Units of Storage
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how computers store data using the binary system, starting with bits and progressing through bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes. It highlights that bits (1s and 0s) form the foundation of all data, with eight bits making up a byte, and each larger unit representing increasingly vast amounts of storage. The video covers real-world examples, such as the storage capacities of floppy disks, hard drives, and flash drives, helping viewers understand digital storage terminology and the evolution of storage devices over time.
Takeaways
- 😀 Computers use the binary system, which only consists of two digits: 1 and 0.
- 😀 A 'bit' is the smallest unit of data in a computer, representing a binary digit (1 or 0).
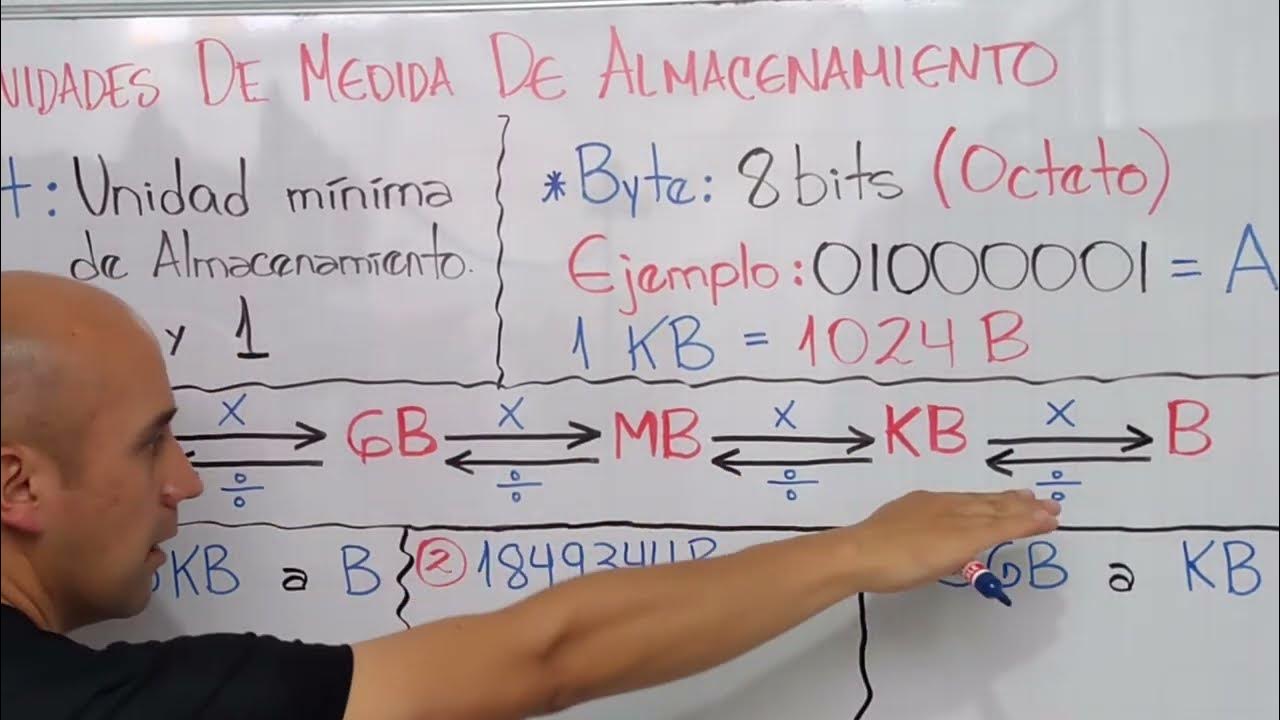
- 😀 When you combine 8 bits, you get 1 'byte', which is enough space to store one letter or symbol in a text document.
- 😀 1 kilobyte (KB) is equal to 1,000 bytes and can hold around two pages of text.
- 😀 The five and a quarter inch floppy disk could store 360 KB of data in the late 1970s and early 1980s.
- 😀 A megabyte (MB) equals 1,000 kilobytes and can store approximately five large books, one photo, or one minute of music.
- 😀 The 3.5-inch floppy disk from the 1980s could store 1.4 MB of data.
- 😀 A gigabyte (GB) equals 1,000 megabytes and can store about 400 books, 1,000 pictures, or 16 hours of music.
- 😀 By the mid-1990s, a 1 GB hard drive cost a couple hundred dollars, but today you can get a 1 GB flash drive for about $5.
- 😀 A terabyte (TB) equals 1,000 gigabytes and can hold around 400,000 large books, 1 million pictures, or two years of continuous music.
- 😀 Today, a 1 terabyte hard drive can be purchased for under $50, showcasing the massive drop in storage prices over the years.
Q & A
What are binary digits, and what is their role in computer data storage?
-Binary digits, also known as bits, are the smallest unit of data in a computer. They can either be a 1 or a 0, and are used to store all types of information, such as text, images, sounds, and more.
What is the significance of a byte in computer data storage?
-A byte consists of 8 bits and is used to store a single character or symbol in a text document. It is a basic unit for measuring data storage, where 1 byte is typically the space required for one letter or symbol.
How does the term 'kilobyte' relate to bytes, and what is its practical use?
-A kilobyte (KB or K) is equal to 1,000 bytes (although technically 1,024 bytes in binary terms). A kilobyte is enough space to hold about two pages of text, and it was used as a common measure for early storage devices like floppy disks.
