Tektonisme/ Tenaga Endogen/ Geografi Kelas X SMA/ Kurikulum Merdeka
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the concept of endogenous forces in geography, focusing on tectonism, seismology, and vulcanism. It covers the processes of tectonic movements, including epirogenetic and orogenetic shifts, leading to folding, faulting, and jointing in the Earth's crust. The video provides real-life examples and illustrations of these geological processes. The host emphasizes the importance of understanding how these forces shape the Earth's surface over time. The session ends with an invitation to viewers to join the next video, which will delve into seismology and earthquakes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Endogenous forces (Tenaga Endogen) come from within the Earth and shape its surface through processes like tectonism, seismic activity, and vulcanism.
- 😀 Tectonism is the movement of the Earth's crust, which includes folding, faulting, and crustal deformation.
- 😀 Epirogenetic movements are large, vertical shifts in the Earth's surface, occurring over long periods of time and affecting broad areas.
- 😀 Positive epirogenetic movement results in land sinking, causing a rise in sea level (e.g., Banda Islands, Teluk Hudson).
- 😀 Negative epirogenetic movement involves land rising, leading to a visible drop in sea level (e.g., Buton Island, South Africa).
- 😀 Orogenetic movements are rapid, localized shifts that can be vertical or horizontal, typically affecting smaller areas.
- 😀 Folding occurs when the Earth's crust bends under pressure, forming features like mountains with peaks and valleys.
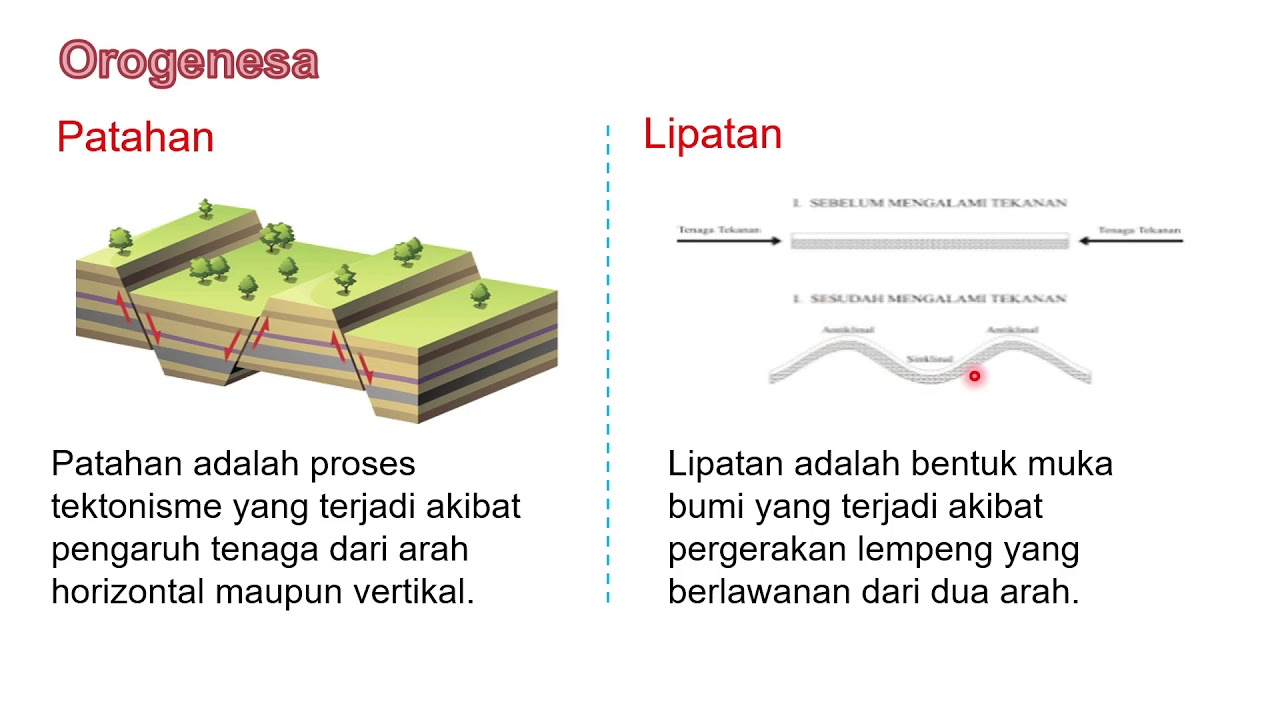
- 😀 Faulting results from the breaking of the Earth's crust under stress, leading to the formation of faults like normal and reverse faults.
- 😀 Fracturing happens when the Earth's crust cracks without movement, resulting in formations like joints or fractures.
- 😀 The types of faults include normal, reverse, strike-slip, and oblique-slip, each with distinct movements and characteristics.
Q & A
What is the definition of endogenous forces in geography?
-Endogenous forces are forces that originate from within the Earth, influencing and shaping the Earth's surface over time. These forces include tectonism, seismic activities (earthquakes), and vulcanism (volcanic activities).
What are the three types of endogenous forces mentioned in the script?
-The three types of endogenous forces mentioned in the script are tectonism, seismic activities (earthquakes), and vulcanism (volcanic activities).
What is tectonism, and how does it affect the Earth's surface?
-Tectonism refers to the movement of the Earth's crust, which leads to changes in the position and shape of the Earth's surface. This includes processes like folding, faulting, and the formation of mountains, valleys, and other landforms.
What are the two main categories of tectonic movement?
-The two main categories of tectonic movement are epirogenetic and orogenetic movements. Epirogenetic movements are large-scale vertical movements that occur over long periods, while orogenetic movements are rapid and can be either vertical or horizontal, affecting smaller areas.
What is the difference between positive and negative epirogenetic movements?
-In positive epirogenetic movement, the land subsides, causing the sea level to appear to rise. In negative epirogenetic movement, the land rises, making the sea level appear to fall.
