What is SCADA?
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth exploration of SCADA systems, which combine software and hardware to supervise and control industrial processes remotely. It outlines the historical evolution from manual controls to advanced automation, highlighting significant developments like telemetry and open system architectures. Today's SCADA systems, equipped with modern IT standards like SQL databases, enable real-time data access and enhanced operational efficiency. The video emphasizes the importance of interoperability among various vendors, improving troubleshooting and compliance, and invites viewers to further their skills in PLC programming at realpars.com.
Takeaways
- 😀 SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, and it encompasses both software and hardware components.
- 🔧 SCADA systems allow for real-time supervision and control of industrial processes from both local and remote locations.
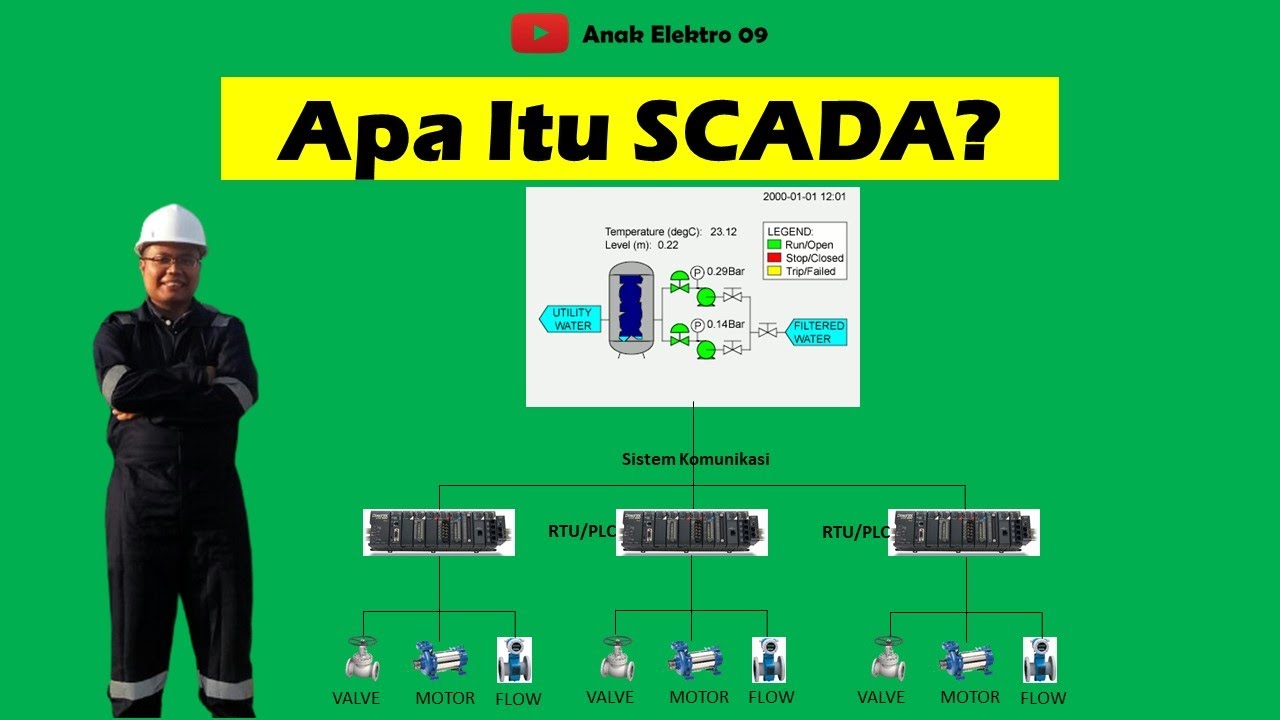
- 📊 The Human-Machine Interface (HMI) software enables interaction with field devices such as pumps, valves, and sensors.
- 🕒 SCADA systems log historical data for analysis, improving decision-making and process management.
- 🔌 Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are essential components that communicate with field devices.
- 🏭 Prior to SCADA, monitoring industrial processes relied on manual controls, which required personnel to be on-site.
- 🚀 The evolution of SCADA began in the 1950s and progressed through various technological advancements in automation and telemetry.
- 🌐 The 1980s and 90s saw the rise of distributed SCADA systems that allowed for networking but often used proprietary communication methods.
- 🔗 Modern SCADA systems have adopted open system architectures, enabling compatibility with various vendors.
- 🌍 Today’s SCADA systems utilize SQL databases and web-based applications, allowing for global access to real-time data.
Q & A
What does the acronym SCADA stand for?
-SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition.
What are the main components of a SCADA system?
-A SCADA system consists of both software and hardware components that include Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), Human Machine Interface (HMI) software, and networked devices.
How does SCADA collect and process data?
-SCADA collects real-time data from field devices, processes this data through PLCs or RTUs, and displays it for operators to analyze and respond to system events.
What role do RTUs and PLCs play in SCADA systems?
-RTUs and PLCs are microprocessors that communicate with field devices, collecting data and sending it to SCADA computers for further processing and display.
What technological changes facilitated the evolution of SCADA systems?
-The introduction of automation in the 1950s, the development of Local Area Networking (LAN) in the 1980s and 1990s, and the adoption of open system architectures in the late 1990s contributed to the evolution of SCADA systems.
How has the use of SCADA systems changed over time?
-Initially large and stand-alone, SCADA systems have evolved to become more integrated with open architectures, allowing for connectivity with various vendors and remote monitoring capabilities.
What advantages do modern SCADA systems have over older systems?
-Modern SCADA systems utilize SQL databases and web-based applications, enabling real-time data access from anywhere, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced data analysis capabilities.
What was a significant drawback of early SCADA systems?
-Early SCADA systems were typically proprietary, limiting communication and integration with systems from different vendors.
How does historical data collection in SCADA systems benefit industries?
-Historical data collection allows for trending analysis, which helps improve plant processes and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
What types of devices can SCADA systems interact with?
-SCADA systems can interact with a variety of field devices such as pumps, valves, motors, and sensors, provided they use a compatible communication protocol.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Pengenalan SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition)

What is SCADA, How SCADA Works, Components, Architecture & Applications. SCADA Tutorial
DISTRIBUTE CONTROL SYSTEM (DCS) SISTEM KONTROL TERDISTRIBUSI - DALAM OTOMASI INDUSTRI

What is SCADA? Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition

Introduction To SCADA System

CompTIA Security+ Full Course: Security Assessments and Vulnerabilities
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)