What is SCADA, How SCADA Works, Components, Architecture & Applications. SCADA Tutorial
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, which allow industries to monitor and control processes remotely. It explains the key components of SCADA, including field instruments, control systems like PLCs and RTUs, communication layers, and operator control rooms. The video breaks down how SCADA systems are structured into four main layers: field instrumentation, control, communication, and monitoring/control. SCADA systems collect real-time data, process it, and provide operators with the ability to monitor and manage processes efficiently, enhancing productivity and safety in industrial environments.
Takeaways
- 🖥️ SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, used to monitor and control industrial processes from a central location.
- ⚙️ Supervisory control allows operators to manage operations remotely, such as starting/stopping pumps or opening/closing valves.
- 📊 Data acquisition involves collecting real-time data from sensors and field instruments, like temperature, flow, or pressure readings.
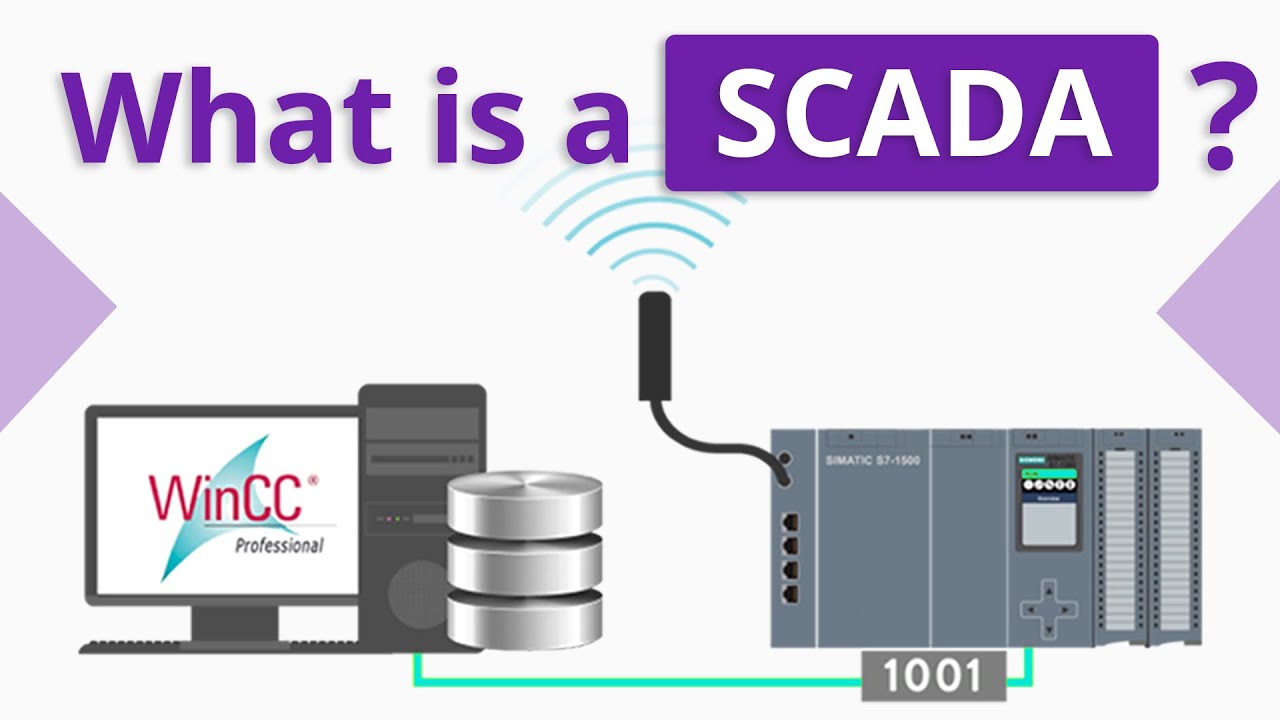
- 💻 SCADA is not just software; it is a complete system including hardware, software, communication networks, and human-machine interfaces (HMIs).
