Pangkat dan Akar | Sifat 4: Aturan Pembagian Akar
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script focuses on the properties of square roots, explaining three key attributes: addition, subtraction, and multiplication of radicals. The instructor clarifies common mistakes, such as incorrectly adding radicals by combining both the coefficient and the radicand. The script also covers simplifying square roots and introduces the concept of dividing radicals with a non-negative radicand and a positive denominator. Practical examples, including mathematical expressions and biological growth rates, are used to illustrate these properties, aiming to enhance understanding and provide real-world applications.
Takeaways
- 📘 The video discusses the properties of square roots, specifically focusing on three key attributes.
- 🔢 The first property covered is the rule of addition under a square root, where like terms with the same radicand can be added together by summing their coefficients.
- ❌ A common mistake is adding the radicands themselves, which is incorrect and should be avoided.
- ➖ The second property is the rule of subtraction under a square root, which is similar to addition but involves subtracting the coefficients instead.
- ✅ The third property is about multiplication under a square root, allowing the separation of the square root into the multiplication of the individual square roots, given that both numbers are non-negative.
- 🚫 Negative numbers under a square root are not allowed when using the multiplication property, as it would lead to an undefined result.
- 🌱 An example is provided involving the growth of two types of algae, demonstrating the application of exponent rules in a biology context.
- 💡 The video suggests a method for comparing large exponential expressions without manual calculation by normalizing the base and then comparing the exponents.
- 📉 The conclusion from the algae growth example is that Alga type B has a larger population than Alga type A after a certain number of generations, highlighting the practical use of square root properties.
- 👨🏫 The presenter encourages viewers to rewatch the video for better understanding and to practice the problems provided to solidify their grasp of the material.
Q & A
What are the three properties of square roots discussed in the video?
-The video discusses three properties of square roots: 1) The addition rule, which allows for the calculation of square roots when the radicands are the same by simply adding the coefficients. 2) The subtraction rule, which is similar to the addition rule but involves subtracting the coefficients when the radicands are the same. 3) The multiplication rule, which states that when you have a square root of a product, you can separate it into the product of the square roots, provided that both numbers are non-negative.
How does the addition rule for square roots work?
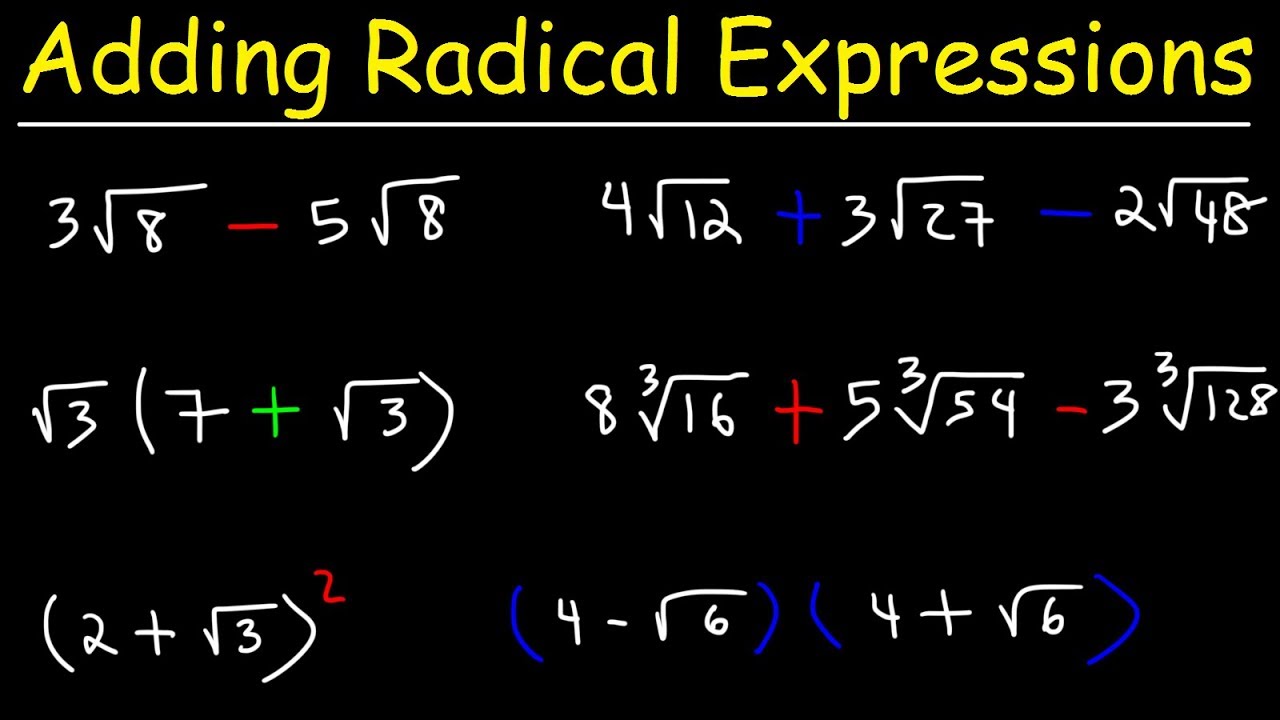
-The addition rule for square roots works by adding the coefficients in front of the square roots when the radicands are the same. For example, if you have 3√2 + 5√2, you add the coefficients 3 and 5 to get 8√2.