What are the three types of orogenetic movements described in the script?
-The three types of orogenetic movements are folding (lipatan), faulting (patahan), and jointing (kekar). These movements lead to the formation of mountains, valleys, and cracks in the Earth's crust.
What is the process of folding (lipatan) in tectonism?
-Folding occurs when the Earth's crust is subjected to pressure, causing it to bend and form mountain ranges with peaks (anticlines) and valleys (synclines). This process is the result of both vertical and horizontal tectonic forces.
What are the types of folds, and how do they differ?
-The types of folds include vertical folds (formed under equal pressure), tilted folds (formed under unequal pressure), and overfolds (formed under continuous pressure). Other types include hanging and reclining folds, which occur due to constant pressure over time.
How do faults (patahan) differ from folds (lipatan)?
-Faults occur when the Earth's crust is broken due to pressure, leading to displacement of the crust, while folds are bends in the Earth's crust. In faults, there is significant movement, whereas in folds, the crust remains intact but changes shape.
What are the types of faults discussed in the script, and how do they differ?
-The types of faults include normal faults (where the hanging wall moves down), reverse faults (where the hanging wall moves up), and strike-slip faults (where movement occurs horizontally). Oblique faults combine vertical and horizontal movements.
What is the concept of joints (kekar), and how do they form?
-Joints are fractures in the Earth's crust where no displacement occurs. They form due to tectonic stress, including tension, compression, or shear forces, and they can be classified into types based on their formation, such as columnar joints, sheet joints, and tectonic joints.
What is the relationship between tectonism and the Earth's landscape?
-Tectonism plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth's landscape by creating mountains, valleys, and other landforms. Through processes like folding, faulting, and jointing, tectonic forces reshape the Earth's surface over time.
What role does time and scale play in the different types of tectonic movements?
-Epirogenetic movements occur over long periods and affect large areas, often leading to subtle changes that are not easily noticed. In contrast, orogenetic movements happen more rapidly and affect smaller, localized areas, resulting in more dramatic changes such as the formation of mountains.
How can the movement of tectonic plates lead to natural disasters like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions?
-The movement of tectonic plates can lead to stress and fractures in the Earth's crust, causing earthquakes (seismic activity) and volcanic eruptions. These events are the result of the release of energy accumulated due to plate movements and the shifting of the Earth's crust.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
Tenaga Endogen & Eksogen (Tektonisme) #kumer

Os agentes INTERNOS e EXTERNOS do relevo (Endógenos e Exógenos) - Geografia Física

Tenaga Endogen - Dinamika Litosfer - Materi Geografi
Materi Tenaga Pembentuk Muka Bumi - Tenaga Endogen - Tektonisme

Geografi Kelas X (20) Tenaga Pembentuk Muka Bumi | Tenaga Endogen dan Eksogen

SMA KELAS X Geografi Fase E : Fenomena Geosfer Di Indonesia "LITOSFER"
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
