Composite Function | General Mathematics @MathTeacherGon
Summary
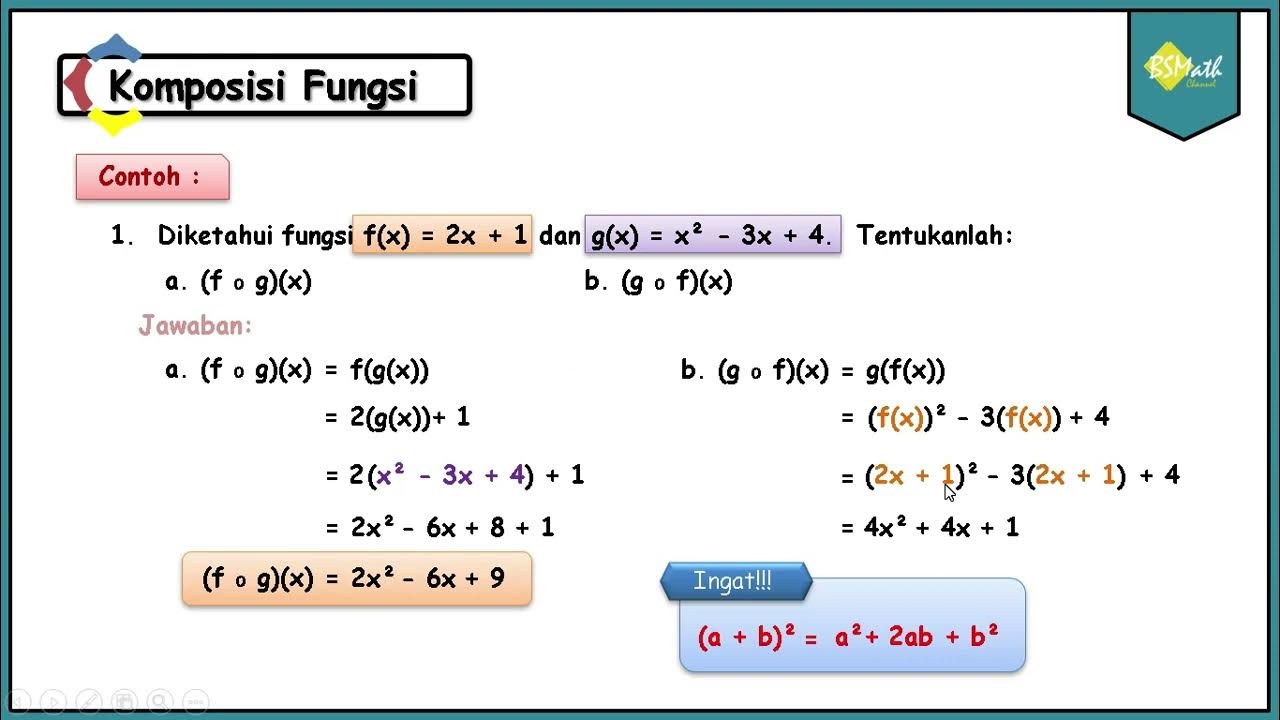
TLDRIn this educational video, the host, 'Teacher,' delves into the concept of function composition, a topic distinct from operational function evaluation due to its reliance on substitution. The video explains the process using two functions, f(x) = x^2 + 5x + 6 and g(x) = x + 2. Through step-by-step examples, the host demonstrates how to compute f(g(x)), g(f(x)), and specific values like f(g(4)), guiding viewers through the substitution and simplification process. The tutorial is designed to help viewers understand and perform function composition effectively.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video discusses the concept of function composition, which is a method of combining two functions to create a new function.
- 🔢 The functions used as examples are f(x) = x^2 + 5x + 6 and g(x) = x + 2, where f and g are the primary functions being composed.
- 🎯 The video explains how to find the composition of functions, specifically f(g(x)) and g(f(x)), by substituting one function into another.
- 📐 The process involves replacing the variable x in the function with the entire expression of the other function, demonstrating the substitution method.
- 🧮 The video provides a step-by-step calculation for f(g(x)) by substituting g(x) = x + 2 into f(x), resulting in a simplified expression.
- 📉 For g(f(x)), the process is reversed, with f(x) substituted into g(x), leading to another simplified expression.
- 📝 The video emphasizes the importance of simplifying expressions by combining like terms and using algebraic properties.
- 📈 An example with a specific value (f(g(4))) is used to demonstrate how to evaluate the composition of functions at a given point.
- 👨🏫 The presenter, Teacher, encourages viewers to practice and understand the concept of function composition, suggesting it's different from evaluating operational functions.
- 📢 The video concludes with a call to action for viewers to like, subscribe, and stay updated with the channel for more educational content.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is the composition of functions.
What are the two functions provided in the video?
-The two functions provided are f(x) = x^2 + 5x + 6 and g(x) = x + 2.
What does the notation 'f ∘ g' represent?
-The notation 'f ∘ g' represents the composition of the function f with the function g, which means applying g first and then f to the result.
How is the composition of functions different from evaluating operational functions?
-The composition of functions involves a lot of substitution, where one function is used as the input for another, which is different from evaluating operational functions where you directly substitute the variable.
What is the result of the composition f(g(x))?
-The result of the composition f(g(x)) is f(x + 2), which simplifies to x^2 + 9x + 20.
What is the result of the composition g(f(x))?
-The result of the composition g(f(x)) is g(x^2 + 5x + 6), which simplifies to x^2 + 5x + 8.
What is the value of f(g(4))?
-The value of f(g(4)) is 72, after evaluating g(4) to get 6 and then substituting 6 into f(x) to get f(6).
What is the process for evaluating a composition of functions?
-The process involves substituting the inner function into the outer function, simplifying the expression, and then evaluating if a specific input is given.
What is the significance of the distributive property in the context of the video?
-The distributive property is significant as it is used to expand and simplify the expressions when substituting and evaluating the compositions of functions.
How does the video script guide viewers through the process of function composition?
-The video script guides viewers step-by-step through the process of function composition by providing clear examples and explanations of how to substitute and simplify expressions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)