Composition of Functions - Grade 11 - General Mathematics
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the teacher explains the concept of composite functions, denoted as f(g(x)) or f circle of G of X. The video uses f(x) = 3x - 5 and g(x) = x^2 + 2 to demonstrate how to evaluate f(g(2)) and g(f(-1)). The process involves substituting g(x) into f(x) for the former, and f(x) into g(x) for the latter, with calculations resulting in f(g(2)) = 13 and g(f(-1)) = 66. The teacher emphasizes the importance of understanding the order of functions in composite notation.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is about composite functions or function composition.
- 🔢 The notation for composite functions is read as 'f circle of G of X' or 'F composite G of X', which is written as 'f(g(x))'.
- 💡 In 'f(g(x))', the function 'f' comes first, making 'g(x)' the input to function 'f'.
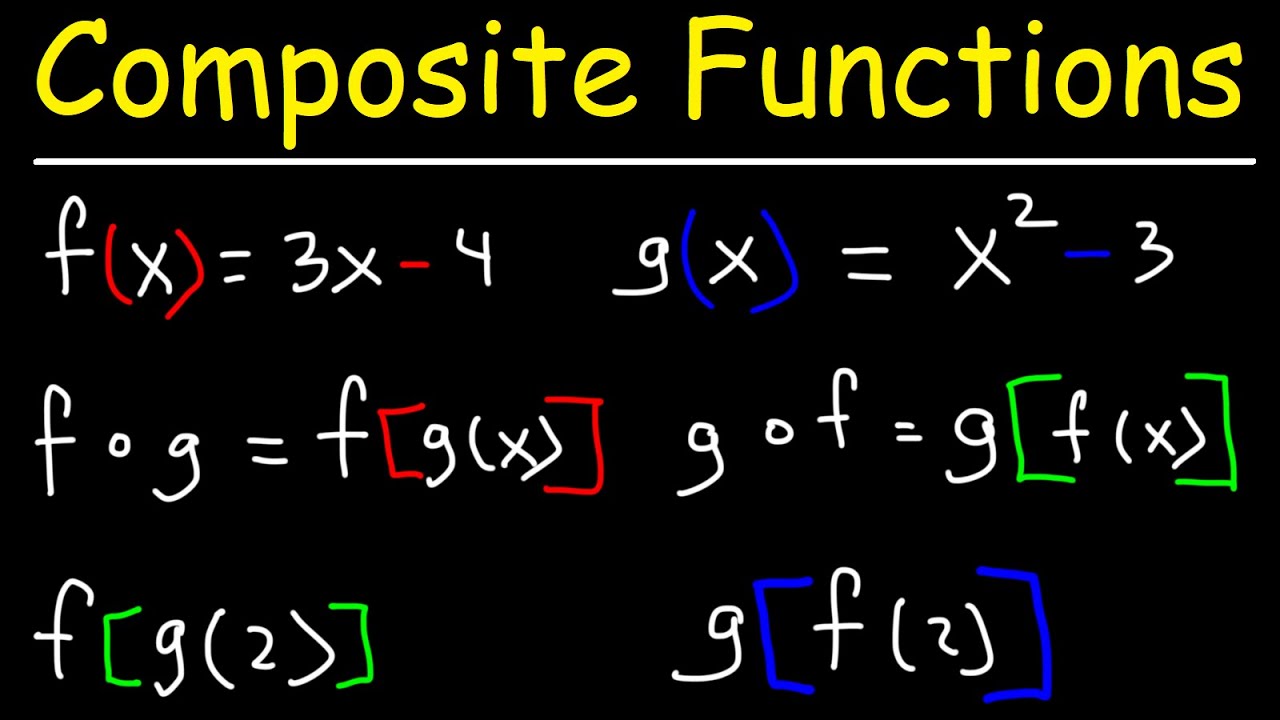
- 📐 The problem involves evaluating 'f(g(2))' and 'g(f(-1))' given two functions: f(x) = 3x - 5 and g(x) = x^2 + 2.
- 🧮 For 'f(g(2))', substitute 'x^2 + 2' for 'x' in the function 'f', resulting in '3(x^2 + 2) - 5'.
- 🔄 Simplify 'f(g(2))' to '3(2^2 + 2) - 5', which equals '3(4 + 2) - 5' or '3*6 - 5', resulting in 18 - 5 = 13.
- 🔄 For 'g(f(-1))', substitute '3x - 5' for 'x' in the function 'g', resulting in '(3x - 5)^2 + 2'.
- 🧮 Simplify 'g(f(-1))' to '(3*(-1) - 5)^2 + 2', which equals '(-3 - 5)^2 + 2' or '(-8)^2 + 2', resulting in 64 + 2 = 66.
- 📌 The video emphasizes that the order of functions in composite notation determines which function is the input.
- 🎯 The video aims to teach viewers how to evaluate composite functions and encourages them to like, subscribe, and hit the bell for updates.
