What is GIS?
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we explore the basics of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), including its components and how it works. GIS stands for Geographic Information System, which combines geography, information, and technology to capture, store, display, query, and analyze geographic data. The system utilizes two types of data: spatial data (such as points, lines, and polygons) and non-spatial data (like attributes stored in tables). Key GIS components include hardware, software, data, people, and procedures. With these elements, GIS enables the creation of digital maps and real-world simulations to support various applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 GIS stands for Geographic Information System, which is a system for capturing, storing, displaying, querying, and analyzing geographic data.
- 😀 The term 'Geography' refers to the study of the Earth's land, inhabitants, and surface objects.
- 😀 'Information' in GIS refers to the details of features on the Earth's surface, such as the name of a building or population of a state.
- 😀 'System' in GIS represents the technology and methods used to capture objects and integrate them with geographic information.
- 😀 GIS involves two main types of data: spatial data (location/extent of geographic features) and non-spatial data (attribute information).
- 😀 Spatial data is categorized into three types: point (no width/length), line (length but no width), and polygon (area with width and length).
- 😀 Non-spatial data is stored in a tabular format and includes attributes like text, numeric values, dates, and boolean values.
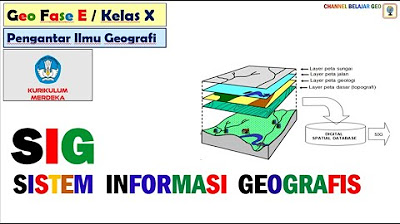
- 😀 Layers are a fundamental building block of GIS, grouping similar objects for better management and analysis.
- 😀 GIS enables users to combine different layers (e.g., customers, buildings, roads) to visualize and analyze data on a digital platform.
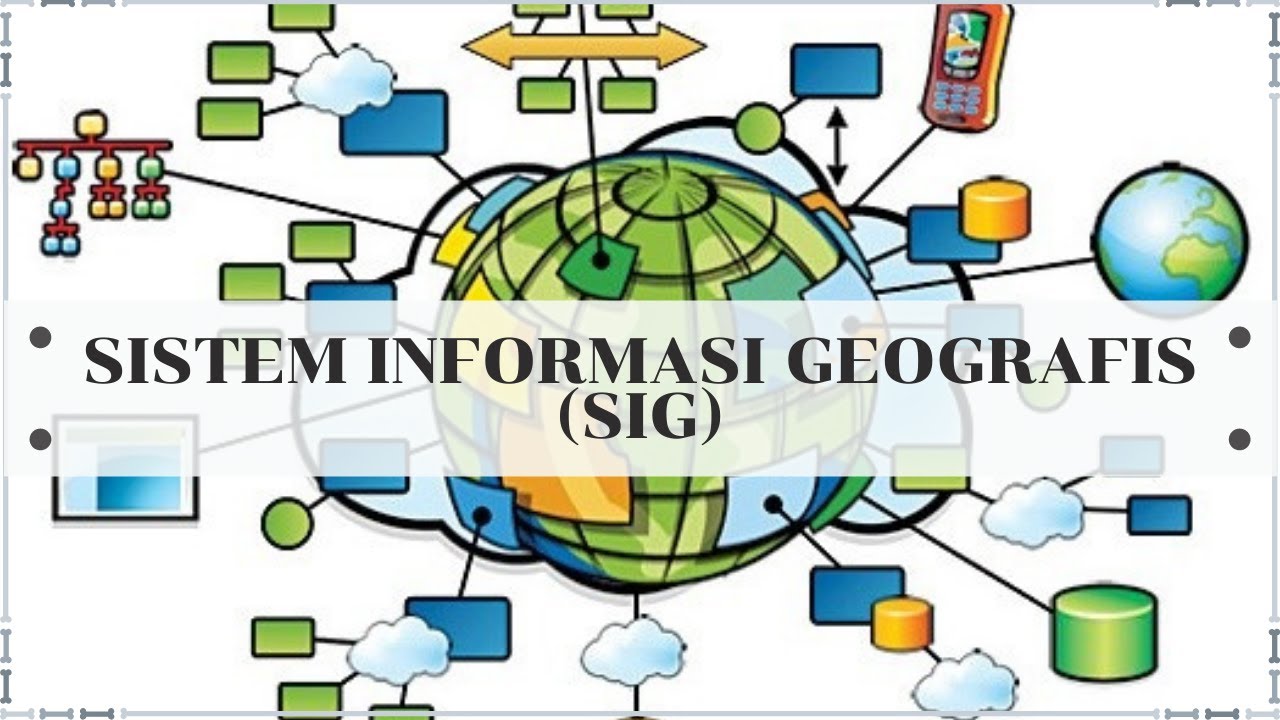
- 😀 The five components of GIS are: hardware (servers and computers), software (GIS tools and functionalities), data (accurate and high-quality), people (users and managers), and procedures (standard methodologies).
- 😀 Data quality is crucial in GIS, as 'garbage in, garbage out' means the system's output is only as good as its input data.
Q & A
What does GIS stand for?
-GIS stands for Geographic Information System, which is a system used to capture, store, display, query, and analyze geographic data.
What are the two main types of data in GIS?
-The two main types of data in GIS are spatial data and non-spatial data.
What is spatial data in GIS?
-Spatial data refers to the location or extent of geographic features, such as the location of a landmark or a road network. It is represented as points, lines, or polygons.
Can you explain the three types of spatial data objects in GIS?
-Yes. The three types of spatial data objects are: Point (objects with no length or width, e.g., the location of a hospital), Line (objects with length but no width, e.g., a highway), and Polygon (objects that cover a large enclosed area, e.g., a state boundary).
What is non-spatial data in GIS?
-Non-spatial data, also known as attribute data, refers to information that is stored in a tabular format. This can include details like the name, height, and construction date of a building or the population of a state.
What is a GIS layer?
-A GIS layer is a logical grouping of similar objects. For example, all buildings can be grouped into one layer, while roads and land use features can be grouped into other layers.
How does GIS use layers to represent geographic data?
-GIS combines different layers to display geographic data on top of each other, allowing for a digital representation of the real-world features and enabling better analysis.
What are the five basic components of a GIS system?
-The five basic components of a GIS system are: hardware (servers and computers), software (GIS applications), data (geographic and attribute data), people (users who manage and update the data), and procedures (standards and methodologies for maintaining the system).
Why is data quality important in a GIS system?
-Data quality is crucial in GIS because of the principle 'garbage in, garbage out'. If the input data is incorrect or poor in quality, the resulting analysis and output will also be inaccurate or unreliable.
What role do people play in a GIS system?
-People play a critical role in a GIS system by managing and updating the data, ensuring its accuracy, and ensuring that the GIS system functions effectively over time.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)