What does a megabyte represent, and how much data can it store?
-A megabyte (MB) is equal to 1,000 kilobytes. It is enough space to store about five large books, one photo, or one minute of music. In the 1980s, a 1.4 MB floppy disk was a common storage option.
How much data can a gigabyte hold, and how was it used in the 1990s?
-A gigabyte (GB) is equal to 1,000 megabytes. It can hold about 400 books, 1,000 pictures, or 16 hours of music. In the mid-1990s, a 1 GB hard drive was priced at several hundred dollars, and today, a 1 GB flash drive costs only a few dollars.
What is a terabyte, and what does it store?
-A terabyte (TB) is equal to 1,000 gigabytes. It can hold around 400,000 large books, 1 million pictures, or two years of continuous music. Modern hard drives can now hold 1 TB of data for under $50.
What is the relationship between bits, bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes?
-The relationship is sequential: 8 bits make up 1 byte, 1,000 bytes make up 1 kilobyte (KB), 1,000 kilobytes make up 1 megabyte (MB), 1,000 megabytes make up 1 gigabyte (GB), and 1,000 gigabytes make up 1 terabyte (TB).
Why is the value of a kilobyte sometimes considered as 1,024 bytes instead of 1,000?
-The value of 1,024 bytes in a kilobyte comes from the fact that computers use binary, and powers of 2 (like 2^10) are more natural in this system. However, for simplicity, 1,000 bytes is often used in general discussions.
How have the prices of storage devices changed over time, according to the script?
-In the 1990s, a 1 GB hard drive cost a few hundred dollars, but today, a 1 GB flash drive can be bought for just about $5. Similarly, the price of a 1 TB hard drive has dropped to under $50.
What role do storage units like kilobytes, megabytes, and gigabytes play in understanding digital storage?
-These units help quantify and measure how much data can be stored in a device. Understanding them allows people to estimate how much space different types of data, such as text, images, or music, will occupy on storage media.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Computer Skills Course: Bits, Bytes, Kilobytes, Megabytes, Gigabytes, Terabytes (OLD VERSION)

Y2Mate is Units of Storage 5Yr70zL8ZPc 720p 1654520016982

12. OCR GCSE (J277) 1.2 Units of data storage

Sistem Komputer

Medidas de Almacenamiento en Informática
✅Cómo convertir bites y bytes, b, B, KB, MB, GB, TB😎 !!MÉTODO COMPLETO Y FÁCIL!! con ejemplos.👌
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