Q & A
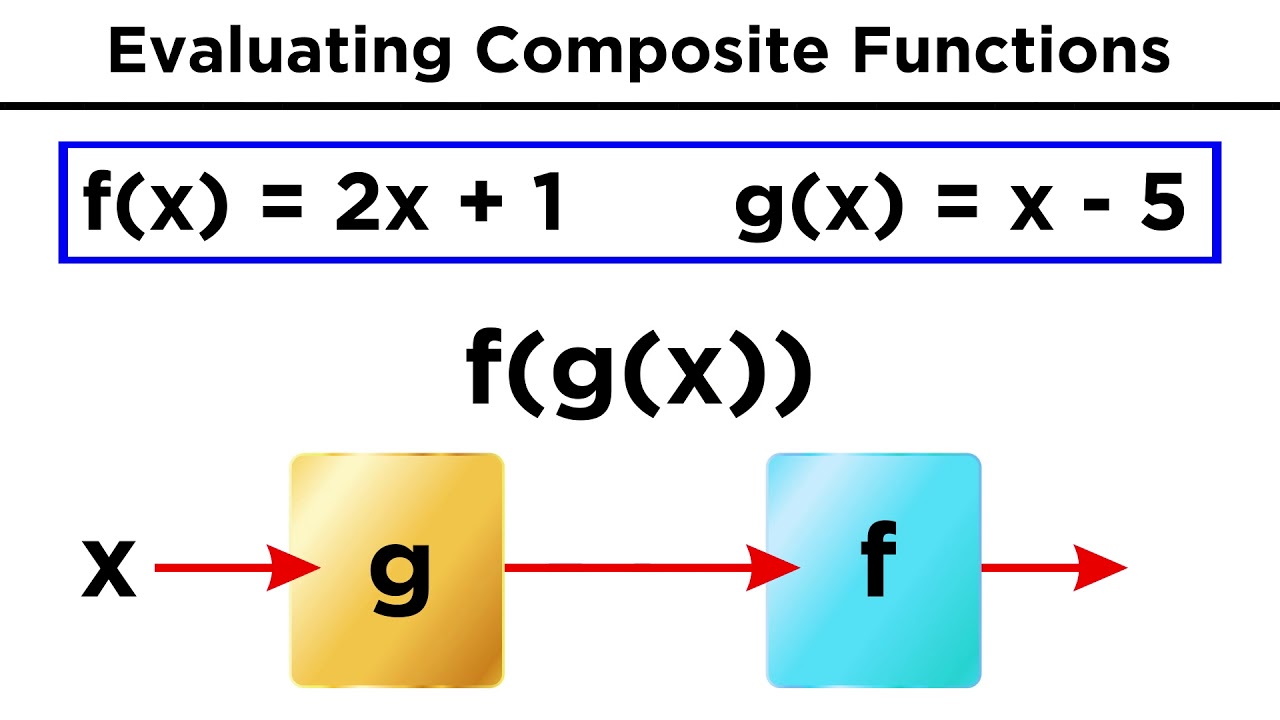
What is a composite function?
-A composite function is a function that is formed by applying one function to the result of another function. It is denoted as f(g(x)) or f circle of g of x.
How is f(g(x)) different from g(f(x))?
-f(g(x)) means that the function g(x) is used as the input for the function f, while g(f(x)) means that the function f(x) is used as the input for the function g. The order of the functions matters.
What are the given functions in the transcript?
-The given functions are f(x) = 3x - 5 and g(x) = x^2 + 2.
How is f(g(x)) evaluated when x is replaced by 2?
-To evaluate f(g(2)), you first calculate g(2) which is 2^2 + 2 = 6, then substitute this into f(x) to get f(6) = 3*6 - 5 = 18 - 5 = 13.
What is the result of f(g(2))?
-The result of f(g(2)) is 13.
How is g(f(x)) evaluated when x is replaced by -1?
-To evaluate g(f(-1)), you first calculate f(-1) which is 3*(-1) - 5 = -8, then substitute this into g(x) to get g(-8) = (-8)^2 + 2 = 64 + 2 = 66.
What is the result of g(f(-1))?
-The result of g(f(-1)) is 66.
What does the notation f circle of g of x mean?
-The notation f circle of g of x means the composition of function g with function f, which is read as 'f composite g of x'.
Why is it important to follow the order of functions when evaluating composite functions?
-The order of functions is important because it determines which function's output becomes the input for the other function. Changing the order can lead to different results.
What is the significance of the variable x being replaced by another function in composite functions?
-In composite functions, replacing the variable x with another function allows for the application of one function's output to another function, which is the core concept of function composition.
How can one avoid confusion between the notations f(g(x)) and g(f(x))?
-To avoid confusion, remember that the function that comes first in the notation is the outer function, and the one that comes second is the inner function whose result is used as the input for the outer function.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
Composite Functions
Manipulating Functions Algebraically and Evaluating Composite Functions
Composite Function | General Mathematics @MathTeacherGon
Composition of Function by Ma'am Ella Barrun
Reconocer una composición de funciones | Khan Academy en Español

Verifying inverse functions by composition | Mathematics III | High School Math | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
