Os agentes INTERNOS e EXTERNOS do relevo (Endógenos e Exógenos) - Geografia Física
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Paulo, a geography teacher, simplifies the concept of internal and external agents of relief for students. He explains how relief, or the Earth's surface features, is shaped by both endogenous (internal) and exogenous (external) forces. Internal forces like tectonism, earthquakes, and volcanism create relief, while external forces such as weathering and erosion sculpt it. The video also includes a mind map summarizing the material, designed to help students better understand and remember the topic. Paulo encourages viewers to engage by liking, sharing, and downloading the mind map for further study.
Takeaways
- 😀 Relief refers to the various forms that the Earth's surface presents, also known as geographical accidents.
- 😀 The Earth's relief is shaped by two forces: endogenous forces (internal) and exogenous forces (external).
- 😀 Endogenous forces come from inside the Earth and are primarily responsible for creating structural macroforms like mountains.
- 😀 Endogenous forces include tectonicism (vertical and horizontal movements), earthquakes, and volcanism.
- 😀 Tectonic plates, which are massive blocks of rock, are in constant movement and are responsible for shaping the Earth's surface.
- 😀 Exogenous forces come from outside the Earth and primarily work to sculpt and shape the relief.
- 😀 Exogenous forces include water, wind, the sun, and living organisms, all of which contribute to modifying the Earth's relief.
- 😀 Weathering, which is the degradation and decomposition of rocks, is an important exogenous force and includes physical, chemical, and biological processes.
- 😀 Erosion is another exogenous force that, along with weathering, works to break down and reshape the Earth's surface.
- 😀 A mind map is provided in the video to help viewers understand and retain the concepts of internal and external relief agents more easily.
Q & A
What is relief in geography?
-Relief refers to the various forms or features of the Earth's surface, including mountains, valleys, plains, and plateaus. These forms are created by different forces acting on the Earth's surface.
What are endogenous forces, and how do they impact the relief?
-Endogenous forces are forces that act from within the Earth. These include tectonic movements (both vertical and horizontal), earthquakes, and volcanism. These forces are responsible for creating large structural features like mountain ranges and tectonic faults.
What is the structure of the Earth?
-The Earth is made up of three main layers: the core, the mantle, and the crust. The crust is the thinnest and most rigid layer, subdivided into tectonic plates that are constantly in motion.
What are tectonic plates, and how do they affect the relief?
-Tectonic plates are large, rigid blocks of the Earth's crust that move due to internal forces. The movement of these plates results in the creation of geological features such as mountain ranges, earthquakes, and volcanoes.
What are the three types of endogenous forces?
-The three types of endogenous forces are tectonism (which includes epirogenesis and orogenesis), earthquakes (seismic shocks), and volcanism.
What is the difference between epirogenesis and orogenesis?
-Epirogenesis refers to vertical movements of tectonic plates, typically resulting in features like faults and ridges. Orogenesis refers to horizontal movements of tectonic plates, often creating folds and mountain ranges.
What are exogenous forces, and how do they affect the Earth's relief?
-Exogenous forces are external forces that act on the Earth's crust. These include the forces of water, wind, sunlight, and biological agents. They shape and modify the existing relief through processes like weathering and erosion.
What is the process of weathering?
-Weathering is the breakdown or decomposition of rocks due to external forces. It is divided into three types: physical weathering (caused by temperature changes), chemical weathering (caused by chemical reactions), and biological weathering (caused by living organisms).
Can you give examples of how exogenous forces cause weathering?
-Examples of weathering include the action of the sun causing rocks to expand and contract with temperature changes, the wind and water gradually wearing down rocks, and the activity of organisms like ants, which release formic acid that degrades rocks.
How do endogenous and exogenous forces differ in terms of shaping the Earth's relief?
-Endogenous forces create the basic structure of the relief by forming large geological features like mountains, while exogenous forces sculpt and modify the surface, such as through weathering and erosion, which wear down and reshape rocks over time.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Conheça quais são os 5 PRINCIPAIS CONCEITOS da Geografia
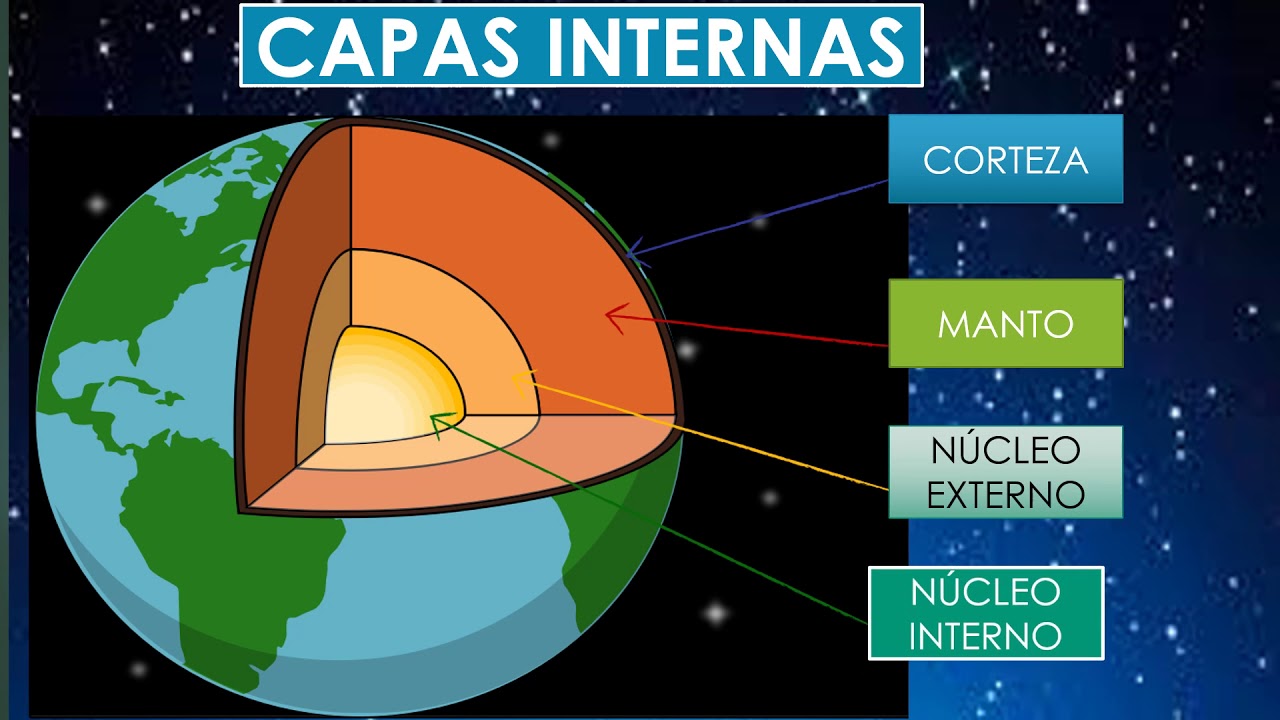
VIDEO DE LAS CAPAS EXTERNAS E INTERNAS DE LA TIERRA. AUTORA VICTORIA GUAMÁN.

Conheça a Estrutura Geológica da Terra (interna e externa) - Geologia
Os Elementos e Fatores Climáticos (Climatologia)

Conurbação, Aglomerado Urbano, Metrópole e Megalópole - Geografia Urbana para o ENEM

Os agentes internos e externos do relevo
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)