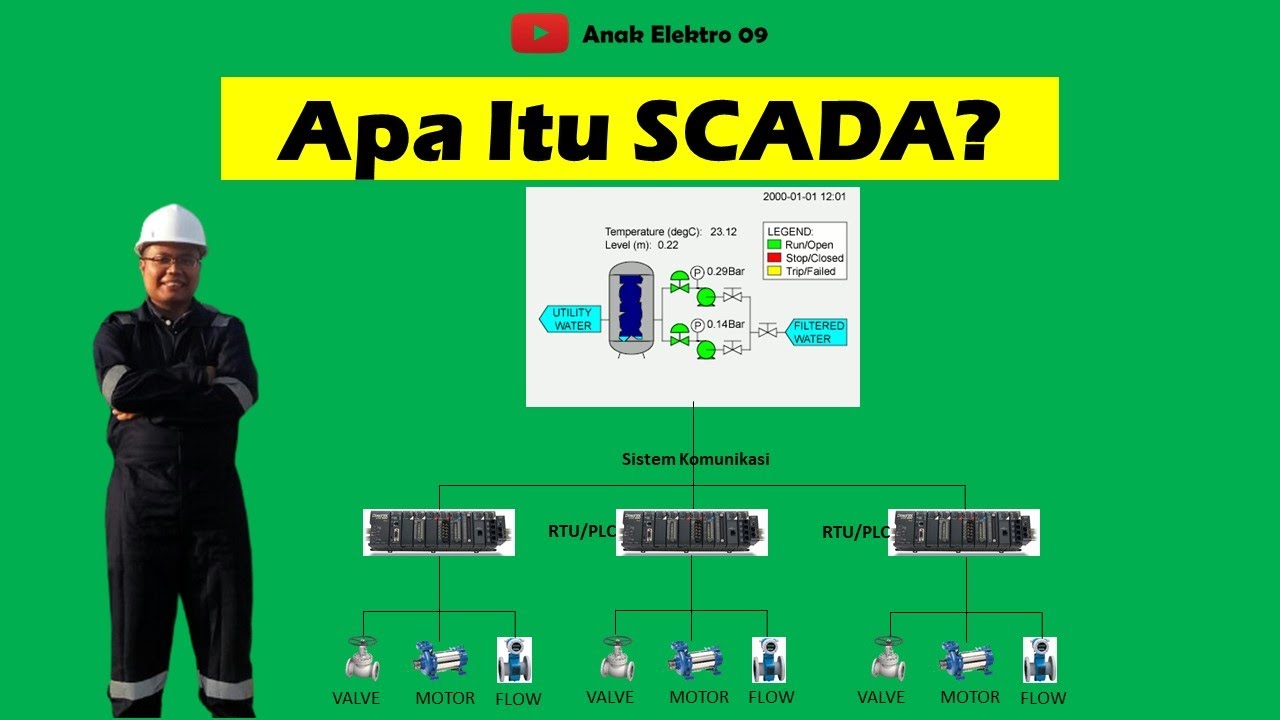
- 🏗️ A SCADA system is structured into four main layers: field layer, control layer, communication layer, and monitoring/control layer.
- 🌡️ The field instrumentation layer contains sensors and transmitters that continuously measure key process variables.
- 🔗 The control layer consists of RTUs or PLCs that gather sensor data, process it, and send control signals to the SCADA system.
- 📡 The communication layer transmits data between field controllers and the central SCADA system using wired or wireless networks.
- 📺 The monitoring and control layer displays live data, allows remote control of devices, acknowledges alarms, and provides historical trend analysis.
- 🎯 SCADA enables quick response to process abnormalities, such as low pressure alerts, ensuring efficient and safe industrial operations.
- 📚 The video also highlights online courses for beginners and professionals to upskill in instrumentation and control systems, making learning accessible and affordable.
Q & A
What does SCADA stand for and what is its purpose?
-SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. It is a system used to monitor and control industrial processes from a central location, allowing operators to supervise and control operations remotely.
What are the key components of a SCADA system?
-A SCADA system consists of four key components: field instruments (sensors and transmitters), controllers (RTUs or PLCs), a communication network, and the monitoring/control layer, which includes the SCADA software and human-machine interfaces.
How does the field instrumentation layer function in SCADA?
-The field instrumentation layer is the first layer of a SCADA system and consists of sensors and transmitters installed on the process. These devices continuously measure process variables such as temperature, pressure, flow, and level, and send the data to the control layer.
What role do RTUs and PLCs play in a SCADA system?
-RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) and PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) form the control layer in a SCADA system. They receive data from field sensors, process it, apply any necessary control logic (like turning a pump on or off), and then send the control signals to the SCADA system.
How is data transmitted from the field devices to the control room in a SCADA system?
-Data is transmitted through the communication layer, which acts as a data highway between the field devices (RTUs or PLCs) and the central SCADA system. This communication can occur via wired or wireless networks such as Ethernet, fiber optics, GSM, or satellite.
What is the purpose of the monitoring and control layer in SCADA?
-The monitoring and control layer is the topmost layer of a SCADA system. It is where the collected data from the field is displayed, analyzed, and acted upon. Operators use this layer to monitor live data, control devices, acknowledge alarms, and view historical trends for analysis and troubleshooting.
Can SCADA be considered just software?
-No, SCADA is not just software. It is a complete system made up of hardware, software, communication networks, and human-machine interfaces. The software is only one part of the entire setup that enables remote monitoring and control of industrial processes.
What happens if there is a drop in pressure in a SCADA-monitored system?
-If there is a drop in pressure, the sensor detects the change, the PLC processes the data, and the communication system sends it to the SCADA. The operator then sees a low-pressure alarm on the screen and can take immediate action to address the issue.
Who can benefit from SCADA training courses?
-SCADA training courses are designed for beginners, students, technicians, engineers, and working professionals who want to build or strengthen their understanding of instrumentation and control systems, including SCADA.
Why is it important for industries to use SCADA systems?
-SCADA systems allow industries to monitor and control processes from remote locations, improving operational efficiency, reducing manual intervention, ensuring real-time monitoring, and enabling quick responses to any abnormalities or process disruptions.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)