves as the energy currency of the cell.
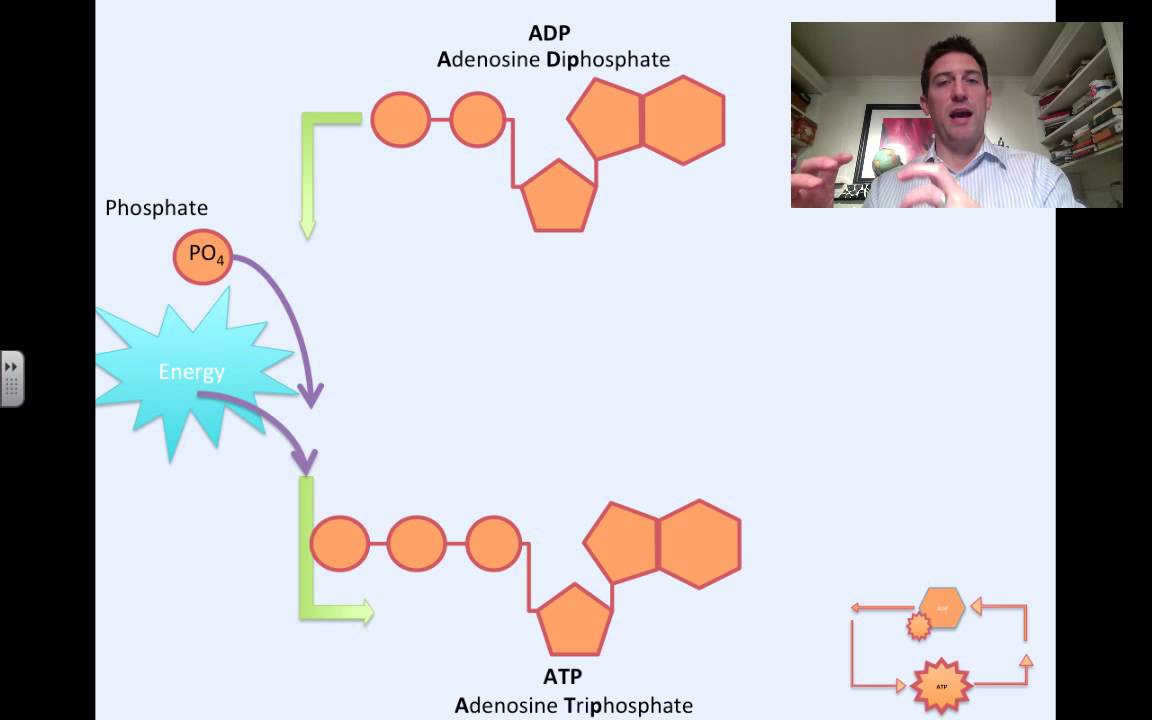
- 🔄 The ATP-ADP energy cycle involves the conversion of ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate, releasing energy.
- ⚡ Phosphorylation is the process that converts ADP to ATP, which requires energy (endergonic reaction).
- 🌌 There are two main types of phosphorylation: oxidative phosphorylation (90% ATP production) and substrate-level phosphorylation (10% ATP production).
- 🏋️♂️ Substrate-level phosphorylation is crucial during intense muscle exertion when ATP demand exceeds mitochondrial production.
- 🧬 Glycolysis, a cytoplasmic process, is where substrate-level phosphorylation occurs and generates ATP.
- ⚙️ The electron transport chain facilitates oxidative phosphorylation by creating a proton gradient in the mitochondria.
- 💧 ATP hydrolysis is an exergonic reaction, breaking ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate, releasing energy for cellular activities.
- 🔗 Magnesium ions play a significant role in stabilizing ATP and ADP during metabolic processes.
- 🔍 Energy production from ATP hydrolysis can vary significantly based on cellular conditions, with values around -52 kJ/mol in human red blood cells.
Q & A
What is the ATP-ADP energy cycle?
-The ATP-ADP energy cycle is a process through which cells convert ATP (adenosine triphosphate) into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and inorganic phosphate, releasing energy for cellular activities, and then recycle ADP back into ATP.
Where is ATP primarily produced in the cell?
-ATP is primarily produced in the mitochondria, which is often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell.
What are the two main types of phosphorylation that produce ATP?
-The two main types of phosphorylation are oxidative phosphorylation, which produces 90% of ATP, and substrate-level phosphorylation, which produces 10%.
How does oxidative phosphorylation occur?
-Oxidative phosphorylation occurs through the electron transport chain, where a gradient of protons and electrons is created, driving ATP synthesis via ATP synthase.
What is substrate-level phosphorylation and how does it work?
-Substrate-level phosphorylation involves the direct transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate to ADP to form ATP, commonly occurring during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
What happens during ATP hydrolysis?
-During ATP hydrolysis, ATP is converted into ADP and inorganic phosphate, releasing energy that can be used for various cellular processes.
What is the significance of magnesium ions in ATP and ADP?
-Magnesium ions stabilize ATP and ADP, helping to prevent unwanted bonding between oxygen atoms in these molecules and assisting in the conversion of ADP back into ATP.
What is the standard Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) for ATP hydrolysis?
-The standard ΔG for ATP hydrolysis typically ranges from -28 to -34 kJ/mol, but can be as low as -52 kJ/mol in specific conditions, such as in human red blood cells.
How does ATP get recycled in the mitochondria?
-In the mitochondria, ADP is re-phosphorylated back into ATP using inorganic phosphate and the enzyme ATP synthase, completing the energy cycle.
Why is ATP referred to as the energy currency of the cell?
-ATP is referred to as the energy currency of the cell because it is the primary molecule used for energy transfer in biological systems, fueling various cellular processes.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)