What is the mistake often made when adding square roots?
-A common mistake is adding the radicands themselves, not just the coefficients. For instance, incorrectly adding 2 + 2 to get 4 and then calculating 8√4, which is wrong because you should only add the coefficients, not the radicands.
Can all mathematical expressions with square roots be simplified?
-Not all mathematical expressions with square roots can be simplified. If the radicands are different, such as √3 and √5, they cannot be further simplified using the properties discussed.
What is the condition for using the multiplication rule for square roots?
-The multiplication rule for square roots can be used when both numbers under the square root are non-negative. Negative numbers are not allowed because the square root of a negative number is not defined in the set of real numbers.
How can you simplify the expression √0.64 using the properties of square roots?
-To simplify √0.64, first convert 0.64 to the fraction 64/100. Then, using the property of square roots, separate the square root into √64 / √100. Since √64 is 8 and √100 is 10, the expression simplifies to 8/10, which can be further reduced to 4/5.
What is the purpose of the multiplication rule for square roots?
-The multiplication rule for square roots is used to simplify the expression by reducing the value of the radicand or the number inside the square root, ideally getting it closer to one.
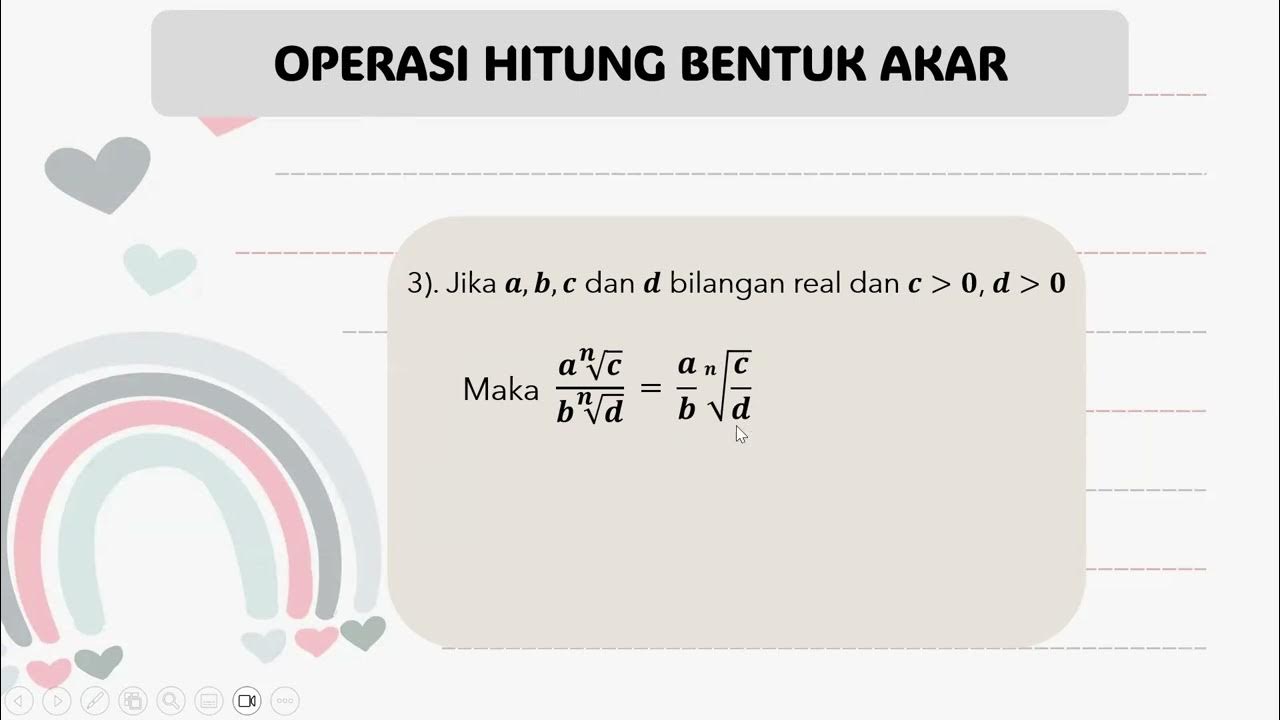
How does the division rule for square roots differ from the multiplication rule?
-The division rule for square roots involves separating the square root into the square root of the numerator and the square root of the denominator, similar to converting a fraction to a division expression. The key condition is that the numerator must not be negative, while the denominator must be positive, as division by zero is undefined.
What is an example of using the division rule to simplify a square root expression?
-An example of using the division rule is with the expression √2.25. Convert 2.25 to the fraction 225/100, then separate the square root into √225 / √100. Simplify √225 to 15 and √100 to 10, resulting in the simplified expression 15/10, which can be further reduced to 3/2.
How can you compare the population growth of two different algae species using the properties of exponents?
-You can compare the population growth by expressing the growth as powers of the same base and then comparing the exponents. For example, if one species grows as 3^20 and the other as 9^15, you can convert 9 to 3^2 and rewrite 9^15 as (3^2)^15, which simplifies to 3^30. Since 3^30 has a higher exponent, the species with this growth rate will have a larger population.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

BENTUK AKAR Kelas 10 Kurikulum Merdeka

Tips Mudah Menyederhanakan Bentuk Akar || Bab Bilangan Berpangkat (Part 2)
Adding and Subtracting Radical Expressions With Square Roots and Cube Roots

SIMPLIFICACIÓN DE EXPRESIONES CON RADICALES - Ejercicio 1

Komposisi Fungsi Part 1 - Operasi Aljabar Pada Fungsi [ Matematika Wajib Kelas X ]
Asinkronus Topik Bentuk Akar W 2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
